Anterior Pituitary - Endocrine Flashcards
Name the main hormones secreted from the anterior pituitary.
Describe the function of each hormone from the anterior pituitary.
Describe diseases related to anterior pituitary hormones.
5 Distinct Cell Types of the Anterior Pituitary:
- Lactotrophs (PRL)
- Gonadotrophs (FSH, LH)
- Thyrotrophs (TSH)
- Corticotrophs (ACTH)
- Somatotrophs (GH)
Pituitary Gland Hormones:

Gondadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
Released from ?
Regulates?
Hypothalamus releasing hormone
- Stimulates LH + FSH to be released from the anterior pituitary
- Gonadotrophs
- Regulates Gonads (Ovary and testis)
- Target Tissues
Prolactin releasing factors (TRH and PRH)
Released from?
Regulates?
- Hypothalamus releasing hormone
- Stimulates PRL to be released from the anterior pituitary
- Lactotrophs
- Regulates Mammary Glands
- Target Tissues
Prolactin Inhibiting Factor (Dopamine)
Released from?
Regulates?
- Hypothalamus releasing hormone
- Inhibits PRL to be released from the anterior pituitary
- Lactotrophs
- Regulates Mammary Glands
- Target Tissues
Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone
(TRH)
Released from?
Regulates?
- Hypothalamus releases hormone
- Stimulates TSH in the anterior pituitary
- Thyrotrophs
- Regulates thyroid gland
- Target tissue
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone
(GHRH)
Released from?
Regulates?
- Hypothalamus releases hormone GHRH
- Stimulates GH in anterior pituitary
- Somatotrophs
- Regulates bone, liver and muscle
- Target Tissues
Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone (Somatostatin)
Released from?
Regulates?
- Released from the hypothalamus
- Inhibits GH release from anterior pituitary
- Somatotrophs
- Regulates bone, liver and muscle tissues
- Target tissues
Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
Released from?
Regulates?
- Hormone released by hypothalamus
- Stimulates ACTH release from the anterior pituitary
- Corticotrophs
- Regulates the adrenal cortex
- Target tissue
Prolactin is inhibited by________ from the ________.
Inhibited by dopamine
From the hypothalamus
Prolactin:
- Single chain protein
- Produced by lactotrophs in the anterior pituitary
- Peptide hormone
- Structure is close to GH and only differs by 8 AA
- Synthesis is increased during pregnancy and augmented by estrogen
- Secretion is stimulated by suckling
When is prolactin synthesis increased?
During pregnancy and augmented by estrogen
Functions of Prolactin:
Mammary gland development (during pregnancy):
- High estradiol allows ductal network to grow
- Promotes alveolar epithelial cells differentiation into secretory cells
- High progesterone levels suppresses milk production
Milk Production:
- Prolactin induces lactogenesis (milk production)
- Triggered by stimulus of suckling
- Triggered by decreased progesterone levels at the end of a pregnancy
Target of Oxytocin is ______
Muscle cells
Target of Prolactin is ________
Milk producing cells
T of F: Prolactin is involved in the milk-ejection reflex.
False.
Oxytocin is involved in the milk-ejection reflex
Prolactin and Oxytocin:

Prolactin:
- Produced by lactotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland
- Number of lactotrophs will increase during pregnancy to the physiological response and need to produce breast tissue
- Involved in mammary gland development during pregnancy
- Acts on alveolar epithelia cells
- Role in milk formation (lactation)
Oxytocin:
- Produced in the posterior pituitary
- Acts on myoepithelial cells
- Function in milk release
- Stimulates the milk ejection reflex, lactation
- Lack of oxytocin in a nursing mother would prevent the milk-ejection reflex
Control of Prolactin Secretion:
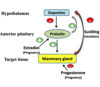
Dopamine is the main regulator for the production and secretion of prolactin
- Inhibitory control by dopamine (restrictive)
- More dopamine = less prolactin released
- Prolactin has (+) short feedback loop on hypothalamus to increase production of dopamine
- Inhibits prolactin secretion
- During pregnancy = increased estrogen–>> increases prolactin production and secretion
- Mammary gland development
- Progesterone inhibits milk formation
After birth:
- Progesterone levels drop
- Milk production begins
- Lactation
- Suckling is the major stimulator of prolactin secretion
Suckling Stimulates Prolactin Production

Role of Prolactin in Males
- Low, but measurable levels in males
- PRL receptors present in male reproductive and non-reproductive organs and tissues
- Enhanced luetenizing hormone receptors
- Leydig cells in testes
- Result in testosterone secretion
- Leads to spermatogenesis
- Enhanced luetenizing hormone receptors


