Abo-oto Flashcards
Aminoglycosides and incidence of HL? which part of the cochlea does it effect? how soon after therapy do pt’s start to experience HL?
-10% -basal and inner row of hair cells -3-4 days
Branchial Arches define?

Dermal filler for patients with AIDS

Treatment for anaphylaxis
- 3-0.5mg of 1:1000 epi every 15-20min.
- repeat every 15-20min
- parenteral anti-histamine
Serum markers for anaphylaxis
- histamine have an immediate raise and lasts for 30-60min
- tryptase elevates 30-60min after and stays elevated up to 6 hrs
Innervation of the carotid sinus and/or carotid body tumor?
- Afferent CN IX: info about hypoxia, hypercap, acidosis
- Efferent: superior cervical plexus
Bacteriocidal antibiotics?
Bacteriostatic?
Very Finely Proficient At Cell Murder
-Vanco, Fluoroquinolones, Pens, Aminoglycosides, Cephs, Metro
ECSTaToC
- Erythro (macrolides)
- Clinda
- Sulfa
- Tetra
- Trimethoprim
- Chloramphenicol
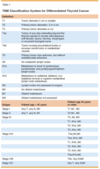
PTC staging
Sunderland Classifications

Contributing vessels to Little’s area

Growth pattern of hemangioma’s of infancy
Rapid growth over first 6 mo’s.
50% resolve by 5 yo
70% resolve by 7 yo
Hemangioma of infancy subgottic risks
50% of subglottic will have cutaneous manifestations
60% of hemangiomas in the bearded area will be assc with subglottic ones
2nd most common region for otosclerosis?
Round window
Phases of wound healing

Friedman staging for UPPP and success?

What is the definition of surgical success and UPPP?
50% reduction or AHI < 20
Indication for RAI for follicular thyroid CA
- tumor > 4cm
- gross extracapsular extension
- extensive intravascular invasion
- elevated post op TG
- known or suspected metastatic disease.
Only facial muscle not innervated by FN?
levator palpebrae superioris - innervated by CNIII
What kind of hearing loss do you get with quinine?
reversible at 4kHz
Contra-Indications for a partial laryngopharyngectomy?
- involvement of the pyriform
- extension to the post cricoid region
- ipsilateral TVC paralysis
- encroachment into the cricopharyngeus
Sequence of local anesthetic blockage
-Sympathetic fibers -> pain/temp -> touch/motor
Relationship between pH and pKa for local anesthetics
-the closer the pKa is to pH, the more likely the anesthetic will be in unprotonated/hydrophobic state and therefore faster onset of action
Dennie Lines
Assc with AR
-occur due to spasm of Mueller’s muscles in chronic AR

Brow lift and facial nerve anatomy in relation









