8 Flashcards
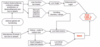
What are the components of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis
there’s a
- releasing hormone CRH from the hypothalamus
- trophic hormone ACTH (corticotropin) from anterior pituitary
- Adrenal hormones released from adrenal glands: cortisol and androgens
Where are adrenal hormones metabolzied?
adrenal hormones are metabolized in liver and excreted in kidney
What is CRH stimulated and inhibted by?
Stimulated by decreased palsam cortisol, hypoglycemia, and strress
Inhibited by increased plasma glucocorticoid level
What stimulated ant. pituitary stimulation of ACTH
AVP and CRH
What is the location of adrenal gland
dorsal and medial- more towards the central axid of the body
near the kidneys
The Adrenal gland is a __ organ
The Adrenal gland is a steroidogenic organ
Describe the make up of adrenal gland
- Surrounded by fibrous capsule and adrenal divided into functional layers
- cortex is about 90 % of adrenal mass, inner medulla about 10 %
- vcortex has 3 zones: (top to bottom) Zona glomerulosa, Zona fasciculatam, Zona reticularis; followed by adrenal medulla
- Zona f. is thickest (about 75 % of cortex)

Which hormones are produced by each zone + medulla?
Zona glomerulosa- aldosterone
Zona fasciculata- cortisol; corticosterone
Zona reticularis- sex streoids (androgens)
Medulla- Catecholamines (epinephrine & norepinephrine)
Describe why each zone is able to make it’s own unique hormones
Name the unique charactestic of each zone
different machinery-> different hormones are produced
Zone F nad Z Reticularis both have P450c17 , but Z retuclaris also has 17, 20 lyase-> DHEA-> androstenedione
Zone F and Zone G both produce croticosterone via P450c11, but Zone Glomerulosa expresses aldosterone synthase-> able to convert croticosterone into aldosterone

__ is the key enzyme that regulates androgen synthesis.
P450c17 is the key enzyme that regulates androgen synthesis.
What are the sources of cholesterol?
Main source is the diet, but can also be synthesized from acetyl-CoA
sterotogenic cells can store __ and use it in steroidogenic pathway
sterotogenic cells can store cholesterol and use it in steroidogenic pathway
What determines what steroid is produced in a cell or tissue
Cell specific expression of enzymes determines what steroid is produced in a cell or tissue
Where are the enzymes of steriogenic pathways located? What is the consequence of this?
Some enzymes are in the mitochondria others in the endoplasmic reticulum. Steroid intermediates shuttle between ER and mitocho
How do steroids differ?
Most steroids differ by minor enzymatic modifications of side groups, often through the addition/removal of hydroxyl groups
What is the common step in the prodcution of all steroid hormones? WHere does it occur?
The first step common to all steroids is the formation of pregnenolone from cholesterol in the mitochondria
What is the enzyme common for all steroid hormone produciton pathways? What is it’s role and location
p450scc, an enzyme that converts cholesterol to pregnenlone, a molecule, from which steroid hormones are made (1st step of Steroidogenesis)
located in the mitochondira
On inner mitochondrial membrane, P450scc (side-chain cleavase) cleaves the side chain of cholesterol to produce pregnenolone
Where does the cholesterol go for first step of Steroidogenesis occur? why?
choelsterol is moved to mitochondria as this is where
What is the limiting step of Steroidogenesis
How is it regulated?
Uptake of cholesterol is a rate limiting step
Regulated by StAR protein (Steroid Acute Regulatory protein)
describe StAR, how does it work, when is it activated
StAR is cAMP-inducible gene and increases in response to tropic hormones (i.e. ACTH in the adrenal gland and gonadotropins in gonads)
called acute regulatory protein as it usese Cyclic AMP responsive gene.
Increase in cAMP levels-> StAR gene expression-> protein becomes functional
Increase in cholesterol synthesis happens acutely/incredibly fast (StAR shuttles CH into the mitochondria)
- Thus the name
- Any protein hormone that can bind to G-coupled protein can increase cAMP levels, leading to StAR gene expression and leading to stereognosis
WHat is the main steroid of the zona fasciculata
cortisol
How is cortisol prodcuton of the zona fasciculata stimulated?
CRH from hypothalamus causes pituitary to release ACTH which can act upon adrenal cells in the Zone fasciculata-> cortisol synthesis
Is cortisol stored?
Like any steroid, these are not stored-> Cortisol is produced only when it is required
What is the half-life of cortisol?
How does it get inactivated?
The half-life of cortisol varies is 70-120 minutes
Converted to inactive cortisone and other metabolites by liver (for excretion in urine) and by other target cells- using enzyme 11BHSD2