7-10 Revision Questions Flashcards
(73 cards)
Orbit Rotundum Ovale
Stylo IAM IAM Jug Jug
Jug Mag Hypo

Fill out this table:


The 5 secondary vesicles are:
TEL, DI, MES, MET, MY.
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Metencephalon
Myelencephalon
Name a structure derived from pharyngeal arch III:

The RHOMBENCEPHALON forms which secondary vesicles?
The RHOMBENCEPHALON sort of constricts to form the myelencephalon and the metencephalon.
The true spinal cord terminates at which vertebral level?
It terminates at about the level of the 1st or 2nd lumbar vertebrae (in the lower back region). The cone-shaped termination of the true spinal cord is called the conus medullaris.
Remaining cords hang down below the conus medullaris, forming the causda equina.
The Telencephalon gives rise to what adult structures?
Telencephalon - expands into 2 parts which form the cerebral hemispheres
X vagus - Which structures does it innervate, and with what type of innervation?
X vagus
Special sensory (taste) from root of tongue and epiglottis
General and visceral sensory from inferior larynx, pharynx, thoracic and abdominal organs
Voluntary motor to soft palate, pharynx, intrinsic laryngeal muscles and palatoglossus
Parasympathetic to abdominal and thoracic area
What is Broca’s area?
Broca’s area – the motor planning area specifically for speech. This is located in a lateral and inferior frontal gyrus, usually only in the dominant hemisphere (if you are right-handed, your dominant hemisphere is the left one). Neurons originating in this area communicate with those in the primary motor cortex that control movement of muscles in the larynx and some of the articulators.
Where is the primary motor cortex located, and what is its function?
Primary motor cortex – also known as the pre-central gyrus, this is a gyrus located directly anterior to the central sulcus. It is the area of initiation of all voluntary movement (information sent to skeletal muscles).

What passes through the hypoglossal canal?
Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
Name a structure derived from pharyngeal arch I:
Blood vessels: maxillary artery
Nerves: CNV2, CNV3
Bones: maxilla, mandible, zygomatic part of temporal bone
Muscles: TMJ muscles, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor veli palatine, tensor tympani (middle ear muscle)
What is the difference between static and dynamic balance?
Static systems evaluates the position of the head relative to gravity and also linear acceleration or deceleration.
• utricle and saccule (found in the vestibule). They are involved in static balance.
Dynamic balance is sensing movement of the body in space. three body planes (sagittal, coronal and horizontal) at 90 degrees to one another. This arrangement allows us to sense movement of the head in the three planes
• three semicircular ducts in the semicircular canals. They are involved in dynamic balance.
Draw the cirlce of Willis, ensuring you label the following areas:
Anterior cerebral arteries
Anterior communicating artery
Internal carotid arteries
Posterior cerebral arteries
Posterior communicating arteries
Middle Cerebral Artery
Basilar Artery
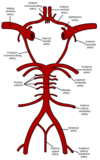
The basilar artery is formed by which other blood vessel(s)?
As the vertebral arteries pass through the foramen magnum they join with one another to form a single basilar artery.

What are the differences between Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area?
Broca’s area is the motor planning area for speech, whereas Wernicke’s area is the language formulation area, used to put together words into cohesive sentences.
What is Cleft Lip?
Cleft Lip
It is the failure of the lip and nasal tissue to fuse properly that causes cleft lip.
Central sulcus:
Central sulcus runs perpendicular to the longitudinal fissure, separates the frontal lobe and parietal lobes.
In the spinal cord, what is the arrangement of grey matter versus white matter?
In the spinal cord, the grey matter is deep, and the white matter is superficial.
XI accessory -Which structures does it innervate, and with what type of innervation?
XI accessory -
Voluntary motor to pharynx and soft palate
What passes through the stylomastoid foramen?
Facial nerve (VII)
Describe grey matter in the spinal cord:
The grey matter in the spinal cord has anterior horns which contain the cell bodies of motor neurons. Posterior horns contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons.
The central cavity of the neural tube enlarges in 4 areas to form what?
Central cavity of the neural tube enlarges in 4 areas to form the ventricles.
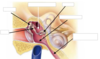
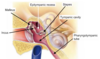
Label this diagram of the inner ear: