Anticoagulants Flashcards
Indications for anticoagulants

Parenteral anticoagulants

MOA of anticoagulants

Three phases of coagulation

MOA of heparin

Coagulation cascade

Effects of thrombin
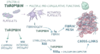
Effects of antithrombin III

Fractionated vs. unfractionated heparin

HMWH has effect on _________ and factor X

Low molecular weight heparins

Enoxaparin, dalteparin, tinzaparin
Administered SubQ with more predictable bioavailability
Longer half life and less need to monitor (unless child or obese)
Cleared by the kidneys and low risk of HIT

Indications and use for heparin and warfarin
Binds to endothelium and to plamsa proteins
Levels of heparin-binding proteins vary from person to person so there is an upredictable anticoagulant response
Monitoring and titration required

How is heparin monitored, and what is the reversal?

Major adverse effect of heparin
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Risk of clots because of antibody production that creates a prothrombotic environment, incidence is ~5%

Low molecular weight heparin indications

LMWH boxed warning
Spinal/epidural hematoma that could lead to paralysis
Risks of Fondaparinux

Indication for Argatroban
Treatment for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia

Indication for Bivalirudin
IV infusion used as alternative to heparin in patients undergoing PCI

Direct oral anticoagulants
Direct thrombin inhibitor/Factor Xa inhibitors

Indications for oral anticoagulants

MOA of warfarin

Impact of genotype on S-warfarin clearance

How long does warfarin typically take effect?
About 7 days














