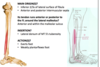
9-1a. Lateral Compartment Conference Flashcards
what is an arthrodesis?
surgical immobilization of a joint
to perform an arthrodesis on the posterior portion of the subtalar joint, which 2 locations would you mark on the patient?
- lateral malleolus
- location of fibular/ peroneal trochlea/ tubercle
Specifically, incision starts 4 cm above the tip of the lateral malleolus on posterior border of fibula & curve it forward passing over the fibular trochlea, parallel to the course of the fibularis longus

on which dermatomes is this incision made?
(4 cm above lateral malleolus on posterior border of fibula –> curved fwd passing over fibular trochlea parallel to fibularis longus course)
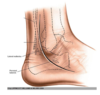
S1 & L5 dermatomes

which 2 structures are running IN THE SUPERFICIAL FASCIA, and are posterior to the incision site?
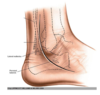
- Small saphenous vein
- Sural nerve

With an incision posterior to the lateral malleolus, which 5 structures are encountered at the various locations when skin flaps are retracted?
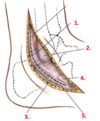
- superior peroneal retinaculum
- lateral malleolus
- inferior peroneal retinaculum
- fibularis brevis
- fibularis longus
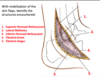
By incising the retinacula (peroneal fascia), you can observe the relationship between Fib longus, Fib brevis, and Fib trochlea.
What is this relationship?
- fibularis LONGUS is superficial to the Fibularis brevis and crosses over becoming more inferior/superficial
- Both fib longus and fib brevis pass POSTERIOR to the fibular trochlea

By retracting the fibularis tendons (longus and brevis) –> you open site for incision of TALOCALCANEAL JOINT CAPSULE;
what ligament needs to be cut transversely to open this joint capsule?
calcaneofibular ligament

W/in the surgical field for this arthrodesis of subtalar joint (posterior to lateral malleolus),
do you have to be cautious of disrupting nerve supply to Fib longus or Fib brevis?

NOPE,
both muscles receive fibers from the SUPERFICIAL FIBULAR NERVE proximal to the surgical field;
*Also, the superficial nerve itself is superficial at this level

what are the contents of the LATERAL OSTEOFASCIAL COMPARTMENT?
- muscles:
- Fibularis BREVIS - more MEDIAL
- Fibularis longus - more LATERAL
- nerve: Superficial fibular nerve
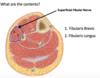
lateral compartment of the leg: overview
- motor innervation
- main blood supply
- common function
- inn: superficial fibular nerve
- blood supply:
- branches of the fibular & anterior tibial arteries
- fxn: eversion of foot and weak ankle plantarflexion
where does the popliteal artery branch? and what are the 2 branches?
- popliteal artery branches into the;
- ANTERIOR tibial artery &
- POSTERIOR tibial artery at the SOLEAL LINE

trace the FIBULAR artery:
where does it begin?
- branch off the posterior tibial artery
- begins 2.5 cm distal to the inferior border of the poplietus (where it divides into ANT/POST tibial arteries)
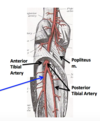
name the branches off of the FIBULAR ARTERY?
- Nutrient branch off of Fibular A.
- Perforating branch
- Communicating branch
- & Posterior lateral malleolar artery –> gives rise to lateral calcaneal branches

what is the course of the FIBULARIS LONGUS tendon with regards to structures of the ankle?
The tendon runs posterior to the LATERAL MALLEOLUS
Continues to run INFERIOR to the PERONEAL TROCHLEA –> PERONEAL NOTCH, travelling in close correspondence w/ the PERONEAL SULCUS
FIBULARIS LONGUS:
origins, insertions, and actions
- o:
- HEAD & sup. 2/3 or 1/2 of lateral surface of FIBULAR SHAFT
- ant & post INTERMUSCULAR SEPTA
- CRURAL fascia
- lateral tibial condyle (usually)
- ASTFL, anterior superior tibiofibular ligament (sometimes)
- ins:
- MT 1 base (mainly)
- medial cuneiform
- act:
- everts foot
- weakly plantarflexes foot