Anatomy GI Flashcards
The superior epigastric artery is a continuation of what?
internal thoracic (mammary) arteries

The internal thoracic arteries are branches of what?
The internal thoracic artery (internal mammary artery) is a long, paired vessel that originates from the proximal part of the
subclavian artery.

Subclavian artery branches: Mnemonic:
‘Very Tired Individuals Sip Strong Coffee Served Daily’. It covers the following structures:
Vertebral artery
Thyrocervical trunk
Inferior thyroid artery
Superior cervical artery
Suprascapular artery
Costocervical trunk
Supreme intercostal artery
Deep cervical artery
What is the motor and sensory nerve of the diaphragm?
phrenic nerves

What nerve provides PNS to the organs of the thorax and abdomen?
vagus nerves

At what level is the oesophageal hiatus?
T10
Remeber:
aortic hiatus = 12 letters = T12
Oesophagus = 10 letters = T10
Vena cava = 8 letters = T8
What level is the IVC opening
T8
Remeber:
aortic hiatus = 12 letters = T12
Oesophagus = 10 letters = T10
Vena cava = 8 letters = T8
What level is the aortic hiatuus
T12
Remeber:
aortic hiatus = 12 letters = T12
Oesophagus = 10 letters = T10
Vena cava = 8 letters = T8
When does the primordial gut tube develop?
4th week of human development
What is the primordial gut tube derived from?
Endoderm lining the yolk sac
Name the parts the primordial gut tube is divided into?
Foregut
Midgut
Hindgut

What is the artery of the foregut?
celiac trunk

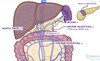
Name the Foregut Structures
Primordial pharynx
Oesophagus
Stomach
Duodenum
Liver

Where is the duodenum proximal to?
The opening of bile gut

Name the constrictions of the oesophagus
Cervical
Thoracic
Diaphragmatic

Where is the cervical constriction of the oesophagus found?
15cm from incisor teeth C6
What is the cervical constriction of the oesophagus called?
Pharyngo-esophageal

Where is the thoracic constriction of the oesophagus found?
Crossed by arch of aorta and left main bronchus T4
Where does the diaphragmatic constriction of the oesophagus pass?
Though the oesophageal hiatus of the diaphragmatic t10

What is the thoracic constriction of the oesophagus called?
Broncho-aortic

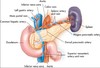
Name the parts of the stomach?

Cardia
Fundus
Body
Pyloric part

How many curvatures are in the stomach?
2

Define pyloric sphincter
Ring of smooth muscle that connects the stomach and small intestine
What is the function of the pyloric sphincter?
Control discharge of stomach contents into the duodenum