40 - Pulmonary Medchem Flashcards
What Pulmonary Drug Class?
DILATION of Bronchial Passages
Vasodilation in muscle + Liver
Relaxation of uterine muscle // release of insulin
by
AGONISING –>
SYMPATHETIC/Adrenergic Receptors
- *BETA-ADRENERGIC AGONISTS**
- *-TEROL** / -TERENOL / Terbutaline
- *B2: Relaxes**
A1: Contracts minor
FROM:
EPINEPHRINE

Beta-Adrenergic Agents
Originate from what Endogenous Compound?
- *CATECHOLAMINES**
- *Epinephrine / Norepinephrine**
Only the R** **enantiomer = ACTIVE

What are the 3-point interactions for RECEPTOR BINDING
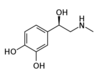
EPINEPHRINE
1) Para/Meta -OH
2) Beta -OH
3) -NHR
Metabolism:
MAO / COMT
Beta-Adrenergic Agent Parent Structure:
What is ESSENTIAL for BINDING?
- *1*_ or _2***
- *AMINO GROUP**
seperated by:
TWO CARBONS
Beta-Adrenergic Agent Parent Structure:

What INCREASES BETA-2 SELECTIVITY?
- *BULKY N-SUBSTITUENT**
- *N-Tertiary Butyl**
or
Aromatic MethylHydroxy Substitution
Beta-Adrenergic Agent Parent Structure:

What give PROTECTION from MAO?
LARGER AMINO SUBSTITUENT
- *Alpha Carbon Sub**
- but also decreases alpha/beta activity*
Beta-Adrenergic Agent Parent Structure:
What does a
ALPHA-CARBON SUBSTITUTION
do?

- DECREASED*
- *Alpha + Beta Activity**
- BUT*:
- *MAO PROTECTION**
- *= longer DOA (drug action) & Oral Bioavailability**
Beta-Adrenergic Agent Parent Structure:

What does the replacement of… do?
CATECHOL –> RESORCINOL
Protection from COMT
↑oral BioAvailability
What Drug?
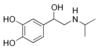
- *ISOPROTERENOL**
- *Short-Acting B-adrenergic Agonist**
Catechol - Based
Isoproterenol
Drug Type / Metabolism / Disadvantages
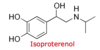
SHORT ACTING - B2 Adrenergic Agent
Catechol-based
Most POTENT** **bronchodialator
Oxidation Labile –> BENZOCHINONE
- Disadvantages:*
- *Cardiac ADR** = NOT B2 specific
Which Drug?

ALBUTEROL** / **SALBUTAMOL
SHORT-ACTING- B2 Adrenergic Agents
N-Tertiary Butyl –> B2 Selectivity
Aromatic MethylHydroxy Substitution –> B2 Selectivity
Alpha Substitution –> MAO Protection
What Drug?

- *TERBUTALINE**
- *Short-Acting B2 Adrenergic Agonist**
Resocinol Based = No COMT Metabolism
N-Tertiary Butyl = ↑B2 Selectivity
- *Alpha Substitution = MAO PROTECTION**
- decreased Alpha&Beta Selectivity*
What Drug?

- *METAPROTERENOL**
- *Short-Acting B2 Adrenergic Agonist**
Resocinol Based = No COMT Metabolism
- *Alpha Substitution = MAO PROTECTION
- decreased Alpha&Beta Selectivity***
What are the SHORT ACTING
Beta-Adrenergic Agonists?
- *Isoproterenol**
0. 5-2 hours
Metaproterenol
3-4 hours
Tertbutaline / Pirbuterol
B2>B1 selectivity, 4-8 hours
Albuterol / Levalbuterol / Salbutamol
B2>B1 selectivity, 4-8 hours
What are the LONG ACTING
Beta Adrenergic Agonists?
All orally active –> not metabolized by BOTH COMT nor MAO
>12 hours
Salmeterol
long lipophylic side chain
Formoterol
prodrug
Bambuterol
prodrug
What are the ULTRA LONG ACTING
Beta-Adrenergic Agents?
INDACATEROL
Racemate, >24 hours
What Drug?

- *SALMETEROL**
- *Long-Acting Beta Adrenergic Agonist**
Long Lipophlic Side Chain
racemate
Orally active –> NOT metabolized with MAO nor COMT
What Drug?
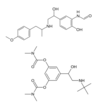
- *Formoterol / Bambuterol**
- *Long-Acting Beta Adrenergic Agonist**
BOTH PRODRUGE
Racemate
Orally active –> NOT metabolized with MAO nor COMT
What Drug?
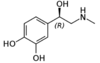
EPINEPHRINE
(R) = Norepinephrine
- NON-SELECTIVE B-adrenergic AGONIST*
- LEAST SELECTIVE*
- *Used for Allergic Reactions**
- *Fast action = half life = 2min**
Which Pulmonary Drug Class?
*ANTAGONIZES* –> M3 RECEPTOR
VVV
↓cGMP
VVV
DILATE Bronchoconstrictor Muscles
↓Mucus Secetion
VVV
Dilation of Bronchial Passages
ANTICHOLINERGICS** = **ANTIMUSCARINIC
BronchoDilator
Tiotropium = LA
Ipatropium = Short Acting
Atropine + Scopolamine
What Drugs?

Atropine** + **Scopolamine
- *Anticholinergics = Antimuscarinics**
- Similar to ACETYLCHOLINE = ACh*
Naturally occuring TROPINE ALKALOIDS

Wuz dis?

TROPANE
Nitrogenous Bi-Cyclic Compound
hydroxylated –> Tropine
Atropine / Scopolamine
Anticholinergics = Antimuscarinics
Wuz Dis?

TROPINE
Hydroxylated TROPANE
Esters of TROPINE = Atropine + Scopolamine
What Drug?

- *IPATROPIUM**
- SHORT-ACTING* Anticholinergic
Phenyl Ring = More Likely to be Oxygenated
SHORT ACTING
does NOT diffuse into the BLOOD –> no SYSTEMIC ADRs
- *QUATENARY AMINE**
- -> does NOT cross the BBB = no AC ADRs
NON-SELECTIVE Antimuscarinic –> but ONLY M3 in the LUNGS

What Drug?

- *TIOTROPIUM**
- *LONG-ACTING Anticholinergic**
does NOT diffuse into the BLOOD –> no SYSTEMIC ADRs
- *QUATENARY AMINE**
- -> does NOT cross the BBB = no AC ADRs
NON-SELECTIVE Antimuscarinic –> but ONLY M3 in the LUNGS

What is ESSENTIAL for
ANTICHOLINERGIC ANTAGONIST = Antimuscarinic
Tiotropium / Ipatropium
R1** **needs to point BACKWARDS

What makes 3 things make an

AntiCholinergic Antigonist
MOST POTENT?
- *R1** = AROMATIC
- -> VanderWals w receptor
- *R2 = HYDROPHOBIC RING**
- limited size*
R3 = HYDROGEN BONDING
Which Drug type?
- Reduce:*
- *inflammation in airways**
- *Lung Damage & airway narrowing** from inflammation
- *Mucus Production**
CORTICOSTEROIDS
Based from Cortisol
↑Expression of B2 Receptors
↑Upregulates expression of LIPOCORTIN-1
–> ↓supresses Phospholipase A2
↓Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Proteins / Cytokines
↓Prostaglandins & Leukotrienes
↓Supresses Cyclo-Oxygenase Expression

What MoA of CORTICOSTEROIDS
are INCREASING / UPREGULATING?
↑Expression of B2 Receptors
↑Upregulates expression of LIPOCORTIN-1
–> ↓supresses Phospholipase A2
What MoA of CORTICOSTEROIDS
are SUPRESSING / REDUCING?
- ↑Upregulates expression of LIPOCORTIN-1*
- -> ↓supresses Phospholipase A2
↓Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Proteins / Cytokines
↓Prostaglandins & Leukotrienes
↓Supresses Cyclo-Oxygenase Expression

Given that CORTICOSTEROIDS
- *do NOT act DIRECTLY on the AIRWAY SMOOTH MUSCLE**
- do NOT provide immediate relief*
WHY ARE THEY INHALED?
AVOIDS FIRST PASS METABOLISM
so we can use lower doses –> systemic absorption
What type of Drug?

ORAL = SYSTEMIC CORTICOSTEROIDS
Anti-Inflammatory Agents

What TYPE of drug?

INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS

Which Leukotriene Modifier?
Blocks the SYNTHESIS of Leukotriens?
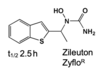
ZILEUTON
Inhibits 5-LIPOXYGENASE
other 2 drugs just block the BINDING
What drug type?
Inhibition of _______
VV
Reduction of Bronchoconstriction & Inflammation
less effective vs Corticosteroids
w/ less side effects

LEUKOTRINE MODIFIERS
Montelukast / Zafirlukast
- *LTRA = Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist**
- Block action of Leukotriene on the Leukotriene Receptor*
- *Zileuton**
- *Inhibitor of 5-Lipoxygenase**
What drug?

- *ZAFIRLUKAST**
- *Leukotrine Receptor Antagonist** = LTRA –> Anti-Inflammatory Agent
Blocks the action of:
Leukotriene on the Leukotriene Receptor
@ lungs & bronchial tubes, by BINDING to it
What drug?

- *MONTELUKAST**
- *Leukotrine Receptor Antagonist** = LTRA –> Anti-Inflammatory Agent
Blocks the action of:
Leukotriene D4 on the Leukotriene Receptor
@ lungs & bronchial tubes, by BINDING to it
What Drug? & MoA?
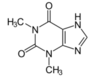
- *THEOPHYLLINE**
- *Methylxanthine**
Relaxing effect on Bronchial Smooth Muscle:
Competitive NON-selective PD-4 INHIBITOR
VV
inhibits Leukotriene Synthesis –> Reduces Inflammation
Which Drug Type?
Prevent & Control ALLERGIC Disorders
Blocking of: Calcium Channels essential for
Mast-Cell Degranulation & Cell Stabilization
VVV
Prevent release of HISTAMINE + Related Mediators
- *MAST CELL STABILIZERS**
- *Chromolyn (Nedocromil) / Chromone**
without intracellular CALCIUM
VV
histamine vesicles CAN’T fuse to the cell membrane & degranulate
Omalizumab = Xolair
Indication / ADR / MoA
For patients with:
- *Severe / Persistant ALLERGIC ASTHMA**
- that is not controlled with HIGH doses of Corticosteroids*
- CAUSES ANAPHYLAXIS*
- does NOT work immediately –> not for ACUTE*
- *SUBQ Inj Q2-4Weeks**
BINDS TO IgE** –> **prevents CROSSLINKING


