B: Nucleic Acids HL Flashcards
1
Q
DNA and RNA
A
DNA
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
2
Q
Nucleotides
A
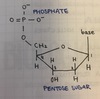
- Nucleic acids are polymers made up of monomers known as nucleotides
- consist of a 5-carbon (pento) sugar, a nitrogen-containing heterocycle called the base, and a phosphate group
- condensation products of a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base
3
Q
Bases
A
All derivates of either purine (secondary amine) or pyrimidine (tertiary amine)
Purine
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
Pyrimidine
- Thymine (T) / Uracil (U)
- Cytosine (C)

4
Q
DNA
A
- A double strand of nucleotides held together by H bonding
- Contains thymine
- contains 2-deoxyribose
- double helix consisting of 2 polynucleotide strands that spiral around an axis
- each complete turn is 10 nucleotides in length
5
Q
RNA
A
- A single strand of nucleotides
- contains uracil
- contains ribose
6
Q
Structure of DNA/ RNA
A
- each strand of nucleotides has a repeating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate backbone
- base attached to each sugar
7
Q
DNA Replication
A
- Involves the unwinding and separating of the two strands of DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs
- exposes nucleotides and allows the bases on each of the DNA strands to be used as a template for the formation of a complementary DNA strand
- Free nucleotides form complementary base pairs with the DNA template strands
8
Q
The Genetic Code
A
- The sequence of bases in DNA determines the primary structure of proteins synthesized by the cell using a triplet code - the universal genetic code
- Chromosomes are long, coiled strands of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones (positively charged –> attracted to negative phosphate groups)
- contains genes
9
Q
Benefits of GMOs
A
- increased nutritional content of crops eg golden rice
- increased yield of crops
- ability of crops to grow in adverse conditions
- improved crop resistance to disease
- enhanced taste, texture, quality
- improved animal health
- improved conservation of water, soil and energy
10
Q
Concerns of GMOs
A
- not enough knowledge about long term effects
- escape of transgenic material into the wild
- upset the current balance of ecosystems and food chains
- alteration of the composition of a balanced diet
- exploitation and monopolisation
- ethical considerations


