Anatomy Flashcards
What are the attachments of the diaphragm?
Anterior - Xiphoid Process
Laterally - Medial aspects of ribs
Posteriorly - Right and left crus

What are the right and left crus
Tendons that attach the diphragm to the verterbral column

What is this and what does it fuse with?

Central tendon
Pericardium
What are the diaphragm openings called and what level are they at?
T8 - Caval Hiatus
T10 - Oesophageal Hiatus
T12 - Aortic Hiatus

What does each hiatus sit in?
Caval - Central tendon
Oesophageal - Right crus
Aortic - Between right and left crus

What arteries supply the superior aspect of the diaphragm?
Internal thoracic which becomes the musculophrenic and pericardiophrenic

What arteries supply the inferior aspect of the diaphragm?
Inferior phrenic artery

What vein supply the superior aspect of the diaphragm?
Internal Thoracic vein

What vein supply the inferior aspect of the diaphragm?
Inferior phrenic vein

What are the three arcuate ligaments?
Median - Connect the right and left crus
Medial and lateral

Where does the abdominal aorta become the common iliacs?
L4
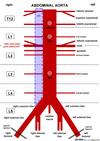
Where does the femoral artery begin from the external iliac arteries?
Inguinal ligament

What three muscles make up the abdominal wall.
What else?
Transversus abdominis
Internal oblique
External oblique
Aponeurosis

What runs down the middle of abdomen, what is it formed from and what does it separate?
Linea Alba
aponeurosis of Abdo muscles
Rectus abdominus

What surrounds the rectus abdominis and what forms it?
Rectus sheath
Aponeurosis of other abdo muscles

What demarcates the lower limit of the posterior line of the rectus sheath?
Arcuate line of rectus sheath

How is the rectus abdominis surrounded above and below the arcuate line?

Where is the femoral canal and what is in it?
Lymphatics

Where can retrograde blood flow occur?
Distal oesophagus
Which part of the tract has longitudinal muscle?
Ascending colon
Which part has no serosal covering?
Proximal oesophagus


