Antibiotics and Shock Flashcards
Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis
Cephalosporins
Penicillins
Vancomycin
Bacitracan
Carbapenems
Drugs that inhibit protein synthesis
Chlorapheminicol
Erthromycin
Streptomycin
Tetracylcine
Drugs that inhibit the synthesis of essential metabolites
sulfa
trimethoprim
Drug that inibits plasma membrane
Plymyxcin B
Drugs that inhibit nucleic acid/transcription
Quinoles
Rifampin
Xolair
Reduces the antibody IgE.
Attached to mast cells and signal a reaction when an antigen binds to the receptor site.
Immunizations

Common antibiotic allergies

Superinfections

Immunogloins

Cytokines

Innate immunity

Adapted immunity

Active vs passive immunity

organs involved in immunity

older aduts immunity

Newborn immunity

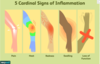
Cardinal signs of inflammation
Endoethelial cells in inflammation

platlets in inflammation

Neutrophils in inflammation

Monocytes and macrophages in inflammation

Esonophils in inflammation

Basophils and mast cells in infalmamation

Plasma cells in inflammation

stages of inflammation

Septicemia

Sepsis

septic shock

septic shock treatment

renal failure as a shock complication

Gi complications as a result of shock

DIC as a result of shock

lactic acidosis as a result of shock

hyperglycemia as a result of shock

fever as a result of shock

Electrolyte imbalances from shock

Shock causing lung damage

Allergy treatment

Anaphylaxis treatment

Hypovolemic shock

compensatory measures to hypovolemic shock

treatment for hypovolemic shock

Right vs left sided HF

bacteria resistance

streptococcus pyogenes

Beta lactam drugs

Cephalosporins

Bacitran

first choice for MRSA

tetracyclines

Macolides

Fluoroquinolones

Flagyl



