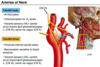
53. Physiological Challenges Flashcards
(205 cards)
What are some different measures for metabolic rate?
[IMPORTANT]
- O2 consumption
- CO2 production
- Combined heat and work output
What is exercise?
The voluntary exertion of muscles.
In exercise, what do we use as a typical indicator of metabolic rate?
Oxygen consumption
What is the symbol for oxygen consumption?
VO2
What is the basal oxygen consumption?
[IMPORTANT]
250ml/min (at STP)
Under what conditions is basal oxygen consumption quoted?
- Morning
- Lying down
- Fasted
- Neutral temperature (no shivering or sweating)
- Body temperature 37*C
- No exciting thought
For a normal mixed diet, how much energy is each ml of oxygen consumed associated with?
20J
Estimate the power dissipation of the body under basal conditions.

How does power dissipated by the body change from the basal state to doing mild exercise (stepping up on a box repeteadly)?
Oxygen consumption rises hugely, so the power dissipated does also.
Describe how you can calculate the efficiency of exercise, such as climbing stairs.
[EXTRA]

Draw a graph of useful energy output against total energy expended for different intensities of exercise.
[EXTRA?]

When doing some exercise experiments, only expired gas is collected. How can oxygen consumption be determined from this?
- We assume nitrogen balance, so that the amount of oxygen breathed in is the same as the amount breathed out
- This allows us to know how much air is being breathed in and therefore how much oxygen is being breathed in
- By measuring the expired oxygen, the consumption can be calculated
What type of exercise has a mechanical efficiency of 0?
[EXTRA]
Isometric
What are the ATP yields per molecule of:
- Glucose (aerobic)
- Glucose (anaerobic)
- Fatty acids
[IMPORTANT]
- Glucose (aerobic) -> 36-39 ATP/molecule
- Glucose (anaerobic) -> 2-3 ATP/molecule
- Fatty acids -> 16 ATP/CH2CH2 unit
Draw a graph to show how the usage of different fuel sources changes over time in exercise.

Draw the process of actin-myosin cross-bridge cycling.

What is the respiratory quotient?
[IMPORTANT]
- The ratio of CO2 produced to O2 consumed
- RQ = CO2 eliminated / O2 consumed
Compare the respiratory quotient for pure carbohydrate metabolism and pure lipid metabolism.
[IMPORTANT]
- Carbohydrate -> RQ = 1
- Lipid -> RQ = 0.7
How do the ratio of carbohydrate to lipid usage and the respiratory quotient change during prolonged exercise?
[IMPORTANT]
- At first, carbohydrates provide most of the energy, meaning the RQ is closer to 1
- As time goes on, lipids provide progressively more of the energy, meaning the RQ is closer to 0.7

State the total amount of energy stored in these energy stores:
- ATP
- Creatine phosphate
- Glycogen
- Lipid

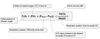
Write an equation for the oxygen concentration of arterial blood.

Write an equation for the oxygen concentration of venous blood.

Write an equation for the oxygen consumption of the body.

How much does oxygen consumption increase by during exercise?
It can increase up to 12-fold, from 250ml/min to 3000ml/min.