6 - Anatomy of the Hip Flashcards
The left and right hip bones are known as …………… bones.
Innominate

What are the three articulations of the hip bones?
- Sacroiliac joint
- Pubic symphysis
- Hip joint

Describe the composition of the hip bone (innominate bone).
3 parts:
- Ilium
- Pubis
- Ischium
Separated by the triradiate cartilage in a child, with complete fusion by age 20-25
For a cup-shaped socket called the acetabulum
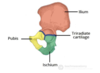
Where in the hip bone is the ilium located? What are it’s key osteological features?
- Located superiorly
- Iliac crest - top of the ilium
- Iliac fossa - concavity on the internal surface (iliacus muscle)
- Iliac wing - convex on external surface (gluteal muscles)
- ASIS/AIIS
- PSIS/PIIS

On the posterior aspect of the ilium there is an indentation, what is this called?
Greater sciatic notch
Where is the pubis located and what are it’s key osteological features?
- The most anterior portion of the hip bone
- Pubic symphysis - articulates with the oppostie pubic body
- Superior pubic ramus - laterally from pubic body to acetabulum
- Inferior pubic ramus - laterally from pubic body to inferior ischial ramus
The superior and inferior rami enclose the obturator foramen

Where is the ischium located and what are it’s key osteological features?
- Posteroinferior part of the hip bone
- Ischial tuberosity - on the postoinferior aspect
- Ischial spine - posteromedial projection

Which two main ligaments attach to the ischium and create the sciatic foramina?
- Sacrospinous ligament - ischial spine to the sacrum - greater sciatic foramen
- Sacrotuberous ligament - ischial tuberosity to the sacrum - lesser sciatic foramen

What type of joint is the hip joint?
Ball and socket synovial joint

What are the two articulating surfaces of the hip joint?
Head of the femur and the pelvic acetabulum

Describe the factors that stabilise the hip joint.
- The acetabulum - cup-like socket
- The acetabular labrum - deepens the acetabulum (increases contact area by 10%)
- Ligamentum teres - connects the head of the femur to the acetabulum
- Joint capsule - attached to intertrochanteric line anteriorly and femoral neck posteriorly
- Extracapsular ligaments - iliofemoral, pubofemoral and ischiofemoral
- The muscles surrounding the joint
Which bones does the femur articulate with?
- Hip bone (innominate bone)
- Tibia
- Patella
The depression in the centre of the femoral head is called the ….. …… . What attaches here?
- Fovea capitis
- Ligamentum teres attaches here
The large bony prominences at the proximal end of the femur are called …?
The greater and lesser trochanters
What structures connect the greater and lesser trochanters:
- anteriorly?
- posteriorly?
- Anteriorly connected by intertrochanteric line
- Posteriorly connected by intertrochanteric crest
The ridge on the posterior of the femoral shaft is called the ….. ……
Linea aspera
The linea aspera diverges into what structures at its proximal and distal ends?
- Proximal - gluteal tuberosity (lateral) and pectineal line (medial)
- Distal - medial and lateral supracondylar lines
The medial supracondylar line terminates at what structure on the medial condyle of the femur?
Adductor tubercle
Where does the lateral supracondylar line terminate?
Lateral femoral condyle
What structures separate the femoral condyles on the anterior and posterior surfaces?
- Anterior - intercondylar notch
- Posterior - trochlear (patellofemoral) groove


