Anatomy Lecture 2 -- Posterior Abdominal Wall Flashcards
Upper attachments of the psoas major
- Sides of vertebrae T12 to L5
- IV discs
- Transverse processes

Lower attachment of the psoas major
Lesser trochanter of the femur with iliacus muscle (iliopsoas)

Upper attachment of the psoas minor
- Sides of vertebrae T12 to L1
- IV discs
- Transverse processes

Lower attachment of the psoas minor
Superior ramus of the pubic bone (pectineal line)

Posterior abdominal wall muscles that cross under the inguinal ligament
- Psoas major
- Iliacus
Posterior abdominal wall muscle that passes over the inguinal ligament
Psoas minor
Upper attachment of the quadratus lumborum
- Medial 1/2 of inferior border of the 12th rib
- Transverse processes of L1 to L5

Lower attachment of the quadratus lumborum
- Iliolumbar ligament
- Iliac crest

Upper attachments of the iliacus
- Superior 2/3 of iliac fossa
- Ala (wing) of sacrum
- Anterior sacroiliac ligaments

Lower attachment of the iliacus
Tendon of psoas = iliopsoas

5 muscles of the posterior abdominal wall
- Psoas major
- Psoas minor
- Quadratus lumborum
- Iliacus
- Transversus abdominus
3 origins of the muscle fibres of the diaphragm
- Sternum
- Ribs (costal margin)
- Lumbar vertebrae
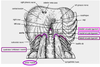
Diaphragmatic muscle that wraps around the esophagus
Right crus

Diaphragmatic muscles on either side of the aorta
Right and left crus

Nerve that travels alongside the IVC. How does its corresponding nerve pierce the diaphragm?
- Right phrenic nerve
- Left pierces diaphragm on its own
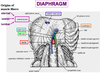
Where do the muscle fibres of the diaphragm converge?
Central tendon
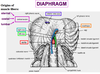
Ligament of the diaphragm that forms the hole through which the aorta enters
Median arcuate ligament
Ligament of the diaphragm that lets the psoas pass underneath
Medial arcuate ligament

Ligament of the diaphragm that lets the quadratus lumborum come through
Laterla arcuate ligament

Define the caval foramen
Hole in the central tendon through which the right phrenic nerve and lymphatics pass

How does the sympathetic trunk pierce the diaphragm
On either side of the abdominal aorta just inside the medial arcuate ligament

Define somatic nerves
Any nerve that is not in the gut (i.e. arms, legs and body wall; motor and sensory)
Define a reflex arc
A neural circuit that creates a more or less automatic link between a sensory input and a specific motor output

Describe how the simplest spinal reflexes are mediated
3 element chain:
- Sensory neurons
- –> interneurons in the spinal cord
- –> motor neurons
(–> means activate)
2 roots that branch from the spinal cord and the structure that the subsequently form
Dorsal and ventral roots –> spinal nerve
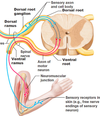
What does the spinal nerve branch into?
Dorsal and ventral rami (ramus singular)

What do dorsal rami innervate?
The deep muscles of the back (motor)
Horizontal strips of skin (sensory)
Alternative name for the ventral rami in the thoracic region
Intercostal nerves
What are the communicating branches?
Rami communicantes, which go to each ganglion all the way down the sympathetic trunk to a point
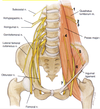
What do the lumbar nerves form when they join together?
Major nerves that go down the leg
Identify these 7 nerves of the lumbar plexus

- Subcostal nerve
- Iliohypogastric nerve
- Ilioinguinal nerve
- Genitofemoral nerve
- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh
- Femoral nerve
- Obturator nerve
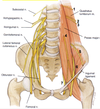
Lumbar plexus nerve that crosses the iliacus
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (5)

Lumbar plexus nerve the is on the lateral side of the psoas
Femoral nerve (6)

Completely straight nerve of the lumbar plexus that goes down inside the pelvis through the obturator foramen
Obturator nerve (7)

Nerve of the lumbar plexus that branches into a Y at the bottom
Genitofemoral nerve (4)
How do the right and left vagus nerves enter the abdomen?
As the posterior and anterior vagal trunks, respectively, through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm
What does the vagus nerve supply?
Motor parasympathetic fibers to all the organs except the suprarenal (adrenal) glands, from the neck to the second segment of the transverse colon
From where do the pelvic splanchnic nerves arise?
Ventral rami of the S2 - S4
Describe the trajectory of the pelvic splanchnic nerves from their origin
- Arise from ventral rami of S2 - S4
- Travel from each side of pelvis to corresponding inferior hypgastric plexus
- Travel to distal 1/3 of transverse colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, bladder and genitalia
- Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres synapse in walls of organs
Location of inferior hypogastric plexus
Bilaterally on the walls of the rectum
Where do the white rami stop? What does this mean?
- After L2
- Preganglionic fibers must travel down the sympathetic chain from higher levels
6 ganglia of the abdominal region
- Celiac
- Aorticorenal
- Superior mesenteric
- Inferior mesenteric
- Superior hypogastric
- Inferior hypogastric

Sympathetic nerves that form the greater splanchnic nerve
T5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Sympathetic nerves that form the lesser splanchnic nerve
T10, 11
Function of the general visceral sensory (afferent) fibers (GVA)
Conduct sensory impulses (usually pain or reflex sensations) from the viscera, glands and blood vessels to the central nervous system. (Considered to be part of ANS but afferent fibers are not classified as either sympathetic to para)
From what is the cortex of the adrenal gland derived?
Mesoderm
From what is the medulla of the adrenal gland derived?
Embryonic neural crest cells
How are hte cells of the adrenal medulla innervated?
Preganglionic sympathetic fibers (no postganglionic fibers)
Define the cisternae chyli
Start of the thoracic duct

What nerves do the GVA usually accompany? Which nerves are the exception?
- Sympathetic efferent fibres
- Abdominal GVA that DO NOT follow this pathway = those that innervate structures in the distal half of the sigmoid colon and the rectum (follow the path of the parasympathetic efferent fibers back to the vertebral column)


