83 + 84 CNS Tumors Flashcards
Gliomas
- What are the three types of glioma classes?

Astrocytoma
- How common are these?
- What time of life do they occur?
- Where do they usually occur in the brain?
- What are the 3 most common presenting signs/symptoms?

Astrocytomas
- What are the 3 groups of astrocytomas, based on histological features?

Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?

A fibrillary astrocytoma, WHO grade II, with mildly pleomorphic astrocytes with minimally increased cellularity is shown
Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?

An anaplastic astrocytoma, WHO grade III, with increased cellularity, nuclear pleomorphism and a mitotic figure in the center of the field
Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?
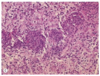
Glioblastoma multiforme, WHO grade IV, with prominent microvascular proliferation
Astrocytoma
- What kind is shown?

Glioblastoma multiforme, WHO grade IV, with significant nuclear pleomorphism and hyperchromaticity and a central focus of tumor cell necrosis
Astrocytoma
- Diffuse astrocytomas
- How long do these remain static?
- What is the mean survival time?
- What happens to patients as the disease progresses?
- What is notable about the prognosis when histologic features start to show?

Astrocytomas
- What is notable about the gross morphological features of grade II and grade III astrocytomas?

Astrocytomas
- What is notable about the gross morphological features of multiforme glioblastomas?

Astrocytomas
- Diffuse Astrocytomas, Grade II
- What are the 3 characteristics for these?
- What is notable about the transition b/w neoplastic and normal tissue?

Astrocytomas
- Anaplastic Astrocytomas, Grade III
- What are the 2 notable features about the regions that have anaplastic astrocytomas?
- What type of figures are present?

Astrocytomas
- Glioblastoma
- What are the 2 histologic features that separate this from anaplastic astrocytomas?

Astrocytomas
- Brainstem Gliomas
- When do these occur?
- How common are these?
- What are the 3 types?
- How aggressive are the three types?
- When do these occur?

Oligodendrogliomas
- How common are these, relative to other gliomas?
- When do they occur in life?
- Where do they usually occur in the brain?
- What are the 2 main types, and what is the prognosis like for each?

Oligodendrogliomas
- Grade II WHO, well differentiated
- What do these look like, grossly?
- Microscopically
- What do the nuclei look like?
- What does the cytoplasm look like?
- What is notable about the blood supply?
- What is notable about calcifications`?
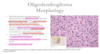
Oligodendrogliomas
- Who is notable about anaplastic oligodendrogliomas (grade III), compared to grade II ones?

Gliomas
- Genetics
- What is the common mutation associated in grade II astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas?
- What mutation gives glioblastomas and other astrocytes immortality?
- What genes are deleted in many oligodendrogliomas?
- What mutations are seen in CNS tumors that are also seen in tumors outside the CNS?

Astrocytomas
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma
- How aggressive are these?
- Who do they affect?
- Why would a patient have neurologic symptoms after incomplete resection of this tumor?

Astrocytoma
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma
- What often accompanies these tumors?

Astrocytoma
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma
- What shape do these cells have?
- What substance do they test positive for?
- What kind of fibers are often present?
- What shape do these cells have?

Astrocytoma
- Pilpcytic Astrocytoma
- Genetics
- How is the MAPK signalling pathway actiated?
- Genetics

Ependymomas
- What time of life do they usually occur?
- Where in the brain do these usually arise, relative to the age of patients?
- Which age/area is related to neurofibromatosis type 2?
- What area has good prognosis?

Ependymomas
- What do these tumors look like when they occur in the 4th ventricle?

Ependymomas
- What do the nuclei of cells look like?
- What are they filled with?
- Relate the morphology of these cells to blood vessels

Neuronal Tumors
- How common are these, compared to gliomas?
- What symptom usually accompanies them?

Neuronal Tumors
- What are the two main neuronal markers?
- What are the 3 types of neuronal tumors that we talked about?

Neurocytoma
- What stains can you use for this?
- How serious are these?
- Where do they usually occur?


What is shown?
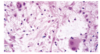

Embryonal Neoplasms
- What do most of these look like?
- What is the most common one?

Embryonal Neoplasms
- Medulloblastoma
- Who usually gets these?
- Where do they always occur?
- How aggressive are these?
- What is the prognosis like with and without treatment?

Embryonal Neoplasms
- Medulloblastoma
- Who gets midline cerebellum tumors?
- Who gets lateral ones?
- What do the tumors look like, grossly?

Embryonal Neoplasms
- Medulloblastoma
- What do these cells look like on a histological scale?
- What is notable about the cytoplasm and nuclei?
- What do these cells look like on a histological scale?

Embryonal Neoplasms
- Medulloblastoma
- Genetics
- What are the genetic mutations/pathways related to these?
- Which one involved Beta-catenin?
- Which one involves PTCH1?
- Which one has the poorest prognosis?
- What are the genetic mutations/pathways related to these?
- Genetics

Other Parenchymal Tumors
- Primary CNS Lymphoma
- What cells are affected?
- Who is this most common in?
- What do these tumors always test positive for?
- What is the prognosis like?

Other Parenchymal Tumors
- Germ Cell Tumors
- Where do these usually occur in the brain?
- Who do these affect the most? At what age?
- What region is associated with males?
- What is the most common germ cell tumor?
- What does it resemble?

Meningiomas
- Are these usually benign?
- What cells are usually affected?
- Who usually gets this?

Meningiomas
- What usually brings attention to patients?
- What determines the prognosis of these?

Meningiomas
- What should a patient be checked for if they have multiple meningiomas?
- What type of mutation can cause this?

Meningiomas
- Grade I
- What do these generally look like?
- Do they invade the brain?
- Do they invade the skull?
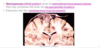
Meningiomas
- Histology
- What are the 4 types of patterns that these tumors can have?

Metastatic Tumors
- How common are these?
- What 5 areas account for 80% of them?
- What do they look like?
- What do they cause?

Tuberous Sclerosis
- What type of inheritance does this have?
- What develops in the brain?
- What are the subtypes of this?
- Which one is associated with seizures?

Tuberous Sclerosis
- What are the 4 major extracerebral lesions?
- Where cysts usually found?
- What are the 4 skin lesions associated with this?

Tuberous Sclerosis
- What is this?

Angiofibromas
Tuberous Sclerosis
- What is this?

shagreen patch
Tuberous Sclerosis
- What is this?

Tuberous Sclerosis
- What is this?

ash leaf patches (hypopigmented)
Tuberous Sclerosis
- What two genes are associated with this?
- What do they negatively regulate?

Tuberous Sclerosis
- What do cortical hamartomas look like?
- What do these cells lack, compared to normal cells?

von Hippel-Lindau Disease
- What kind of inheritance does this have?
- What kind of tumor develops?
- Where
- Where do cysts develop?
- How is this treated?

von Hippel-Lindau Disease
- What gene is affected?
- What does this gene help degrade?
- Tumors
- What do tumor cells have high expression of?

von Hippel-Lindau Disease
- What is the principal neurologic manifestation of this disease?
- Where does this usually occur?
- What do lesions look like on a microscopic scale?



