9-3. 1&2 muscular layers - Overview Flashcards
(33 cards)
which is thicker?
the heel pad or the distal plantar skin
heel pad is much thicker than the distal plantar skin

what needs to be exposed to reveal the proximal attachment of the plantar aponeurosis?
the calcaneal tuberosity needs to be exposed
how to prepare to expose the first muscular layer?
- free up the plantar aponeurosis from the more dorsal structures
- (e.g. FDB takes part of its origin from the central plantar aponeurosis)
- cut the digitations of the central aponeurosis as far distally as possible
- reflect each of these digitations proximally, and free the underlying muscle from the aponeurosis
- once you reflect the central PA, hold it out of the way

what are the 4 intrinsic muscles of the foot innervated by the medial plantar nerve (L4-S3)?
All four intrinsic muscles are innervated by the medial plantar nerve
Mnemonic: LAFF
- L - first Lumbrical
- A - Abductor hallucis
- F - Flexor hallucis brevis
- F - Flexor digitorum brevis
what innervates the rest of the intrinsic muscles of the foot?
(except the 4 intrinsic muscles of the LAFF mnemonic)
LATERAL PLANTAR NERVE (S1-S3)
Flexor digitorum brevis can be dually innervated by which muscles?
MEDIAL PLANTAR nerve, and the LATERAL PLANTAR nerve
Review the motor innervation for the various muscles

What is the major segmental innervation to the FOOT INTRINSICS muscles?
What are the motor and sensory functions?
- S2 - innervates the foot intrinsics
- Motor:
- flex metatarsophalangeal, and
- extend interphalangeal joints of 4 lateral toes
- ADduction and ABduction of toes against resistance
how do you test intrinsic flexors?
what makes this difficult?
- intrinsic flexors can be tested along w/ the extrinsic flexors as shown below in the “paper grip test” for the lesser toes
- pt plantarflexes the toes to prevent the card from sliding out from under forefoot
- the big toe can be tested on its own
- assessing the strength of intrinsic muscles in isolation can be difficult because MOST individuals lack fine motor control of their toes

what is the collective function of intrinsic muscles during weight-bearing activity, as indicated by studies
role during quiet standing is unclear;
*in general, active during terminal stance phase to provide stabilization for forefoot propulsion
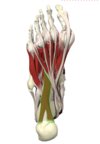
muscles and innervation of the 1st layer?
2 ABDUCTORS, 1 FLEXOR
- Medial 2 are innervated by the medial plantar nerve (L4-S3)
- Lateral 2* innervated by the lateral plantar nerve (S1-S3)
Therefore, FDB can be dually innervated!

recall the muscles in the 3 different compartments?
(LATERAL, CENTRAL, MEDIAL)
LATERAL
- *ABductor digiti minimi
- Flexor digiti minimi
CENTRAL
- *Flexor digitorum brevis
- Quadratus plantae
- Lumbricals
- ADductor hallucis
MEDIAL
- *ABductor hallucis
- flexor hallucis brevis

Relationships of the Flexor digitorum brevis
to other muscles
- Lies deep (dorsal/superior) to central portion of PA and between medial and lateral intermuscular septa
- Lies superficial (plantar/inferior) to lateral plantar neurovasculature
Name the origins of the flexor digitorum brevis
- medial process of calcaneal tuberosity
- medial and lateral intermuscular septa
- central portion of plantar aponeurosis
After entering the fibrous flexor sheath near the respective MTPJ (2-5) each tendon…
Review the plantar view of a lateral digit:
course of Flexor Digitorum Brevis Tendon
- 1st bifurcation: level of fibrous flexor sheath
- Reunion
- 2nd bifurcation
- Insertion onto MP/ IP

review the “ILL-FATED LOVE STORY” for the path of the
Flexor digitorum brevis tendon

what is the “nicer love story” version for the course of the FDBT

describe the digital insertions of the:
extensor digitorum brevis &
and extensor digitorum longus
- 2-4th digits; 5th if EDB tendon present
- As Extensor digitorum brevis tendon crosses the proximal phalanx, joined by the Extensor digitorum longus tendon
- At proximal phalanx head, combined tendons trifurcate into 1 middle and 1 lateral and 1 medial slip
- Middle slip attaches to IP base
- Medial and lateral slips reunite & attach at DP base

where does the flexor digitorum brevis insert?
both sides of the middle phalanges (2-5)
ABductor hallucis
origins and insertion
- origin:
- medial process of calcaneal tuberosity
- flexor retinaculum
- medial part of plantar aponeurosis
- medial intermuscular septum
- insertion:
- Plantar metatarsophalangeal ligament
- MTPJ capsulemedial sesamoid &
- base of HPP
which muscle:
- lies on the medial aspect of foot, and can be palpated
- is one of the largest & most superficial intrinsic muscle
- covers neurovasculature entering the plantar foot?
ABDUCTOR HALLUCIS
in the 1st layer of muscle
ABductor digiti minimi:
origins and insertion
- origin
- medial & lateral process of calcaneal tuberosity
- lateral intermuscular septum
- lateral portion of plantar aponeurosis
- insertions
- MTPJ capsule
- MT 5 head
- Proximal phalanx 5 base (as does FDMB)
which muscle:
- is slender, lateral muscle of 1st layer
- lateral plantar neurovasculature pass along its medial border
ABDuctor digiti minimi;
one of the 1st layer muscles
what do you call the muscle made of Abductor Digiti Minimi fibers forming a distinct belly and then inserting onto the MT 5 base and shaft?
ABDuctor ossis metatarsi digiti minimi (AOMDM)