Anatomy Flashcards
What does the urinary tract consist of?
The anatomical structures through which urine passes from its production to its excretion.

What is the function of the detrusor muscle?
Contracts to empty the contents of the bladder when full.
Which structures are involved in a lower UTI?
Urethra and bladder.
Which structures are involved in an upper UTI?
Kidneys.
What structures are found in the upper urinary tract?
Kidneys (left and right).
Ureters (left and right).
What structures are found in the lower urinary tract?
The bladder.
The urethra.
Which body cavities does the urinary tract pass through?
Abdomen.
Pelvis.
Perineum.
What structures of the urinary tract are found in the abdomen?
Kidneys.
Proximal ureters.
In the retroperitoneum.
What structures of the urinary tract are found in the perineum?
Distal urethra.
What structures of the urinary tract are found in the pelvis?
Distal ureters.
Bladder.
Proximal urethra.
What structure is in contact with the anterior surface of the kidneys?
Visceral peritoneum.

What is the renal hilum?
Root of the kidney (arteries, veins and urinary structures entering and exiting the kidney).
Where are the kidneys located?
Posterior to their own visceral peritoneum.
Enclosed within the renal fat/fascia/capsule.
Surrounded by skeletal muscles:
- Muscles of the posterior abdominal wall.
- Muscles of the antero-lateral abdominal wall.
- Muscles of the back.
- Muscle guarding can protect the kidneys from trauma.
Where do the kidneys lie exactly?
Anterior to the quadratus lumborum.
Lateral to psoas major and lower thoracic/upper lumbar vertebral bodies.
What vertebral bodies is the left kidney in line with?
T12-L2.
What vertebral bodies is the left kidney in line with and why?
L1-L3.
Liver pushes kidney inferiorly.
Which ribs can lacerate the kidneys in trauma?
Floating ribs 11 and 12.
Where do the renal veins lie in relation to the renal arteries?
The renal veins are anterior to the renal arteries.
Where does lymph drain to from the kidneys?
The lymph from the ureters drains to the lumbar nodes & the iliac nodes.
The iliac nodes are located around the common, internal & external iliac vessels.
Where does the abdominal aorta bifurcate?
At the level of the umbilicus.
Where does the ureteric arterial blood supply come from?
Branches of the following:
- Renal artery.
- Abdominal aorta.
- Common iliac artery.
- Internal iliac artery.
- Vesical (bladder) artery.
Where does lymph from the kidney drain to?
The lumbar nodes located around the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava.
Where do the common iliac arteries lie in relation to the common iliac veins?
The common iliac arteries are anterior to the common iliac veins.
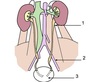
What is the pathway of urine drainage from the kidney?

What is the largest tube of the kidney drainage pathway?
The renal pelvis.
What are the anatomical sites of ureteric constriction?
The pelviuteric junction - cl**inically important as kidney stones can get stuck here.
Ureter crossing the aspect of the common iliac artery (often crosses the bifurcation).
Ureteric orifice.

What can cause ureteric obstruction?
Internal obstruction - an impacted renal calculus or a blood clot.
External compression - an expanding mass (e.g. a tumour).
What is hydronephrosis?
Water inside the kidney due to urine back pressure into the calyces compressing the nephrons within the medullary pyramids leading to renal failure.
Very painful due to the renal capsule stretching.
What is the false pelvis?
The area from the iliac crests to the pelvic inlet.

- It is part of the abdominal cavity.*
- Light green on image.*
What is the true pelvis?
The pelvic inlet to the pelvic floor.

Dark green on image.
What are the pelvic floor muscles?
Levator ani (pelvic diaphragm).
Which cavity is the bladder found in?
Pelvic cavity.
What forms the pelvic floor?
Formed by the shape of the pelvic diaphragm and is made up of muscles including the levator ani.
What is the function of the openings in the pelvic floor?
To allow the distal parts of alimentary, renal and reproductive tracts to pass through from the pelvic cavity into the perineum.
What is the course of the ureters?
The ureters pass anterior to the common iliac vessels to enter the pelvis.
They run anteriorly (along the lateral walls of the pelvis),
At the level of the ischial spine, they turn medially to enter the posterior aspect of the bladder.
This route is completely “sub” peritoneal.
The ureters enter the posterior bladder wall in an inferomedial direction.
Helps prevent reflux of urine back into the ureters when the bladder contracts.
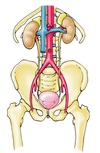
What is the rectovesicle pouch?
In the male peritoneal cavity, it is the deepest part of the peritoneal cavity.
What is the vesico-uterine pouch?
Pouch between the bladder (vesical) and uterus.
What is the deepest peritoneal space in the female body, when standing upright?
Vesico-uterine pouch.
Rectouterine pouch (of Douglas).
What is the deepest peritoneal space in the male body, when standing upright?
The rectovesicle pouch.
In the female, where does the ureter run?
The ureter runs inferiorly to the uterine tubes and the uterine artery.
Water under the bridge.
In the male, where does the ureter run?
The ureter runs inferiorly to the vas deferens.
Need to know the arterial supply of the vesicle.

What does the uterine artery supply?
Uterus.
What does the middle rectal artery supply?
Rectum.
What does the vaginal artery supply?
Vagina.
What does the vesical artery supply?
Bladder.
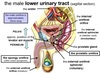
What forms the corners of the triangular shape of the internal aspect of the bladder called the trigone?
2 ureteric orifices.
Internal urethral opening (where the bladder empties).
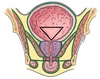
What is the purpose the fibres of the detrusor muscles encircling the ureteric orifices?
Ensures no urine reflux into ureter as these fibres also contract when detrusor contracts for the bladder to empty.
What is the internal urethral sphincter?
Only present in the male.
Sits at the opening of the internal urethral orifice around the neck of the male bladder.
Contracts during ejaculation to prevent retrograde ejaculation of semen back into the bladder.
What is the position of the bladder in the female?
In the female, the body of the uterus usually lies superior to the bladder (in an “anteflexed” position), it is separated from the bladder by the uterovesical pouch.
As a result, most of the weight of the uterus is borne by the bladder.

What is the position of the bladder in the male?
The prostate gland lies inferior to the bladder and the rectum.

Where does an empty bladder lie?
WIthin the pelvis.
Peritoneum covers its superior surface only.
Why can’t you perform a suprapubic catheterisation of an empty bladder?
Can risk piercing the peritoneal cavities.
Where does a full bladder lie?
A full bladder can extend out of the pelvis: its superior part lies superior to the pubic bone.
Peritoneum still only covers its superior surface.
What are the 2 routes of catheterising a patient’s bladder?
Urethral.
Suprapubic (must not be done on an empty bladder).
What is the control of the internal urethral sphincter?
Involuntary control so it contracts at the point of ejaculation.
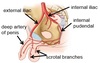
What is the spongy urethra?
The part of the urethra sitting within the corpus spongiosum.
Where are sperm stored?
In the epididymis.
Where does the testis sit within the scrotum?
The testis sits within a sac called the tunica vaginalis.
What is a hydrocele?
Where excess fluid (abnormal) sits within the tunica vaginalis.
What is the main arterial supply of the testis?
The testicular artery.
What surrounds the kidney?
A fibrous capsule.
What is a papilla in a kidney?
The round apex of the medullary pyramids.