Anatomy of - lecture 2 part 2 Flashcards
(22 cards)
Describe somatic pain and give examples
sharp, well localised stabbing
- Joint pain
- fibrous pericardium
- Muscular bony
- intravertebral disc
- Nerve
Describe visceral pain
dull, aching, nauseating, poorly localised
- Eosophageal
- Tracheal
- Heart lungs other organs
what is radaiting pain and reffered pain
Radiating pain - Central chest pain - radiating to the back, neck, upper limbs,
What is Reffered pain
This pain is only felt at the site distant to the tissue damage in the chests - pain felt
- Neck
- Upper limb
- back in heart attack
What is the pathway of pain
- action potential passes through anterior ramus
- Will travel to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
- Will synpase with a second neurone which cross over to the opposite side in the spinal cord
- This neurone will then travel to the cerebral cortex where it will gian conciousness

What are the different parts of the brain
- Central sulcus divides the cerebrum into anterior into frontal and parietal lobes
1. Pre-Central Gyrus - Just anterior to the central sulcus
- Somato-motor area –will bring about contraction of smooth muscle
2. Post-Central Gyrus
- Just posterior to the central sulcus
- Somato-sensory – Aps that arrive here are sensory – pain

What is the sensory humanculus
He illustrates the areas of the cerebral neocortex (the outermost layer of the cerebral hemispheres) where sensations from different body wall structures (soma) reach consciousness. There is an equivalent somatic motor homunculus
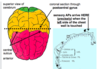
What are somatic central chest pain sources
Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
- Chicken pox lie dorment in posterior root ganglion
- Can get pain and blisters anyhwere in that dermatome
- If its T4/T5- you can get sharp central chest pain

Muscle, bone and joint causes of central chest pain
- Pectoralis major or intercostal muscle strain
- Dislocated costochondral joint
- Costovertebral joint inflammation
- “Slipped” thoracic intervertebral disc
- All can be felt as central chest pain
Types of visceral chest pain

What are the 4 divisions of the mediastinum
- Superior - T4
- Inferior
- anterior
- posterior
- middle

what is the level of the superior mediastinum
T4
Structures in the right side of the mediastinum

Structures of the left side of the mediastinum
- Phrenic nerve is located on the top of the root on the lung
- The Arch of the Aorta – can only be visualized from the left side
- Descending aorta - Thoracic aorta
- Ligamentum Arteriosum – remimenant embryological structure that connects the arch of the aorta to the pulmonary trunk
- On Left hand side – vagus nerve crosses the aorta –(important to orientate your self during examination when asked about vagus nerve)
- Left vagus nerve – branches into recurrent laryngeal nerve
- Thoracic Duct – Lymph drainage

What is the vagus nerve found on right and left side
- Right side - surface of trachea
- Left side - crosses the aorta
- Branch - Recurrent laryngeal nerve
what are the structures of the posterior mediastinum

How does pain get to the CNS
Visceral afferent
- Visceral afferents will travel along side cardiopulmonary splanchic nerves
- Will follow sympathetics within spinal cord to reach the cerebral cortex
- Specifically post central gyri
Visceral afferents and somatic seconsory enter the spinal cord at the same site what is the problem with this?
- The somatic sensory fibers are also plugging in at same area as the visceral afferents (cardiopulmonary nerves)
- Confusion due to close proximity of the 2 pain fibers- cant decided where the pain is coming from – heart or somatic structures?
- Somatic sensory fibres & visceral afferents are BOTH entering the spinal cord
What are the different types of MI
- Anterior MI
- Inferior MI
- Anterior-lateral MI
What coronary arteries are dominant i.e myocaridum is supplied most by which artery
- 70% individuals right coronary artery is dominant - so myocaridum is supplied mostly by the right coronary artery
- 15% individuals the left coronary artery is dominant
In coronary atherosclerosis which sites are commonly affected
- Left anterior descending - 40%
- Right coronary artery
- Circumflex
- Main stem of left coronary artery

Leads and arteries



