9: Lactation & The Breast Flashcards
What is mammary tissue in non-pregnant, non-lactating women?
Small part of breast tissue
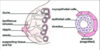
What is the mammary gland made up of?
15-20 lobulated masses of tissues
What connects the lobes of the mammary gland?
Fibrous tissue and adipose tissue

What is each lobe of the mammary glands made up of? (4 things)
- Lobules of alveoli (site of milk production)
- Blood vessels
- Lactiferous ducts
- Myoepithelial cells (SMC surrounding alveoli)

What are the constituents of breast milk? (5 things)
- Water
- Lactose
- Fat
- Protein
- Minerals + Vitamins
How is mammary tissue developed at puberty? (mammogenesis) (2 steps)
- Oestrogen causes ducts to sprout & branch → ends form masses of cells
- Masses of cells become alveoli
How do the mammary glands develop during pregnancy?
Increased progesterone / oestrogen ratio → favours alveoli development
But NO secretion
How do the mammary glands develop after giving birth?
Progesterone levels decrease → alveolar cells responsive to prolactin (secreted from ant. pituitary)
What does suckling do to prolactin secretion?
Initiates and maintains prolactin secretion
via Neuro-endocrine reflex:
- Impulse goes to hypothalamus
- Decreases dopamine secretion
- Decreases vaso-active intestinal peptide secretion
This increases prolactin secretion
How is milk “let down”?
Suckling → reflex promotes milk “let down”:
- Increased oxytocin secretion → contracts myoepithelial cells → ejects milk from breast
How is lactation stopped?
Suckling stops → decreased prolactin → less milk production
Why can’t lactating mothers take certain drugs?
Because drugs go into milk
Example of these drugs: WARFARIN
What are the types of breast cancer? (2 types)
- Ductal Carcinomas In Situ
- Invasive Carcinomas
How are Ductal Carcinomas In Situ limited?
By BM supporting epithelium → stops tumour invading adjacent tissue
What are risk factors of breast cancer? (6 things)
- Gender
- Age
- Reproductive history
- Obesity
- Oestrogen exposure
- Fatty diet
GAROOF
What will give Ductal Carcinoma In Situ a good prognosis?
Mastectomy
What is Paget’s disease?
When Ductal Carcinoma In Situ reaches nipple
How does Invasive Carcinoma metastasise? (2 things)
- Lymphatics
- Blood
Where does Invasive Carcinoma metastasise to?
- Lymph nodes
- Lungs
- Liver
- Brain
What breast cancer patients have good outcomes?
- Grade 1 breast cancer
- Oestrogen Receptor (ER) Positive
Why do Oestrogen Receptor (ER) Positive women have better outcomes?
They respond to Tamoxifen (ER antagonist) treatment
What is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer?
HER2 oncogene
What are the 3 main breast cancer investigations?
- Clinical
- Radiographic imaging
- Pathology
What are the clinical ways of investigation breast cancer? (3 things)
- History
- Family history
- Examination
What are the radiographic imaging ways of investigation breast cancer? (2 things)
- Mammography
- US
What are the aims of mammography?
To detect small impalpable / pre-invasive cancers
What are the patholical ways of investigating breast cancer? (2 things)
- Fine needle aspiration cytology
- Core biopsy


