Assessing Kidney Function Flashcards
What are the functions of the kidneys?
- Excretion of products of metabolism.
- Water regulation.
- Electrolyte regulation.
- Maintaining Hb.
- Maintaining calcium homeostasis.
What is glomerular filtration rate and how can it be used to assess kidney function?
- GFR is proportional to the number of functioning glomeruli present - so reflects ‘function’ of the kidney.
- Mainly looks at clearance: urinary output of ‘x’ / minute relative to its concentration in the blood.
- GFR is the volume of plasma filtered / unit time = 120mL/min.
- ‘X’ needs to be freely filtered, not reabsorbed, not secreted, not modified / metabolised after filtration and not variably produced.

What are the molecules which can be infused into a patient to assess kidney function?
What is the problem with these?
- Inulin and polyfructosan: plant extracts, non-toxic.
- Requires infusion, multiple sampling of urine and plasma concentrations.
- The problem is they need to be infused into patients to produce a steady state and this is difficult because it can be a laborious process and not practical for patients coming into an outpatient clinic.
- BUT, there are biologic molecules present in the blood which can fulfil this criteria.
Describe the use of creatinine as a measure of kidney function.
- Metabolic product of creatinine and phosphocreatinine.
- Exogenously acquired from meat MW113 Da.
- Does not bind plasma proteins.
- Freely filtered.
- Almost never reasborbed.
BUT
- Secreted by tubules - over estimated by up to 10%.
- If you have a higher creatinine level, more is excreted in the tubules. So, when there is increased filtration there is an overestimated creatinine level.
- Increased error at lower GFR.
- Creatinine related to muscle mass.
- Severe malnutrition / elderly / no meat diet.
- Drugs trimethoprim / cimetidine compete for secretion.
Describe the use of urea as a measure of kidney function.
- Metabolic product of amino acids.
- Exogenously acquired from protein intake.
- MW60 Da.
- Freely filtered
BUT
- 50% is reabsorbed by PCT: depends on water / Na reabsorption.
- Liver disease reduces urea plasma levels.
- Protein degradation in intestine increases urea.
What are the indications for a clearance measurement when estimates based on serum creatinine may be inaccurate?
- Extremes of age and body size.
- Severe malnutrition or obesity.
- Disease of skeletal muscle.
- Paraplegia or quadriplegia.
- Vegetarian diet
- Rapidly changing kidney function.
- Pregnancy.
What happens to GFR with age?
- GFR declines with age - you would not say that someone has reduced kidney function without validating this against age - they may be older and have a physiological reduction in GFR in health.
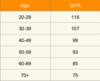
What is cystatin C useful for?
- Rises very sharply if there is any reduction in GFR - good to assess acute kidney injury.
- It is a cysteine protease inhibitor that is produced in nearly all nucleated human cells.
- Independent of body mass, age, sex, inflammation or malignancy.
- MW 13Da.
- Freely filtered.
- Reabsorbed and metabolised by proximal tubule cells.
- Serum levels correlate with GFR.
- Better for elderly populations.
- BUT not yet vaildated.
What is eGFR?
- Formulae based on sigle serum creatinine alone.
- Weight surrogate for muscle mass.

What is modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD)?
- Computerised.
- Useful if stable serum creatinine.
- Less accurate if near normal GFR (under-estimate if >60 mL/min/1.73m2).

Describe renal blood flow.
- Affects GFR due to the hydraulic pressure in the glomerulus based on afferent and efferent arterioles dilation / constriction.
- Kidneys take 20% of cardiac output - 1L/minute.
- Blood flow within the kidney is not homogenous (there are variations between the cortex and medulla) but for clinical practice total renal blood flow influences understanding of GFR.
- Para-aminohippurate clearance: completely extracted from plasma during a single pass through the kidney and eliminated in urine unchanged.

What happens when ACE-I inhibit AT-II production, or ARBs block AT-II at the receptor?
- ACEI and ARB block cause false creatinine levels.
- Start by checking patient’s bloods before starting the drugs then assess 1-2 weeks later to see if there is any change.
- If the patient has 2 functioning kidneys there should be no change.
- Greater than 25% drop in GFR and more than 30% increase in creatinine makes you think kidney problem and you should stop the drug.

Which types of imaging can be used to assess kidney function?
What are each of these images looking for?
- ERPF = effective renal plasma flow.

Describe this measure of kidney function.

- Clearance closest to inulin.
- Both excreted by glomerular filtration.
- Low radiation dose.
- Smaller fraction of DTPA is bound to proteins than EDTA.
- Not useful if impaired renal function - GFR <30mL/min (20% extracted with each pass through the kidney; 90% within 4 hours).
Describe this measure of kidney function.

- Concentrated in the renal cortex - cytoplasm of the proximal tubules.
- Binds to plasma proteins (retained for longer) - 6 hours.
- 2 hours after injection 50% retained in the cortex of kidneys.
- Relative kidney function - USS may show small kidney which might lead you to think that that kidney is not functioning properly but DMSA scan can then show that function is normal.
- Areas of scarring / non-functioning.
- Not actually that useful in assessing kidney function.
Describe this measure of kidney function.

- Highly protein bound 70-90%.
- Cleared by proximal tubules 89%.
- Extraction fraction is 40-50% (better than DTPA).
- Independent indicator or ERPF and renal function.
Describe the use of urinalysis as a measure of kidney function.
- Urine consists of 95% water and >3000 chemicals.
- Metabolic breakdown products
- Drugs
- Anions / cations
- Environmental chemicals
- Bacterial breakdown products
- Clinically relevant:
- Blood - red cells / free haem
- Bilirubin
- Ketones - DKA / fasting
- Glucose - diabetes
- Protein - specific for albumin
- Nitrites - bacterial product
- Leucocytes - UTI / allergies
- pH - not acurate on dipstick
- Specific gravity
*
Describe the use of proteinuria as an assessment of kidney function.
- Proteinuria on dipstick is actually albuminuria.
- It assesses the integrity of the glomerular filter.
- Albumin is water-soluble
- Un-glycosylated protein
- MW 65,000 Da
- Negatively charged
- Presence is a sign of kidney damage.
- Urinary albumin varies dependent upon posture, exercise, acute diuresis. Dipstick correlates poorly with 24 hour proteinuria.
- False positives if menstruation / UTIs.
- Does not detect light chains in urine.
- Urine albumin: creatinine ratio (ACR) or protein:creatinine ratio (PCR).
- Urinary albumin measurement provides a more specific and sensitive measure of change in glomerular permeability than total protein.
- UACR correlates with early glomerulosclerosis in diabetics - before there is a drop in GFR.
- Guides management.

Describe the role of the kidneys in maintaining Hb.
- Erythropoietin increases reticulocyte production and release from the bone marrow.
- 90% produced in the kidney - 10% in the liver.
- Made in type 1 fibroblastoid cells in peritubular interstitium of the cortex and outer medulla.
- Hypoxia stimulates erythropoietin mRNA synthesis.
- Acidosis reduces O2 affinity of Hb so increases tissue oxygenation, reducing erythropoiesis.
- CKD causes the fibroblastoid cells to become myofibroblastoid so less erythropoietin production.
Describe the role of the kidneys in calcium homeostasis.
- Calcium is regulated by bone turnover and gut absorption.
- 25-30% calcium is absorbed by the gut (duodenum and jejunum). Absorption is increased by vitamin D.
- Calcium is freely filtered and reabsorbed along the nephron, actively entering cells via PTH stimulation.
- Transport across the cell is regulated by vitamin D and out of the cell by both PTH and vitamin D regulation.
- 65% PO4 absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum, enhanced by vitamin D.
- PO4 is freely filtered and reabsorbed. 80% reabsorbed in the PCT, down regulated by PTH.
- Low calcium increases PTH.
- PTH causes bone reabsorption and increases vitamin D synthesis in the kidney.
- Net result should be correction of Ca/PO4 and PTH : these are issues in CKD.


