Anatomy of the Hand and Wrist Flashcards
Most flexors of the forearm attach to where?
Medial epicondyle
What are the anterior muscles of the forearm?
-
Brachioradialis (orange)
- Elbow flexion
- Medial nerve
-
Pronator teres (blue)
- Elbow flexion
- Medial nerve
-
Flexor carpi ulnaris (orange – medial)
- Wrist flexion
- Wrist adduction
- Ulnar nerve
-
Flexor carpi radialis (yellow)
- Wrist flexion
- Wrist abduction
- Supplied by radial nerve, which is unusual as most flexors by median nerve
-
Palmaris longus (green)
- Not everyone has, and not always in both arms

What movement is produced by the brachioradialis?
Elbow flexion
What nerve supplies the brachioradialis?
Median nerve
What movement is produced by the pronator teres?
Elbow flexion
What nerve supplies the pronator teres?
Median nerve
What movements are produced by flexor carpe ulnaris?
Wrist flexion
Wrist adduction
What nerve supplies the flexor carpe ulnaris?
Ulnar nerve
What movements are produced by the flexor carpi radialis?
- Wrist flexion
- Wrist abduction
What nerve supplies the flexor carpi radialis?
- Supplied by radial nerve, which is unusual as most flexors by median nerve
What is an anterior muscle of the forearm that not everyone has?
- Pulmaris longus (green)
How does using muscles of the anterior forearm together differ from using them seperately?
Using muscles together produces flexion of wrist, but individually is adduction/abduction
Where do the posterior muscles of the forearm attach to?
Lateral epicondyle
What are the posterior muscles of the forearm?
-
Extensor carpi ulnaris (pink)
- Extension of wrist
- Adduction of wrist
- Radial nerve
-
Extensor carpi radialis longus (blue)
- Extension of wrist
- Abduction of wrist
- Radial nerve
-
Extensor carpi radialis brevis (yellow)
- Extension of wrist
- Abduction of wrist
- Radial nerve

What movements are produced by extensor carpi ulnaris?
- Extension of wrist
- Adduction of wrist
What movements are produced by extensor carpi radialis longus?
- Extension of wrist
- Abduction of wrist
What movements are produced by extensor carpi radialis brevis?
- Extension of wrist
- Abduction of wrist
What nerve supplies the extensor carpi ulnaris?
Radial nerve
What nerve supplies the extensor carpi radialis?
Radial nerve
What nerve supplies the extensor carpi radialis brevis?
Radial nerve
What muscles are found deep to the superficial flexors of the forearm?
- One intermediate flexor
- Still attaches to medial epicondyle
-
Flexor digitorum superficialis
- Fingers have 3 phalanges, it attaches after the second
- Assists in flexion of every joint it crosses
- Flexion of: elbow, wrist, metacarpophalangeal joints, proximal interphalangeal joints
- Supplied by median nerve
- Then two deep flexors
- Does not attach to medial epicondyle (so not elbow flexors like the rest – only cross wrist joint)
-
Flexor digitortum profundus
- Does not do flexion at elbow as doesn’t cross it, but cross last phalangeal joint of fingers
- So, flexion of: wrist, metacarpophalangeal joints, proximal interphalangeal joints, and distal metaphalangeal joints
- Medial side supplied by median nerve, lateral side by radial nerve
-
Flexor pollicis longus
- Flexion of thumb (interphalangeal joint of the thumb)
- Supplied by median nerve

What does the digitorum superficialis attach to?
- Medial epicondyle
- Fingers have 3 phalanges, it attaches after the second

What movements are produced by the flexor digitorum superficialis?
- Assists in flexion of every joint it crosses
- Flexion of: elbow, wrist, metacarpophalangeal joints, proximal interphalangeal joints
What nerve supplies the flexor digitorum superficialis?
Median nerve
Do the deep flexors attach to the medial epicondyle like other flexors of the forearm?
- Then two deep flexors
- Does not attach to medial epicondyle (so not elbow flexors like the rest – only cross wrist joint)
- Flexor digitortum profundus
- Does not do flexion at elbow as doesn’t cross it, but cross last phalangeal joint of fingers
- So, flexion of: wrist, metacarpophalangeal joints, proximal interphalangeal joints, and distal metaphalangeal joints
- Medial side supplied by median nerve, lateral side by radial nerve
- Flexor pollicis longus
- Flexion of thumb (interphalangeal joint of the thumb)
- Supplied by median nerve

What movement is produced by the flexor digitorum profundus?
- Does not do flexion at elbow as doesn’t cross it, but cross last phalangeal joint of fingers
- So, flexion of: wrist, metacarpophalangeal joints, proximal interphalangeal joints, and distal metaphalangeal joints
What nerve supplies the flexor digitorum profundus?
- Medial side supplied by median nerve, lateral side by radial nerve
What movement is produced by the flexor pollicis longus?
- Flexion of thumb (interphalangeal joint of the thumb)

What nerve supplies the flexor pollicis longus?
Median nerve
What muscles are found deep to superficial extensors?
- Two intermediate extensors
- Still attaches to lateral epicondyle
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Not as specific as flexors in terms of which phalanges they cross
- Deep extensors and abductors
-
Anconeus (red)
- Extension of elbow
- Supinator (yellow)
-
Extensor pollicis brevis (orange)
- Extension of thumb
-
Extensor pollicis longus (blue)
- Extension of thumb
-
Abductor pollicis longus (blue)
- Abduction of thumb
-
Extensor indicis
- Extension of forefinger
-
Anconeus (red)
What do the two intermediate extensors (extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi) attach to?
Lateral epicondyle

What is the orange flexor?

Brachioradialis
What is the blue flexor?
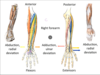
Pronator teres
What is the orange flexor which is more medial?

Flexor carpe ulnaris
What is the yellow flexor?

Flexor carpi radialis
What is the green flexor?

Pulmaris longus
What is the pink extensor?

Extensor carpi ulnaris
What is the blue extensor?

Extensor carpi radialis longus
What is the yellow extensor?

Extensor carpi radialis brevis
What is red?

Anconeus
What is yellow?

Supinator
What is orange?

Extensor pollicis brevis
What is blue?

Extensor pollicis longus
What is blue?

Abductor pollicis longus
What is green?

Extensor indicis
What is the movement produced by anconeus?
Extension of elbow
What is the movement produced by supinator?
Supernation
What is the movement produced by extensor pollicis brevis?
Extension of thumb
What is the movement produced by extensor pollicis longus?
Extension of thumb
What is the movement produced by abductor pollicis longus?
Abduction of thumb
What is the movement produced by extensor indicis?
Extension of forefinger
Describe the movements of the thumb?
- Flexion and extension is towards the floor and roof
- Adduction and abduction are towards the front and back

What is A?

Flexion
What is B?

Extension
What is C?

Abduction
What is D?

Adduction
What is E?

Opposition
Adduction and abduction of fingers is around what?
Adduction and abduction of fingers work around the axial line of the hand (a plane):
- Adduction is moving towards plane
- Abduction is moving away from plane
- So middle finger can do abduction in both directions (moving away from plane through it)



