Amino Acid Metabolism I Flashcards
What is the difference between essential amino acids and nonessential amino acids?
- Essential: cannot be synthesized in you body & have to come from the diet
- Nonessential: they can be synthesized by the body & do not have to come from the diet
What are the 11 non-essential amino aids?
Which 2 are synthesized from essential amino acids?
What molecule are the rest synthesized from?
- Synthesized from Glucose
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartate
- Cysteine (from Methionine)
- Glutamate
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Proline
- Serine
- Tyrosine (from phenylalanine)
What are teh 10 essential amino acids?
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Metionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
- Arginine (not required by adults, but required for growth)
- enough is synthesized in the liver by adults, but not for infants

Where are dietary proteins digested to amino acids?
Amino acids are used to synthesize what products?
- Dietary proteins are digested to amino acids in the stomach & intestine
- amino acids are used to synthesize proteins & other nitrogen-containing compounds (nucleic acids, hormones, heme of hemoglobin)
- in the fed state, amino acids can be stored in the form of glycogen or triacylglycerols
- The carbon skeleton is oxidized for energy & the nitrogen is converted to urea

Which cells secrete pepsinogen?
It is the precursor for what enzyme?
How is it activated?
What is the activated enzymes function?
Chief cells
pepsin
Activated by HCl in the stomach
Pepsin starts digesting proteins in the stomach, turning them into polypeptides
Which cells secrete HCl?
What is the function of HCl in the process of protein digestion?
Chief cells
HCl denature proteins in the stomach (inactivates & partially unfolds) so they are better substrates for proteases
HCl also activates pepsinogen to pepsin
What zymogens are secreted from the pancreas for protein digestion?
What are their active forms & what enzymes facilitate this activation?
What is the combined function of these enzymes?
These enzymes convert the polypeptides into oligopeptides
-
Trypsinogen – enteropeptidase
- ACTIVE: Trypsin
-
Chymotrypsinogen – trypsin
- ACTIVE: Chymotrypsin
-
Proelastase – trypsin
- ACTIVE: elastase
-
Procarboxypeptidase A – trypsin
- ACTIVE: carbodypeptidase A
-
Procarboxypeptidase B – trypsin
- ACTIVE: carbodypeptidase B
How are oligopeptides absorbed?
Aminopeptidases in the brush border of the intestinal epithelial cells act on the oligopeptides, converting them to free amino acids that are absorbed by the epithelial cells & transferred to the blood stream
The coenzyme tetrahydrofolate FH4 is derived from what vitmin?
What is its function in the amino acid pathway
Derived from folate (B9)
FH4 is the primary one-carbon carrier in the body & is required to either accept or donate a on-carbon group in the amino acid pathway
What are the sources of one-carbon units for tetrahydrofolate?
Once combined, what are they called? What are the 3 stages of oxidation for the carbon?
Ultimately forming what products?
serine, glycine, histidine, formaldehyde, formate
once combined with FH4, they are called the “one-carbon pool”
The carbon can be formyl (H) methylene (H2) –> methyl (H3)
And when combined with a precursor, can form products such as dTMP, serine, purines & B12 CH3

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is the active form of what vitamin?
It is required for what types of reactions?
vitamin B6
PLP is the quintessential coenzyme of amino acid metabolism & is required for transamination, deamination, decarboxylation, beta-elimination, and gamma-elimination reactions involving amino acids

What is transamination?
What co-enzyme is required for this reaction? Is this a reversible step?
the process of removing nitrogen from amino acids
it is transferred as an amino group to a-keto acid forming different amino acid
The reactions are reversible & use pyroxal phosphate (PLP)

The carbon skeleton of all non-essential amino acids (other than tyrosine) is derived from what precursor?
Tyrosine is derived from what precursor?
Cysteine requires what additional essential amino acid?
All aa except tyrosine: glucose
Tyrosine: phenylalanine
cysteine: requires methionine for its sulfur
What 4 non-essential amino acids are directly derived from glucose & intermediates of glycolysis?
Which 6 non-essential amino acid are derived from the TCA cycle? Which specific components of the TCA cycle?
- Glucose & its glycolysis intermediates
- Glycine
- Serine
- Alanine (pyruvate)
- TCA
- Citrate
- Glutamate
- glutamine
- proline
- arginine
- a-ketoglutarate
- aspartate
- asparagine
- Citrate
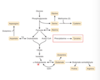
As amino acids are degraded, their carbons can be converted to what two structures?
- compounds that produce glucose in the liver (pyruvate and the TCA-cycle intermediates a-ketoglutarate, sucinyl-CoA, fumarate, and oxaloacetate )
- glucogenic
- ketone bodies or their purecursors (acetoacetate and acetyl-CoA)
- ketogenic
All amino acids are glucogenic EXCEPT -
EXCLUSIVELY ketogenic
lysine & leucine
What amino acids are both glucogenic & ketogenic?
- tyrosine
- phenylalanine
- threonine
- isoleucine
- tryptophan
Which amino acids can be converted into pyruvate?
- Pyruvate
- threonine
- tryptophan
- glycine
- alanine
- serine
- cysteine
What amino acids can be converted to a-ketoglutarate?
- a-ketoglutarate
- glutamate
- arginine
- histidiine
- glutamine
- proline
What amino acids can be converted to Succinyl CoA
- Succinyl CoA
- Valine
- Threonine
- Isoleucine
- Methionine
What amino acids can be converted to fumarate?
- Fumarate
- Asparatate
- Tyrosine
- Phenylalanine
What amino acids can be converted to oxaloacetate?
- oxaloacetate
- aspartate
- asparagine
What amino acids are degraded to acetyl CoA?
What amino acids are degraded to HMG CoA?
What amino acids are degraded to Acetoacetate?
- Acetyl CoA
- threonine
- lysine
- isoleucine
- tryptophan
- HMG CoA
- leucine
- Acetoacetate
- phenylalanine
- tyrosine
Describe the process of serine synthesis from glucose.
and the degradation of serine to glucose
What are the two regulatory steps?
- When serine levels are high, it represses the production of 3-phosphoglycerate that converts 3-phosphoglycerate to 3-phosphyhydroxypyruvate
- When serine levels are high it also inhibits the phosphoserine phosphatase that is responsible for the conversion of 3-phospho-L-serine to serine

Glycine can be synthesized from what two precursors?
- serine (requires PLP & FH4)
- threonine (to lesser extent, also requies PLP)
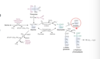
How can glycine cause kidney stones?
- Glycine can be oxidized by D-amino acid oxidase to glyoxylate
- glyoxylate can be oxidized to oxalate
- oxalate is not very soluble & tends to precipitate in kidney tubules, leading to formation of kidney stones
How is energy derived from glycine?
through a dehydrogenase (glycien cleavage enzyme) that oxidizes glycine to CO2 and ammonia


