7 - Hospital Acquired Infections Flashcards
What is a healthcare infection?
- Infections arising as a consequence of providing healthcare
- Not present or incubating at time of admission, therefore onset at least 48 hours after admission
Who is affected by healthcare infections?
- Patients
- Hospital visitors
- Healthcare workers
Why are healthcare infections important?
- Prevalence is high
- Has impact on health and healthcare organisations (cost and bed space)
- PREVENTABLE
What are some types of HCAI?
- UTI (catheter)
- Pneumonia (ventilator)
- GI e.g C.Diff
- Bloodstream (central line)
- Surgical wound infections
- Soft tissue infections
Who is particularly at risk of HCAI’s?
- Very young/very old
- Obese/Malnourished
- Comorbidities (diabetes)
- Cancer
- Immunosuppression
- Smokers
- Surgical patient
- Emergency Admission
What does the depth of infection affect?
Deeper the infection, longer and more expensive to treat
What is the I-Five model?
- Identify (e.g abroad, vomiting, rash)
- Isolate
- Investigate
- Inform
- Initiate
What are the 4P’s of infection prevention and control?

Using the model of infection prevention and control, how do you prevent a person from infecting themselves?

In terms of infection control and prevention, how do hospitals prevent patient to patient transmission?

In terms of infection prevention and control, how do hospitals prevent healthcare worker to patient transmission?
- Healthy workers: Disease-free and vaccinated
- Good practice: hand hygiene, PPE, antimicrobial prescribing, good clinical techniques (sterile touch)
How can the environment transmit HCAI’s to patients?

In terms of the infection prevention and control model, how can hospitals prevent environmental to patient transmission?
- Cleaning: disinfectant, steam cleaning, H2O2 vapour
- Medical equipment: single use, sterilisation and decontamination
- Good food hygiene and clean kitchen facilities
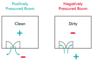
- Built environment: Layout of beds and toilets, hand wash basins, material of furniture, positive (theatre) and negative pressure rooms
What is the function of PPE?
To protect the worker from health and safety risks at work, e.g gloves, aprons, masks
What is the global concern of antimicrobial resistance?
- Increases cost of healthcare (e.g longer stays)
- Makes procedures very high risk, e.g chemo, organ transplant
- Threatens the ability to treat common infectious diseases, therefore more deaths and prolonged illness


