Anatomy: Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Flashcards
Which nerve innervates the larynx?
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
What is indicated by the arrow?

Retropharyngeal space
What is the name given to the narrow band which connects the two lobes of the thyroid gland?
Isthmus
What is indicated by the arrow?

External jugular vein
Where are the parathyroid glands located?
On the posterior surfaces of the thyroid gland lateral lobes

What is the pyramidal lobe?
Variation in the structure of the thyroid that represents a persistent remnant of the thyroglossal duct

What is indicated by the arrow?
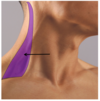
Right posterior triangle of the neck
C1 travels within which cranial nerve to reach the thyrohyoid?
Hypoglossal nerve
What is indicated by the arrow?

Right anterior triangle of the neck
Name the proximal attachment of the sternal head of sternocleidomastoid
Manubrium of sternum
Which fascial compartment is coloured red?

Carotid sheath
Name the vertebral levels between which the thyroid gland is situated
C5-T1
Name the distal attachment of the carotid sheaths
Blend inferiorly with mediastinal fascia
Identify muscle A

Thyrohyoid
Which nerve supplies sternocleidomastoid and trapezius?
CN XI (spinal accessory nerve)
Which vein does the external jugular vein drain into?
Subclavian
Which fascial compartment is coloured purple?

Pretrachial fascia
What is indicated by the arrow?

Anterior jugular vein
What does lymph from the right lymphatic duct drain into?
Right venous angle
Injury to which nerve will result in paralysis of the vocal cords?
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Describe the structure of the thyroid gland
Usually consists of two lateral lobes (right and left) and isthmus (narrow connecting band)

List the 4 strap muscles (superficial and deep) from medial to lateral
Superficial: sternohyoid is medial, omohyoid is lateral
Deep: sternothyroid is medial, thyrohyoid is lateral

What is the foramen caecum?
Point of origin in the tongue of the thyroid gland
Which structures lie anteriorly to the thyroid gland?
Sternothyroid, superior belly of the omohyoid and sternohyoid























