Anatomy 4 - Space occupying lesions Flashcards
What is the problem with space occupying lesions and define what a SOL is ?
Space occupying lesions (SOL) = abnormal tissue taking up space in the skull
The problem with SOL’s is that the base of skull foraminae do not readily permit ‘escape’ of contents ==> Acute or sub acute (expanding) intracranial pathologies can result in increased ICP, in turn the increased ICP can result in herniation
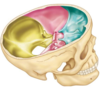
What are the 5 layers of the scalp and how do you remember them ?
SCALP:
- Skin
- Connective tissue
- Aponeurosis
- Loose connective tissue
- Pericranium
What does layer 2 of the scalp contain and why is this important ?
Contains the named arteries of the scalp
The scalp arteries form a rich anastomotic network just deep to the skin – scalp lacerations & incisions can bleed excessively

What are the 4 main sutures of the skull and what is their function ?
- Coronal
- Sagittal
- Lamboid
- Squamous - joins the parietal and temporal bones
Function is to stop fractures spreading (they are fibrous joints)

What are the main bones of the skull ?

What are the main bones of the skull (face)
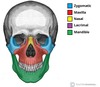
What are the main bones of the base of the skull

Go over some of the features of the skull

What is the pterion and why is it significant ?
It is the thinnest part of the skull formed between the Frontal, parietal, temporal and sphenoid bones
The middle meningeal artery courses deep to it ==> it is at risk to damage
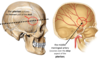
State the following meningeal layers shown


What is the intracranial dura mater mainly innervated by ?
CN V
What is the dura mater adherent to ?
All of the bones of the skull
What is the tentorium cerebelli and the diaphragm sellae ?
Tentorium cereblli = a tough sheet of dura mater ‘tenting’ over the cerebellum
Diaphragm sellae = a tough sheet of dura mater forming a roof over the pituitary fossa

What is the falx cerebelli ?
A midline structure of dura mater splitting the brain into the left and right cerebral hemispheres

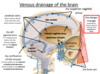
Label the venous drainage of the brain

Main veins to remember:
- Superior sagittal sinus
- Cerebral veins
- Left sigmoid sinus
- Opthalamic veins
- Internal jugular vein
- Facial vein
The dural venous sinuses lie between the periosteal and meningeal layers of the dura mater. They are best thought of as collecting pools of blood, which drain the central nervous system, the face, and the scalp. All the dural venous sinuses ultimately drain into the internal jugular vein