80 + 81 Pediatric Neurology Flashcards
Amblyopia
- What is this?
- Can it be corrected right away?

Amblyopia
- What are the 3 causes of unilateral Amblyopia?

Amblyopia
- How is this usually corrected?

Amblyopia
- When is the sensitivity period for Amblyopia?
- What does this suggest about vidual improvement?
- How common is this in North America?

What is this?

Orbital Cellulitis
Amblyopia
- What is used to detect Amblyopia?

What is this?

Strabismus
Strabismus
- What is this defined as?
- What is horizontal strabismus called?
- What is vertical strabismus called?
- What is it the leading cause of?

Strabismus
- Exotropia
- Is this an outward or inward turning of the eye?
- When does it usually occur?

Strabismus
- How common is this in the US?
- What is accommodative esotropia?
- How common is this?

Pseudostrabismus
- What are the 2 reasons that children can have this?

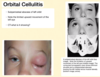
What is this?

Orbital Cellulitis
- What is this?
- What would a CT show?

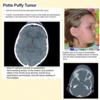
Potts Puffy Tumor
- What is this defined as?
- What will a CT show?
Migraines
- Who gets this more; males or females?
- What is a prodrome?
- When does it occur?
- What is an aura?
- What do the pateints experience?
- What are the red flags?

Migraines
- How do you treat this?

Brain tumors in children
- How common is this?
- How common is death?
- What is the most common type?

Brain tumors in children
- How do these clinically manifest? (3)

Brain tumors in children
- What is the triad?
- What is torticollis?
- How does this affect gait? Vision?

Febrile Seizures
- What will patients have?
- What will they NOT have?
- When do most of these occur? (age, time related to fever)
- What will some patients have a history of?
- What are the risk factors for this? (4)
- What is the prognosis like?

Febrile Seizure
- Differentiate between simple and complex?
- How will a complex febrile seizure present?
- How often does recurrence before the age of 6?
- How does epilepsy relate to this?
- What can cause the fever (6)

Febrile Seizures
- What is NOT indicated in the treatment for this?
- How does acetaminophen and ibuprofen use relate to the treatment of this?

Infantile Botulism
- What does the toxin inhibit?
- When is this most common in life?
- What history do patients usually have?
- What are the manifestations of this?
- What kind of paralysis occurs?

Infantile Botulism
- Are these bacteria gram negative or positive?
- How long is the incubation period?
- Where in the US is this most common?

Non Accidental Trauma
- What are the 6 radiologic red flags?

Non Accidental Trauma
- What age will children start to have tru-self imposed injurtes?

Non Accidental Trauma
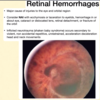
- Shaken Baby Syndrome (Abusive Head Trauma)
- What kind of hemorrhages occurs?
- How often does this Shaken Baby Syndrome in child abuse cases?

Non Accidental Trauma
- What is this?
- What do you consider NAT with it?

Tourette Disorder
- What are the 4 things that a Dx for Tourette Disorder?

Tic Disorders
- What are the criteria for Persistent (chronic) Tic Disorders? (5)
- What do you need to specify?

Tic Disorders
- What disorders may have tics in them?

Tic Disorders
- What is the criteria for provisional Tic Disorders? (5)

Tic Disorders
- Differentiate between simple motor and complex motor tics?
- What can trigger tics?
- What should be on your differential dx when considering if a patient has Tic Disorders?

Tics and Tourrettes
- Clinical Course
- When do patients get this? (Boys, Girls, PEak severity)
- Differentiate between simple vocal and complex vocal tics?
- Why do we think patients have tics?

Partial Arousal Parasomnias
- What happens to these patients?
- When does it occur in life?
- When do symptoms occur at night?
- Why may patients have this?
- How can patients help children who have this?
- What medications are used when this becomes serious?

Breath-Holding Spells
- What should parents do?
- What can this lead to?

Sydenham Chorea
- What is another name for this?
- What condition occurs with about 10 to 20% of cases?
- When usually occurs about a month before this?
- What sex is affected most?
- What age?
- What history can a patient have?
- What part of the brain is affected?

What is this?
What can it cause?


Sydenham Chorea
- What are the clinical hallmarks of this? (3)
- What can help confirm an acute strep infection?
- Can this exclude the Dx?
- What do you give for longterm antibiotic prophylaxis?

Sydenham Chorea
- What is used because if its anti-dopamine effects?
- What ADR does this have?
- What medications are used to control movements?
- What immunomodulatory interventions occur?

Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- What is this?
- Is it mainly motor or sensory?
- Who does this effect?
- What cells are affected?
- What happens before paralysis sets in?
- What bacteria in the GI tract can cause this?
- The respiratory tract?
- What food can cause this?
- What are the viral causes of this?
- What vaccines are associated with this?

Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- What are the inital symptoms?
- Where does weakness begin?
- What kind of paralysis occurs?
- What mood are the children who have this in?

Neurofibromatosis
- Type 1
- What appears on the skin of these patients?

Neurofibromatosis
- Type 1
- What complications arise from this?

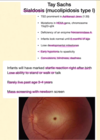
Tay Sachs Sialidosis
- What group of people get this?
- What gene/enzyme is affected?
- When do patients get this?
- How do they present?
- What is seen in the eyes of patients?
Sturge-Weber Syndrome
- What gene is implicated?
- What kind of vascular growth occurs?
- When do seizures occur?
- Relative the port wine birthmark
- What part of the brain is affected?
- Where do convulsions occur?
- Where does hemiparesis occur?

Sturge-Weber Syndrome
- Type 1
- How common is this?
- What kind of angiomas occurs?
- What happens to the eyes?
- When do seizures occur?
- What happens to the cognitive/physical development?

Sturge-Weber Syndrome
- Type 2
- What kind of angioma is seen?
- What happens to the eye?
- What is NOT seen?

Sturge-Weber Syndrome
- Type 3
- What kind of angioma is seen?
- What is NOT seen?
- How do you ID this?

Define these types of cerebral palsy


Spastic Cerebral Palsy
- What is affected spastic CP?
- How common is this?

Cerebral Palsy
- Dyskinetic CP
- What happens in this?
- Ataxic CP
- What happens in this?
- Causes of CP? (5)

Cerebral Palsy
- What are the risk factors?
- What are the signs and symptoms?



