Anterior Abdominal Wall and Surface Anatomy Flashcards
A 26-year-old woman is being prepared for a cesarean section after the physician discovers her baby is in a breech position. The surgeon plans to make a suprapubic incision through the patient’s anterior abdominal wall. In this case, what is the correct order of structures (layers) that will be transected by the scalpel blade from superficial to deep? A.Skin → scarpa’s fascia → camper’s fascia →external oblique aponeurosis → half of internal oblique aponeurosis → rectus abdominis muscle → half of internal oblique aponeurosis → transversalis fascia → transversus abdominis aponeurosis B.Skin → camper’s fascia → scarpa’s fascia → external oblique aponeurosis →rectus abdominis muscle → internal oblique aponeurosis→transversus abdominis aponeurosis C.Skin → camper’s fascia→ scarpa’s fascia →external oblique aponeurosis → internal oblique aponeurosis → transversus abdominis aponeurosis → rectus abdominis muscle → transversalis fascia → parietal peritoneum D.Skin → scarpa’s fascia → camper’s fascia → external oblique aponeurosis → half ofinternal oblique aponeurosis → transversus abdominis muscle → half of internal oblique aponeurosis → transversalis fascia E.Skin → camper’s fascia→ scarpa’s fascia→ internal oblique aponeurosis → external oblique aponeurosis→ transversus abdominis aponeurosis → rectus abdominis muscle → visceral peritoneum transversalis fascia
C
the venous blood entering the liver). A stool sample is tested and shows the presence of Schistosoma mansoni eggs which confirms the cause of this patient’s portal hypertension is due to a type of parasitic worm. The first stage of treatment in this case is a prescription of praziquantel to kill the worms. Now that the physician has identified the underlying cause of the varicose vessels, she tries to explain to the patient what structures can be seen on his anterior abdominal wall. In the accompanying image, what vessel can be seen underlying the skin at the tip of the arrow? A.Thoracoepigastric vein B.Inferior epigastric vein C.Paraumbilical vein D.Superficial epigastric vein E.Superior epigastric vein F.Internal iliac artery G.External iliac artery H.Internal thoracic artery I.Lateral thoracic artery J.Umbilical artery
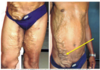
D
A 19 year old woman presents to her physician three weeks after getting a friend to
pierce her anterior abdominal wall. Upon physical examination, the physician notes that
the patient’s skin is inflamed and there is a thick, yellow/orange fluid that is being
discharged from the piercing that is indicated at the tip of the arrow in the accompanying
image. Which of the following groups of lymph nodes would most likely become
enlarged first if the infection is left untreated?
A. External iliac
B. Superfi
cial inguinal
C. Pectoral
D. Deep inguinal
E. Parasternal
F. Axillary
G. Internal iliac

B
When describing the boundaries of the right upper abdominal quadrant, which two
planes (lines) are typically used to separate and distinguish it f
rom the other three
quadrants?
A. Median and transumbilical
B. Transumbilical and midclavicular
C. Midclavicular and transtubercular
D. Transtubercular and subcostal
E. Subcostal and median
A
A 25 year old boxer receives a hard blow to his left upper quadrant (close to the midline) of his
anterior abdominal wall during a high profile competition. A large swelling develops over the
next several hours and medical imaging confirms the palpable mass is a hematoma. In this case,
(i) which vessel was most likely compromised (damaged) to cause the hematoma and (ii) what
relationship does this vessel have with rectus abdominis muscle?
A. Right inferior epigastric artery Superficial to rectus abdominism.
B. Right superior epigastric vein
Medial to rectus abdominis m.
C. Right superficial epigastric artery
Deep to rectus abdominis m.
D. Left inferior epigastric vein
Lateral to rectus abdominis m.
E. Left superior epigastric artery
Deep to rectus abdominis m.
F. Left superficial epigastric vein
Superficial to rectus abdominis m.
E
Which of the following organs is typically described as being located in the left iliac
(inguinal) region?
A. Appendix
B. Gallbladder
C. Sigmoid colon
D. Transverse colon
E. Urinary bladder
F. Left suprarenal gland
G. Spleen
C
A 6 year old boy presents to the emergency department with penetrating trauma
through his right upper quadrant. The surgeon is preparing the patient for exploratory
laparotomy and draws the incisional cut which can be seen in the accompanying image.
In this case, what surface feature of the anterior abdominal wall is represented by the
black dashed line?
A.
Costal margin
B.
Linea semilunaris
C.
Transtubercular plane
D.
Linea alba
E.
Transumbilical
F.
Tendinous intersection
G.
Subcostal plane

D
In the accompanying image, the structure indicated at the tip of the arrow (i) is typically a direct branch of which artery and (ii) creates which peritoneal fold associated with the anterior abdominal wall?
A. External iliac
–
Left lateral umbilical fold
B. Umbilical
–
Left medial umbilical fold
C. Internal iliac
–
Median umbilical fold
D. Umbilical
–
Median umbilical fold
E. External iliac
–
Right medial umbilical fold
F. Internal iliac
–
Right lateral
umbilical fold

A


