Alt-On-Hyp, Trip and Similarity Flashcards
Geometric Mean
x of a and b such that
x2 = ab
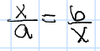
Alt-On-Hyp
The altitude to the hypotenuse of a right triangle is the geometric mean of the segments that the hypotenuse is divided into by the alititude
Leg-Alt-On-Hyp
If we draw an altitude to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, then each leg is the geometric mean of the hypotenuse and the adjacent segment of the hypotenuse
sin(x)
opposite leg
hypotenuse
cos(x)
adjacent leg
hypotenuse
tan(x)
opposite leg
adjacent leg
(slope of the hypotenuse)
sin(30°)
1/2
cos(30°)
sqrt(3)/2
tan(30°)
sqrt(3)/3
sin(60°)
sqrt(3)/2
cos(60°)
1/2
tan(60°)
sqrt(3)
sin(45°)
sqrt(2)/2
cos(45°)
sqrt(2)/2
tan(45°)
1
Law of Sines
sin(A) sin(B) sin(C)
———- = ——– = ——–
a b c
Law of Cosines
a2 = b2 + c2 - 2bccosA
b2 = a2 + c2 - 2accosB
c2 = a2 + b2 - 2abcosC
Identities with Supplementaries
sinA = sin(180-A)
-cosA = cos(180-A)
Inverse Trig Functions
sin-1(opp/hyp) = x
cos-1(adj/hyp) = x
tan-1(opp/adj) =x
To solve SSS and SAS
Use Law of Cosines
To solve ASA, ASS and AAS
Use Law of Sines
To solve HL
Use Pythag and Trig
a < bsinA
No possible triangles
a = bsinA
One possible triangle


