Anatomy of the PNS revision Flashcards
(25 cards)
What is the basic unit of the nervous system and describe its structure
A neuron it is comprised off:
- Cell body
- dendrites
- Axon covered by a myelin sheath

What is a nerve cell body ?
It is the nucleus containing central part of a neron exclusive of its axon and dendrites (this is the major structural element of grey mater in the brain & spinal cord also known as soma)
What is a collection of nerve cell bodies in the CNS called ?
What is a collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS called ?
- In the CNS called a nucleus
- In the PNS called a ganglion
What are the 2 main types of nerons and describe their differences between each other
- Multi-polar neurons - these neurons have > or equal to 2 dendrites and their cell body exists in the CNS these are the motor units of the skeletal muscle and ANS (motor neurons)
- Unipolar neurons - has a doouble process (in terms of axon), cell body exists in the PNS, these are sensory receptors (sensory neurons)

Describe the general function of motor (efferent) neurons
Describe the general function of sensory (afferent) neurons
Motor neurons carry impulses towards body wall, body cavity or organs (away from CNS)
Sensory (afferent) neurons carry impulses towards the brain (to the CNS)
What is a neve and what can it also be known as?
- A collection (bundles) of axons surrounded by connective tissue and blood vessels
- Known as a ‘tract’ in the CNS

What is meant by a single modality nerve, mixed modality nerve and a named nerve ?
Single modality nerve where only one of somatic motor, somatic sensory, special sensory, sympathetic, parasympathetic or visceral afferent exists in the nerve. ‘Tracts’ tend to consist of a single modality
Mixed modality nerve is where there is somatic motor, somatic sensory and sympathetic all together in one nerve. Most nerves are like this
Named nerves these are Larger nerves supplying body wall, body cavities and organs, traditionally been given names e.g. . trigeminal, femoral, radial, phrenic, vagus etc
List the 12 cranial nerves including there what modalities are carried within the nerve and state where they connection to the brain

Label the indicated cranial nerves and the areas of the brain indicated


How many pairs of spinal nerves are there ? and state the different classes of spinal nerves
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves:
- 8 cervical: C1 - C8
- 12 thoracic: T1-T12
- 5 lumbar: L1 - L5
- 5 sacral: S1 - S5
- 1 coccygeal: Co1
Where are spinal nerves only found ?
ONLY found in the intervertebral foramen

Describe how spinal nerves connect to the spinal cord segment and to structures of the soma (body)
- They connect with strctures of the soma (body) via rami
- They connect with the spinal cord segment of the same number (as that spinal nerve) via roots and rootlets
Label the following parts of a spinal nerve

Note the bulge seen just after the posterior root is known as the dorsal root ganglion
Prior to the intervertebral foramen you have rootlets and roots, then in the interveerterbral foramen it is known as the spinal nerve which branches into posterior and anterior rami after the intervertebral foramen
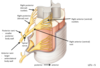
Describe the passage of motor and sensory axons within spinal nerves
ALL sensory axons pass from the spinal nerve into the posterior root then into the posterior rootlets then into the posterior horn of the spinal cord (initially they come from A&P rami)
ALL motor axons pass from the anterior horn of the spinal cord into anterior rootlets then into the anterior root then into the spinal nerve (initially come from A&P rami)
The spinal nerve is where the nerve becomes mixed modality

Describe the segemental innervation of spinal nerves
Each spinal nerve supplies innervation to a unilateral area of the body this results in body wall being ‘segmented’
Each spinal nerve pair supplies a body segment with:
- general sensory supply to all structures
- somatic motor supply to skeletal muscles
- sympathetic nerve supply to the skin and to the smooth muscle of arterioles

What is a dermatome ?
- Dermatome = the area of skin supplied with sensory innnervation from a single spinal nerve
- They also supply sensory innervation to deeper structures
- Note that the innervation of skin by adjacent spinal nerves overlaps
What is a myotome ?
The skeletal muscles supplied with motor innervation from a single spinal nerve
Myotomes may be deep to the dermatome supplied by the same spinal nerve but this is not always true e.g. diaphragm supplied by spinal nerves C3,4,5 but dermatomes C3,4,5 do not lie over where the diaphragm is
Go over these important landmarks for dermatomes:
- Male nipple = T4 segment
- Umbilicus = T10 segment
- Posterior scalp, neck and shoulder = C2-C4
- Upper limb = C5-T1
- Lower limb, gluteal region and perineum = L2-Co1
Go over the foester dermatome map

What is a nerve plexus and what are the main nerve plexuses in the body and there corresponding spinal nerve roots ?
A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibres that arise from the intermingling of the anterior rami of a number of adjacent spinal nerves
- Cervical plexus : C1-C4 - innervates Posterior scalp, neck and diaphragm
- Brachial plexus : C5-T1 - innervates Upper limb
- Lumbar plexus : L1-L4 - innervates Lower limb
- Sacral plexus : L5-S4 - innervates Lower limb, gluteal region and perineum
Go over the peripheral cutaneous nerve supply of the body

Describe sympathetic outflow
- Originates from autonomic centres in the brain
- Passes down spinal cord
- Fibres exit spinal cord with T1-L2 spinal nerves ==>Thoracolumbar outflow
- Presynaptic axons carry ‘motor’ innervation so pass through the anterior rootlets/roots into the paraverterbral or sympathetic chain ganglia
- Sympathetic axons then take 1 of 4 routes within the sympathetic trunk:
First potential route is for the presynaptic sympathetic fibres to ascend and then synapse e.g. innervation of the head and upper limb
other option is for them to synapse at the level of entry e.g. for innervation of middle trunk
other option is for fibres to descend and then synapse e.g. for innervation of the lower limb
other option is for presynpatic sympathetic fibres to pass through the sympathetic trunk without synpasing and to enter an abdominosplanich nerve - this is for innervation of abdominoplevic viscera only
They then from sympathetic trunk
Pass into all spinal nerves (anterior and posterior rami)
Hitch a ride with arteries to all head and neck organs and skin
Supply:
- Skin sweat glands
- Skin arrector muscles
- All arterioles (sympathetic tone)
Go over this pic of the initial part of sympathetic outflow (follow the dotted line initially)
Before passing into the roots/rootlets the sympathetic fibres are arranged in a column of preganglionic nerons that extend from T1-L2 and is referred to as the intermediolateral column of the spinal cord grey mater or lateral horn

Describe the rest of the sympathetic outflow
Heart:
- presynaptic axons synapse in T1 or cervical paravertebral ganglia
- postsynaptic axons pass in cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves to the SA & AV nodes & the myocardium
Lungs:
- presynaptic axons synapse in upper thoracic paravertebral ganglia
- postsynaptic axons pass in cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves to the bronchiolar smooth muscle & mucous glands
Abdominopelvic organs
presynaptic axons synapse in one of the prevertebral ganglia:
- celiac ganglion of celiac plexus (foregut)
- aorticorenal ganglion (kidney)
- superior mesenteric ganglion of SM plexus (midgut)
- inferior mesenteric ganglion of IF plexus (hindgut & pelvic/perineal organs)
Adrenal medulla:
- presynaptic axons pass through the aorticorenal ganglion to synapse directly onto the adrenaline/noradrenaline secreting cells of the adrenal medulla

Describe parasmypathetic outflow
Parasympathetic fibres leave the CNS via:
CN’s III, VII, IX and X (37910) & sacral nerves ==> also known as craniosacral outflow
Parasympathetic then travel via:
CN III ==> Ciliary Ganglion ==> eye
CN VII (note CN IX ==> otic ==> parotid) ==> Parasympathetic ganglia in head (pterygopalatine, otic & submandibular ganglion) ==> lacrimal gland and salivary glands
Vagus nerve - organs of the neck, chest and abdomen as far as the mid-gut
Sacral spinal nerves - hindgut, pelvis and perineum



