B5 - Homeostasis Flashcards
Give 3 things the body needs to maintain the level of
- Blood Glucose
- Temperature
- Water levels
- Ion levels
What do these terms mean?
a) Receptor
b) Sensory Neurone
a) Receptor - Picks up information from outside the body e.g. light receptors / temperature receptors
b) Sensory Neurone - The neurone that picks up information from the receptors and sends it to the CNS
What do these terms mean?
a) Motor Neurone
b) CNS
a) Motor Neurone - neurone which take information from the CNS to the effectors
b) CNS - Central Nervous System - Brain and spine. Co-ordinating information from the sensory neurones
What can this equipment be used to measure?

Reaction time
In this experiment was is the
a) IV - Independent Variable
b) DV - Dependent Variable
c) CV - Control Variable

a) IV - Independent Variable - something that affects reaction time e.g. caffeine / tiredness
d) DV - Dependent Variable - The point the ruler is caught (reaction time)
c) CV - Control Variable - point the ruler is dropped from / volume of caffeine consumed

In this experiment what can be changed to effect reaction time?

- Caffeine
- Tiredness
- Distraction
In this experiment - how is reaction time measured?

Point at which the ruler is caught

In this experiment - what needs to be kept the same

Point at which the ruler is placed above the hand
Position / height of the catching hand
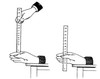
How many times should this experiment be repeated?

Repeat the experiment 3 times and repeat any anomalies
How can an average be calculated in this experiment?

Add all the results together and divide by the number you had.
(remember to remove anomalies first)
What is a synapse?
The gap between 2 neurones.
Signals travel across using chemicals

How does information travel across a synapse?
Chemical transmitters

What is the gap between 2 neurones called?

A synapse

What is a reflex reaction
A nervous reaction that does not do to the brain
This makes it quicker and involuntary.

Why are reflex reactions important?

They are important because they are very quick.
This means they are used to prevent the body from harm e.g. coughing and blinking

Which hormone controls blood sugar level
Where is it made?
Insulin
Made in the pancreas
Where is insulin made?
Pancreas
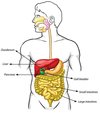
What is insulin used to control?
Blood sugar level
What are the different forms of diabetes?
Type I
Type II
Give 2 facts about type I diabetes
Develops earlier in life
Controlled with insulin
Give 2 facts about type II diabetes
- Develops later in life
- Usually mainly controlled with diet and exercise
How long in the average menstrual cycle?
28 days
In the average menstrual cycle when does ovulation happen?
Day 14

What are are the advantages and disadvantages of these methods of contraception?
a) Contraceptive pill
Advantages
Over 99% effective
Sickness can reduce effectiveness
Disadvantages
Possible side effects e.g. headaches
Does not prevent STI’s
What are are the advantages and disadvantages of these methods of contraception?
a) Contraceptive injection
Advantages
Over 99% effective
Lasts of 3 months
Disadvantages
Possible side effects e.g. headaches
Does not prevent STI’s
What are are the advantages and disadvantages of these methods of contraception?
a) Condoms
Advantages
Protects against STI’s
Disadvantages
Not as effective as hormonal methods such as ‘the pill’
What are are the advantages and disadvantages of these methods of contraception?
a) Sterilisation
Advantages
Highly effective
Permanent
Disadvantages
Can be difficult to reverse (especially in women)


