4 ⼀PREGNANCY/BREAST/REPRO Z Flashcards
etx for Gestational Transient Thyrotoxicosis
βhCG shares α subunit with TSH.
during pregnancy, ⇪ [fetal βhCG] stimulates [Maternal Thyroid gland TSH receptors] ➜ [⇪ TOTAL Maternal T4 and T3] secretion
In [Gestational Transient Thyrotoxicosis], [Multiple gestation or hyperemesis gravidarum] ➜ VERY high [fetal βhCG] ➜ [⇪ ⇪ ⇪ TOTAL Maternal T4 and T3] that resolves by 16WG
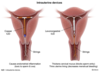
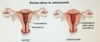
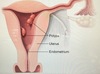
What is Asherman syndrome?
[Intrauterine adhesions and endometritis] from uterine instrumentation (D&C) ➜ [cyclic abd pain and secondary amenorrhea] immediately following instrumentation
Choriocarcinoma (the most aggressive kind of ⬜ ) can follow any type of ⬜ and presents with ⬜-4
________________
What 2 locations does Choriocarcinoma occur?
[gestational trophoblastic neoplasia] ; pregnancy ;
[AFTER PREGNANCY ➜ irregular vaginal bleeding + enlarged uterus + positive pregnancy test]
________________
Vagina | Lung

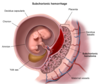
Major causes of Antepartum Hemorrhage - 3
Antepartum = right before childbirth
- Placental abruptio (PAINFUL Anterpartum hemorrhaging)
- Placental previa
- Vasa Previa

CP for Placental Abruptio - 4
Risk factors = HTN, cocaine, smoking, prior abruptio, abd trauma
- sudden PAINNNFFULLL antepartum vaginal bleeding (which can –> hypovolemic shock, [DIC-from decidual bleeding releasing tissue factor 7] and fetal demise) - (UNLESS CONCEALED = then no vag bleeding)
- Distended firm uterus
- abd AND/OR back pain
- [contractions of low intensity]
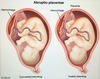
etx: HTN of maternal decidual vessels –> rupture –> premature detachment of placenta from endometrium
pregnant patient 35 WG p/w painless vaginal bleeding
Next step is (⬜ Digital Cervical Exam | TVUS) and why?
TVUS

s/f Placenta PREVIA, in which digital Cervical Exam is contraindicated since it enters endocervical canal. TVUS and speculum do NOT enter endocervical canal
_________________
Placenta Previa
Of the 3 placental demise, which is a/w painLESS antepartum vaginal bleeding?
Placenta Previa

Recurrent UTI refers to (⬜2)
________________
Tx?
[≥2UTI in 6 mo]
or
[≥3UTI in 12 mo]
________________
Postcoital abx prophylaxis
(Bactrim, nitrofurantoin, cephalexin, cipro)
Amniotic Fluid Embolism tx
supportive
__________________________________
release of fetal amniotic fluid into maternal circulation (during labor or immediately postpartum) ➜ maternal massive inflammatory response that causes acute hypoxemia, hypotension, DIC
Amniotic Fluid Embolism etx
_________________
What are the 2 major risk factors for this?
release of fetal amniotic fluid into maternal circulation (during labor or immediately postpartum) ➜ maternal massive inflammatory response that causes acute
hypOxemia
[hypOtension 2/2 obstructive shock]
DIC
_________________
Placenta Previa and Placenta Abruptio
After the Rupture of Membranes, when is it safe for labor to begin?
[1 - 18 hours after ROM] (no sooner ; no later)
________________
labor starting ≥18H after ROM ➜ chorioamnionitis ➜ neonatal sepsis
________________
- Do not confuse this with PPROM (Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membrane)*
- Chorioamnionitis Tx = Abx –> Delivery*
PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes (which occurs before 37 WG)
How do you manage PPROM when it occurs ≥ 34WG?
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio
PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
Define Preterm Labor

regular uterine ctx that ➜ cervical diLation < 37 WG

PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
[Betamethasone antenatal CTS] is given to pregnant patients with [PPROM/Preterm labor]/Severe Preeclampsia] before 37 WG
_________________
What are the 4 major benefits of using [Betamethasone antenatal CTS]?

[Betamethasone antenatal CTS] ⬇︎
- NRDS
- IVH
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Neonatal mortality from prematurity
_________________
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio

PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
How do you manage [PPROM < 34 WG] when it occurs
abx = [PCN + azithromycin]

if baby not compromised, fetal surveillance until 34 WG and then deliver!
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio
Full term infant = 37- 42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG - 2
Pregnant Bitches
When are pts screened for Group B Strep via vaginal and rectal swab?
36-38 WG
results are valid for 5 weeks
When does a breech pregnant patient become eligible to receive [External Cephalic Version]?
≥37 WG
Sickle Cell Disease patients who are pregnant are at ⇪ risk for developing ⬜ , which presents with what 4 s/s ?
_________________
how is this different from [Acute fatty liver of pregancy]? (2)
[Acute Sickle Hepatic Crises 2/2 vasooclusive crisis]
- [RUQ pain w/ slight transaminitis]
- [sickle hemolysis (anemia/jaundice/icterus)]
- NV
- fever
_________________
SAME AS AFLP except…
AFLP = 3rd trimester and AFLP = [TRANSAMINITIS SIGNIFICANT > 300]
[Recurrent pregnancy lost] is defined as ⬜ . What heme/onc abnormality is a/w [Recurrent pregnancy lost]?
how is it managed?
[≥3 consecutive 1st trimester (< 20WG) spontaneous abortions]
_________________
Antiphospholipid syndrome (ASA for thrombosis px)
[Recurrent pregnancy lost] is defined as ⬜ . What anatomical abnormality is a/w [Recurrent pregnancy lost]?
how is it managed?
[≥3 consecutive 1st trimester (< 20WG) spontaneous abortions]
_________________
Uterine septum (tx = hysteroscopic surgical resection)
What is shoulder dystocia? how does it present?
_________________
management? (6)
initial failure to deliver fetal ANT shoulder = OBSTETRIC EMERGENCY!
p/w fetal head retraction into perineum after head delivers
_________________
B.E. C.A.L.M.

Screening for gestational DM is done ⬜ WG
_________________
how is gestational DM screening done?
24-28WG
_________________

inadequate control of gestational DM ➜ ⬜ and ⬜
_________________
Tx for gestational DM? (3)
fetal macrosomia / shoulder dystocia
_________________

1st: diet
2nd: INSULIN
–(alternative)–> [PO glyburide vs metformin]
describe the menopause transition (4)
_________________
What s/s during menopause transition are c/f malignancy? (2)
occurring over years before true menopause (51 yo), involves
[DECREASING menstrual bleeding (amount and # of days)]
[Longer Intermenstrual intervals]
vasomotor sx
_________________
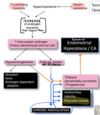
[INCREASED menstrual bleeding] or [shorter intermenstrual intervals] = [endometrial hyperplasia/CA] possible
Diagnostic criteria for this condition? (4)

Bacterial Vaginosis
- gray vaginal discharge
- amine odor after KOH application
- clue cells on wet mount
- vaginal pH >4.5

tx for this condition? (2)
Bacterial Vaginosis
- [metronidazole (PO or PV)]
- [Clindamycin (PO or PV)]
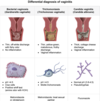
pregnant patient p/w symptomatic Bacterial Vaginosis
Do we treat her? why or why not?
YES - ONLY IF SYMPTOMATIC ; symptom relief
_________________
unclear if tx ⬇︎ obstetric complications (spontaneous abortion/preterm labor) from BV

In addition to ⬜ and ⬜, TDaP is 1 of the 3 vaccines safe during pregnancy _________________
When is TDaP given? why is it given at this time during pregnancy?
[influenza killed] [anti-RhoD IG]
_________________
[3rd trimester ≥28WG]
TDaP given [3rd trimester ≥28WG] facilitates maternal ab immunity AND enables transfer of maternal ab thru placenta
What are the absolute contraindications to combined OCP (7)
- [Migraine with aura (due to ⇪ stroke risk)]
- [SEVERE HTN ≥160/100]
- [SMOKING ≥15 cig/day]
- [Female age ≥35]
- Hypercoagulability (factor 5 leiden/antiphospholipid)
- [ACTIVE BREAST CA]
- [ACTIVE LIVER disease]
pregnant pt p/w asymptomatic bacteriuria
[Pregnant Asymptomatic bacteriuria requires abx treatment.]
Does [NONPregnant Asymptomatic bacteriuria] also require tx?
_________________
What are the 3 abx choices for Pregnant UTI?
NO TX<–(-PRG)–[Female Asx bacteriuria]–(+PRG)–> [CAF abx]
- [cephalexin x 5d]
- fosfomycin x 1
- [amox/clav x 7d]
* repeat urine culture 1 week after abx completion to test for cure*
* tx should be guided by culture susceptibility*
Why is Iron Deficiency anemia common during pregnancy?
_________________
What would you expect on Peripheral Blood Smear?
[⇪ iron demand] and [⬇︎ poor maternal iron intake]
_________________
hypOchromic microcytic RBC

describe [early pregnancy of undetermined location]
_________________
management?
while [βhCG discriminatory zone ≤3500] pregnancy cannot be located/visualized ➜ [repeat βhCG q48h] to determine if INC is c/w normal pregnancy (normal = ≥35% every 48h]
What is the DDx for Urge Incontinence - 4
Sudden urge to urinate all the time
Detrusor hyperactivity 2/2
- UTI
- Estrogen deficiency (urethral closure –> ⬆︎intrabladder pressure –> urge)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- DM
What is the DDx for Overflow incontinence - 2
involuntary dribbling and incomplete emptying (⇪ PVR)
- DM neuropathy
- mechanical obstruction
⬇︎Detrusor activity or mechanical outlet obstruction –> Overdistended bladder –> involuntary dribbling and incomplete empyting (⬆︎PVR)
What is [Genitourinary syndrome of menopause]?
Menopause ➜ VulvoVaginal atrophy ➜ pelvic organ prolapse / dyspareunia / urinary incontinence
Management for [Urge urinary incontinence] (3)
1st: [Timed Voiding bladder training] + [⬇︎ wt / smoking / etoh / caffeine]
2nd: [Oxybutynin vs Tolterodine (Anticholinergic)]
3rd: [BoTox vs perQ tibial nerve stimulation]
________________
detrusor hyperactivity ➜ sudden URGE to urinate

Women with Urinary Incontinence are recommended to restrict daily fluid intake to what amount?
[≤1.9L (or ≤64oz) /day]

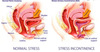
[Intrinsic Sphincter deficiency] and [Urethral hypermobility] are a/w
[⬜ urinary incontinence]
Stress
________________
will have positive bladder stress test (leakage of urine with coughing )

Indications for Pessary - 2
- Pelvic organ prolapse (can also do surgery if good candidate)
- Stress urinary incontinence

Tx for Stress Urinary Incontienence - 4
- URETHRAL SLING
- Kegel exercise physical therapy
- Vaginal pessary
- Bladder neck Injectable bulking if etx is related to sphincter deficiency
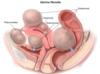
Adenomyosis CP - 3
- symmetrically enlarged TENDER uterus (> 12 weeks in size)
- Menorrhagia
- Dysmenorrhea eventually –> Chronic Pelvic Pain

etx: glands invade uterine myometrium –> blood deposition inside myometrium during cycle –> dysmenorrhea from irregular contractions and menorrhagia from extra deposited blood
What are the risk factors for stress urinary incontinence secondary to pelvic floor weakening - 3
- Pregnancy/Childbirth
- Obesity
- Menopause

Diagnosed with Q-tip urethral hypermobility test
What is the DDx for Stress urinary incontinence - 2
Incontinence with coughing/lifting/sneezing
- Urethral Hypermobility (injury to pelvic floor muscles and/or urethral prolapse –> urethral hypermobility or bladder cystococele can –> bladder prolapse and all of this –> vaginal bulge and incontinence)
- ⬇︎Urethral tone
Tx = Kegel excercises vs urethral sling

Most common causes of Intermenstrual bleeding - 5
“I’m seeing some spotting in between my periods”
- Endometrial Polyps - Painless and light
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial ADC/hyperplasia - Older women
- PID - due to cervicitis
- Cervical CA
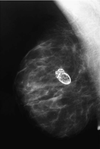
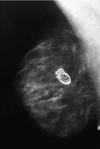
describe Fibroadenoma cp
In teen females,
[Upper/Outer SINGLE rubbery mobile breast mass]
that becomes PAINFUL PREMENSTRUATION
but
RELIEVED POSTMENSTRUATION
What are the sx of Breast Engorgement-4 ; When does this usually occur?
- b/l Breast Fullness
- b/l Breast Tenderness
- b/l Breast warmth
- No Fever
Usually occurs 3 days postpartum when colostrum is replaced with milk, but can occur anytime during breastfeeding
Tx = BREASTFEED, Cool compress, APAP, NSAIDS
How can you differentiate Breast Engorgement from Mastitis? ; How can you differentiate Breast Engorgement from Plugged Ducts?
- Breast Engorgement is BL without fever and Mastitis is uL WITH FEVER (Breast abscess is Mastitis with fluctuance)
- Breast Engorgement is BL and Plugged Ducts is uL
A Woman comes in with c/o breast engorgement (BL tender, swollen, firm) after she elected to not breast feed
How do you induce Lactation suppresion? - 3
- NSAIDs for pain/inflammation
- COMFORTABLE Bra that avoids nipple stimulation
- Cool Compress to breast
Engorgement in and of itself eventually –> Lactation suppresion on its own due to negative feedback! do NOT breast bind as this causes mastitis. Don’t use drugs to treat this.
What are the major risk factors for Breast CA - 8
- 1st degree relative with breast CA
- Prolonged estrogen exposure (menstruating outside of 12-52 y/o range vs utero DES vs HRT)
- Genetics (BRCA 1/2 mutation)
- Alcoholic
- Obesity
- Radiation
- Age 40-70 yo
- White
Average Menopause onset = 51
DDx for palpable breast mass - 5
CCAFF
- CA
- Cyst
- Abscess
- Fibroadenoma
- Fat necrosis
What are the common side effects of OCPs - 6
- HTN
- Breast Tenderness
- ⬆︎TriAcylGlycerides
- Bloating with Nausea
- Breakthrough bleeding = most common (usually with lower estrogen doses)
- Venous thromboembolism (Migraine w/aura is a ctd for Combined OCPs)
Wt Gain is NOT a side effect of combined OCPs and OCPS actually ⬇︎risk of Endometrial and Ovarian CA
Why do women who’ve recently delivered and are breastfeeding have no menstrual cycles?
Elevated Prolactin (responsible for mammogenesis and galactogenesis) inhibits GnRH release –> anovulation and amenorrhea for ≤ 6 months
after 6 months, even with breastfeeding women will start to ovulate again and even before then, this is not a reliable form of contraception
What’s the first steps in w/u for Bilateral breast discharge with no lumps, LAD or nipple changes?-4 ; Why?
Hyperprolactinemia is most common cause of galactorrea
- PROLACTIN levels - Prolactinoma could –> Hyperprolactinemia
- TSH levels - hypOthyroidism could –> ⬆︎TRH & TSH –> Hyperprolactinemia since TRH stimuales prolactin release
- PREGNANCY test - Pregnancy could –> Hyperprolactinemia since TSH shares same α-subunit as bHCG
- MED REVIEW - D2 blockers/Antidepressants/Opioids all –> Hyperprolactinemia
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) are used for _______(indications)-3 ; What are the main side effects of SERMs? - 3
- ⬇︎Breast CA risk
- adjuvant tx for Breast CA (Tamoxifen)
- Postmenopausal Osteoporosis (Raloxifene)
SIDE EFFECTS
A: Hot Flashes
B: Venous Thromboembolism (all estrogen agonist ⬆︎resistance to protein C)
C: Endometrial Hyperplasia/ADC
note: SERMs not only modulate estrogen receptors but they actually block estrogen binding competitively
Which substance actually exacerbates the cyclical bilateral pain associated with Fibrocystic changes of breast?
Caffeine
What’s the most common cause of unilateral discharge (serous or bloody)?
Intraductal Papilloma

CP of Fat necrosis of Breast - 4
- Firm mass after trauma
- IRREGULAR SHAPED mass
- overlying erythema

Mammogram: Oil cyst +/- calcifications that appear malignant but has fat globules and foamy macrophages on bx
Tx for lactational mastitis?-3
Tx = KEEP BREASTFEEDING + Dicloxacillin + Ibuprofen

drain via needle aspiration if abscess is present
tx for acute bacterial prostatits -3
Bactrim
Cipro
suprapubic catherization (bladder decompression)
how do you workup Chronic Prostatitis?
________________
>3 month dysuria + pelvic pain +/- ejactulatory pain
[UA/UCx before and after prostate massage] ➜
UA = [pyuria > 20]
+
Urine Culture: [neg = CP/CPPS] vs [bacteriuria > 10 fold increase = CBS]
________________
- [CP/CPPS = Chronic prostatitis chronic pelvic pain syndrome]*
- [CBS = Chronic BACTERIAL prostatitis]*
how do you differentiate [Chronic prostatitis chronic pelvic pain syndrome] from [Chronic bacterial prostatitis]?
[Chronic Prostatitis chronic pelvic pain syndrome] will have NEGATIVE CULTURE
________________
> 3 month dysuria + pelvic/perineal pain
What is the cause of [Chronic prostatits chronic pelvic pain syndrome]?
________________
Tx?
UNKNOWN
________________
Prostate Enlargement Meds (alpha blockers)
pt p/w severe back pain 2/2 metastatic lesions from hormone-refractory prostate CA
Tx?
EBRT
________________
External Beam Radiation Therapy
pt p/w severe back pain 2/2 metastatic lesions from hormone-refractory prostate CA
Tx?
EBRT
________________
External Beam Radiation Therapy
What is the cause of [Chronic prostatits chronic pelvic pain syndrome]?
________________
Tx?
UNKNOWN
________________
Prostate Enlargement Meds (alpha blockers)
how do you differentiate [Chronic prostatitis chronic pelvic pain syndrome] from [Chronic bacterial prostatitis]?
[Chronic Prostatitis chronic pelvic pain syndrome] will have NEGATIVE CULTURE
________________
> 3 month dysuria + pelvic/perineal pain
how do you workup Chronic Prostatitis?
________________
>3 month dysuria + pelvic pain +/- ejactulatory pain
[UA/UCx before and after prostate massage] ➜
UA = [pyuria > 20]
+
Urine Culture: [neg = CP/CPPS] vs [bacteriuria > 10 fold increase = CBS]
________________
- [CP/CPPS = Chronic prostatitis chronic pelvic pain syndrome]*
- [CBS = Chronic BACTERIAL prostatitis]*
tx for acute bacterial prostatits -3
Bactrim
Cipro
suprapubic catherization (bladder decompression)
Pregnant patients require 3 Prenatal Lab visits: [Initial] [24-8WG] [36-8WG]
_________________
Name the [36-8WG Prenatal lab]

Pregnant patients require 3 Prenatal Lab visits: [Initial] [24-8WG] [36-8WG]
_________________
List the 4 [24-8WG Prenatal labs]
24-8WG testing is performed due to [expanding RBC mass] and [insulin resistance from hPL secretion]

Pregnant patients require 3 Prenatal Lab visits: [Initial] [24-8WG] [36-8WG]
_________________
List all [15 INITIAL Prenatal labs]
iPUB

{ID [HIV|HBV|HCV|Syphilis|[chlamydia PCR (if risk factors)]}
{PX [Rubella immunity|Varicella immunity|Pap (if indicated)]}
{URINE [Cx | dipstick protein]}
{BLOOD [Hgb|Hct|MCV|ferriTin|(RhoD type / Ab screen)]}
_________________
[HBV=HepB Surface Antigen] | [HCV=anti-HCV Ab] | [Syphilis=VDRL/RPR]
describe Gestational Thrombocytopenia
[2nd/3rd trimester] pregnancy, benign asymptomatic [thrombocytopenia< 70K] that spontaneously resolves after delivery
For laboring patients, what are the contraindications to [Epidural Neuraxial analgesia] ?
platelet dysfunction (thrombocytopenia | rapid ⬇︎ platelet) \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_
this is because [ENA] in the setting of platelet dysfxn ⇪ risk for [Spinal Epidural Hematoma]
When is it appropriate to diagnose a teenage boy with [“Delayed” boy puberty]?
lack of testicle enlargement BY 14 Y/O
_________________
obtain bone radiograph / FSH, LH, testosterone
PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
________________
What are 2 px therapies for PPROM?
- Progesterone (vaginal or IM after 1st trimester)
- Cerclage

Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio
What factors indicate ⬆︎ risk for possible Preterm labor? - 4
Full Term delivery = 37 - 42WG
1st best indicator: PRIOR PRETERM DELIVERY = STRONGEST INDICATOR
2nd best: Shortened cervix ≤ 2cm per transVaginal US (or 2.5 if preterm hx present) - hx of cold knife conization?
3rd best: + Fetal Fibronectin BUT ONLY BETWEEN 20-37WG
4th best: Circumstantial (Smoking, multiple gestation, IVF, obesity)

PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes (which occurs before 37 WG)
How do you manage PPROM when it occurs ≥ 34WG?
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio

PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
How do you manage PPROM when it occurs
if baby not compromised, fetal surveillance until 34 WG and then deliver!
Complications = Chorioamnionitis/Endometritis/Cord Prolapse/Placenta Abruptio

Full term infant = 37- 42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 34 to 36 WG - 2
Pregnant Bitches

Full term infant = 37 -42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 32 to 33 WG - 3
Pregnant Bitches Take
Full term infant = 37 - 42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor < 32WG - 4
Pregnant Bitches Take Money

tx for Endometriosis - 5

Homogenous cystic ovarian mass
- observation if asx
- NSAIDs 1st
- Contraceptive (OCP/IUD progesterone)
- Leuprolide (GnRH agonist that ⬇︎Endometrial gland estrogen stimulation)
- Hysterectomy with oophorectomy

- Findings: Gun Powder Burn lesions, Adhesions, Chocolate fluid*
- Dx = Laparoscopy to biopsy endometriotic lesions*
PPROM = Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membranes before 37 WG
________________
Name the 4 possible complications of PPROM?
Which is an Obstetric Emergency and how is it maanged?
- PPROM patients are at ⇪ risk for*
1. [UMBILICAL CORD PROLAPSE = OBSTETRIC 911] : [tx = relieve cord compression ➜ Cesarean STAT]
________________
- Chorioamnionitis
- Endometritis
- Placenta Abruptio

After the Rupture of Membranes, when is it safe for labor to begin?
[1 - 18 hours after ROM] (no sooner ; no later)
________________
labor starting ≥18H after ROM ➜ chorioamnionitis ➜ neonatal sepsis
________________
- Do not confuse this with PPROM (Preterm Premature Rupture Of Membrane)*
- Chorioamnionitis Tx = Abx –> Delivery*
Describe the [Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Testicle] axis starting with [GnRH from hypothalamus]
________________
How does a Prolactinoma affect this axis?
Prolactin inhibits GnRH secretion from hypothalamus ➜ [⬇︎FSH/LH] ➜ [⬇︎ secondary sex characteristics (testicle size/facial hair/libido)]

How does Cervical Cancer present? -4
________________
What does Cervical Cancer in HIV+ patients indicate?
- [friable exophytic cervical mass]
- [irregular vaginal bleeding +/- mucoid vaginal dischage]
- postcoital bleeding
- ulcerative cervical lesions
________________
AIDS DEFINING ILLNESS

How do you work up new [Palpable Breast Mass]?

VesicoVaginal Fistula is a complication of ⬜ that presents how? _________________
name a subtle physical exam finding for small vesicovaginal fistulas
pelvic surgeray ;
small vesicovaginal fistula from bladder to vagina ➜
[continuous PAINLESS malodorous urine leak from Bladder To vagina +/- red area of granulation (if small vv fistula)] ➜
_________________

When is [repeat βhCG] indicated in pregnancy?
for pts with βhCG < 1500, pregnancy of undetermined location warrants [repeat βhCG in 48 hours]
Whats the most frequent complication of TURP?
________________
TransUrethral Resection of Prostate
Retrograde Ejaculation
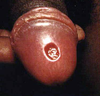
patient p/w balanitis (glans penis inflammation)
What else should they be worked up for? why?
underlying DM ; Balanitis is a/w high blood glucose
Postpartum thyroiditis etx
autoimmune disorder (involves anti-thyroid peroxidase Ab) that within a year of childbirth –> brief HYPERthyroid phase –> [brief hypOthyroid phase (may require thyroid replacement if severe)] –> Euthyroid back to normal
Dx = tSH
Tx for Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy? -3
________________
MAINTAIN MILD HYPERTHYROIDISM DURING PREGNANCY
by trimesters
1st = PropylThioUracil
2ND = METHIMAZOLE
3RD = METHIMAZOLE
________________
[PTU = Hepatotoxic] // [Methimazole = teratogenic during 1st trimester]
how is newborn heart disease related to gestational DM related?
_________________
What is the prognosis for this?
newborns born from gestational DM/maternal DM have ⇪ risk for transient HOCM (2/2 excess glycogen deposition in fetal myocardium ➜ thickened interventricular septum) ➜ [Tachypnea + Respiratory distress]
_________________
even if newborn has transient HOCM sx… MOST SPONTANEOUSLY RECOVER BY 3 WEEKS
(once natural insulin levels start to normalize ➜ ⬇︎myocardial glycogen deposition)
What are the recommendations regarding Exclusive Breastfeeding?
_________________
How does this change if newborn baby is losing weight ?
Exclusive breastfeeding SHOULD BE ENCOURAGED TO ALL.
Within 1st week of life there is [EXPECTED WEIGHT LOSS (≤ 10% from birth)] – so this should not stop breastfeeding!
Primary amenorrhea is defined as ⬜
_________________
How do you workup Primary amenorrhea?
[no menstruation by 13] OR [no menstruation by 15 with breast]
_________________

A postpartum pregnant patient p/w R facial droop
What should you tell her? (3)
PBP = Pregnant Bells Palsy
- Pregnant/Postpartum Patients have INC risk for PF7BP
- PBP tx = [CTS +/- acyclovir]
- PBP pgn = [full recovery ≤3 mo]
_________________
[PF7BP = Peripheral Facial CN7 Bells Palsy]
What is Priapism?
_________________
What are the common risk factors? (4)
[painful erection > 4h] 2/2 impaired penile blood outflow (out of corpora cavernosa) ➜ irreversible ischemic injury = MEDICAL 911
_________________
- PDE5 inhibitors
- [intracavernosal alprostadil injection]
- Trazodone
- Sickle Cell Disease
Priapism
treatment? (3)
[non-Rx ( urination, cold compress)] < (sx 4h) < [{Corpora Cavernosa aspiration} –(if sx persist)-→ {intracavernosal phenylephrine}]
Name the major risk factors for Recurrent UTI -4
- cystitis ≤ 15 yo
- Spermicide use
- New sexual partner
- Postmenopause
cp of Uterine Sarcoma -4
postmenopausal woman with new pelvic pain
uterine mass
ascites
metastatsis (pleural effusion)
________________
tx = hysterectomy
Tamoxifen is a ⬜ that ⇪ risk for ⬜ cancer and ⬜ cancer in postmenopausal women
________________
Describe how this is monitored? -3
SERM ; [endometrial hyperplasia/CA and uterine sarcoma CA]
________________
(sx = endometrial polyp ?)
NO = observation
YES = [transvaginal US] ➜ [endometrial biopsy]
Why should pts taking estrogen for postmenopausal sx also should be taking progesterone if they have a uterus?
Unopposed estrogen –> uncontrolled endometrial proliferation (CA). Progesterone can regulate proper endometrial differentiation
just remember, estrogen replacement therapy can –> postmenopausal bleeding on its own
Lichen Sclerosis MOD
autoimmune chronic inflammation of [vulva, perineum and anal region] that affects [hypOestrogenic women (prepubertal and peri/postmenopausal)] and–> Vulva SQC
________________
THIS DOES NOT AFFECT THE VAGINA!
dx = vulvar punch biopsy

s/s Lichen Sclerosis - 5
- Pruritus SEVERE
- Dyspareunia
- White Grayish pale vulva (distinguishes from postmenopausal vaginal atrophitis)
- Cigarette paper texture vulva (thin, crinkled)
- loss of vulvar anatomy (introitus, labia minora, clitoral hood)
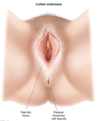
dx = vulvar punch biopsy
Because postmenopausal women suffer from vaginal ⬜, they should all be asked about ⬜ and ⬜ since these are common sx of it
atrophy;
vaginal dryness / dyspareunia
What are the major s/s of menopause - 5
menopause wreaks HAVOC
- Hot flashes 2/2 vasomotor instability
- Atrophy of vagina –> dyspareunia, urinary incontinence, paleness, narrowed introitus
- Vaginal Dryness –> Pruritus
- Osteoporosis
- Coronary artery disease
note: menopause can be 2/2 natural but also chemotherapy, radiation and oophorectomy
What are risk factors for Osteoporosis? - 9
Bone Mineral Density (T-score) ≥ -2.5 SD BELOW the mean
- PERSONAL OR FAMILY HX OF OSTEOPOROTIC FX
- ⬇︎Estrogen (postmenopause)
- LOW BMI (malnutrition/malabsorption)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Poor Ca+ intake (body needs 1000mg/day premenopausal and 1200mg post)
- Smoking
- EtOH abuse
- White race
- CTS
What are the main causes of Premature primary Ovarian Insufficiency? - 4
- natural Menopause
- Chemotherapy - targets rapidly dividing granulosa/theca cells
- Radiation - targets rapidly dividing granulosa/theca cells
- oophorectomy

What are the major s/s of menopause - 5?
_________________
When should menopause patients receive endometrial biopsy?
menopause wreaks HAVOC
- Hot flashes 2/2 vasomotor instability
- Atrophy of vagina –> dyspareunia, urinary incontinence, paleness, narrowed introitus
- Vaginal dryness –> pruritus
- Osteoporosis
- Coronary artery disease
note: menopause can be 2/2 natural but also chemotherapy, radiation and oophorectomy
_________________
[≥45 yo with anovulatory bleeding] c/f endometrial ADC/hyperplasia
Turner syndrome is the sex chromosomal disorder most likely associated with physical findings at birth
_________________
How does Turner Syndrome affect intelligence?
may cause [mild learning disability] BUT DOES NOT AFFECT OVERALL INTELLIGENCE
________________
Most turner syndrome fetuses miscarry within 1st trimester

Turner syndrome is the sex chromosomal disorder most likely associated with physical findings at birth
_________________
Describe the 5 [Comorbidity Screenings] for patients with Turner syndrome (5)
- [EENT ⼀(Strabismus, OME, hearing loss] =renal US
- [CV ⼀Aorta(Coarctation/Dissection (WORST WITH PREGNANCY)/Dilatation), CHD(bicuspid aortic valve), Metabolic Syndrome XDIVe] = 4EBP, EKG, echo, GET AORTIC IMAGING
- [Renal ⼀Horseshoe Kidney] =renal US
- [Bone ⼀Osteoporosis] =DEXA, 25OHvitD
- [autoimmune ⼀Celiac, hypOthyroid] =antI-TED, TSH⼀free T4
________________
- Most turner syndrome fetuses miscarry within 1st trimester*
- 4EBP: 4-Extremity BP*

Turner syndrome is the sex chromosomal disorder most likely associated with physical findings at birth
________________
Name all the sx of Turner Syndrome (12)
- [Learning disability WITH NORMAL INTELLIGENCE]
- [eye (nearsighted, strabismus)]
- low set ears
- webbed neck
- hypOthyroidism
- bicuspid aortic valve
- aortic coarctation (screen via 4-extremity BP and echo)
- aortic dissection ⼀higher risk in pregnancy
- celiac disease
- horseshoe kidney
- scattered pigmented nevi
- [Lymphedema congenitally of hands/feet from abnormal lymphatic system development]
________________
Most turner syndrome fetuses miscarry within 1st trimester

Turner syndrome is the sex chromosomal disorder most likely associated with physical findings at birth
________________
The most fatal comorbidity of Turner syndrome is ⬜ , which risk INC with pregnancy. Why is this?
[Aortic DISSECTION or rupture];
[pregnancy hormones weakening aortic wall + hyperdynamic state of pregnancy can → Aortic DISSECTION]

What’s the most common cause of secondary amenorrhea?
Pregnancy
etx of PCOS
________________
What are the primary effects of this etx?-4
DM/Obesity–>Hyperinsulinemia which –> ⬆︎⬆︎⬆︎LH secretion –> ⬆︎ovarian theca Androgen secretion –>
- Androgen characteristics (acne, balding, hirsutism)
- Follicular atresia ➜ Anovulation ➜ Infertility
- PCOS on US from Follicular atresia
- ⬆︎Estrogen (from Androgen conversion) –> Endometrial ADC
tx = Wt loss ➜ SOCK

Tx for PCOS - 5
[Wt loss–> SOCK]
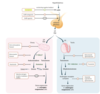
SOCK:Spironolactone,OCP (1st line after wt loss),Clomiphene for infertility,Ketoconazole
________________
etx: DM/Obesity–>Hyperinsulinemia which –> ⬆︎⬆︎⬆︎LH secretion –> ⬆︎ovarian theca Androgen secretion –> Sx
the most common cause of [postpartum hemorrhage ( ≥1L blood)] is ⬜
_________________
how do you manage this? -2
⬇︎TONE of Uterus
_________________
[bimanual uterine massage]
and
[Oxytocin (causes uterine contraction)]
_________________
2nd line uterotonics = methylergonovine/carboprost/misoprostol
In teens females, what is the most common cause of irregular menstrual bleeding?
_________________
Tx for this? -2
[ANOVULATION (up to 2 years post menarche)] 2/2 immature [hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis]
_________________
[Observation (since self-limited to up to 2 years post menarche)] ➜ [OCP if severe]
Menopausal Hormone Therapy consist of ⬜
What are the beneficial✔︎effects of Menopausal Hormone Therapy? (5)
- MHT (combined estrogen & progesterone)*
- BENEFICIAL✔︎ effects =*
- HAVOC Menopause sx
- Bone mass
- Colon CA
- T2DM
- [All-Cause Mortality if < 60 yo]
Menopausal Hormone Therapy consist of ⬜
What are the detrimental❌effects of Menopausal Hormone Therapy? (5)
MHT (combined estrogen & progesterone)
DETRIMENTAL❌effects (with higher risk in Women GOE60yo) =
- STROKE
- Breast CA
- CAD in GOE60yo
- Gallbladder disease
- Venous Thromboembolism
Menopausal Hormone Therapy consist of ⬜
What’s the caveat to the Detrimental❌effects of Menopause Hormone Therapy? (2)
MHT (combined estrogen & progesterone)
❌These MHT Detrimental effects are Higher /more clinically concerning in [Women GOE60yo].
❌MHT Stroke risk in Women < 60 yo is low = MHT can be used safely for short period in [Women < 60 with low risk].
after delivery, topical erythromycin is prophylactically given to prevent neonatal ⬜
GONOCOCCAL conjunctivitis
________________
does NOT treat chlamydia conjunctivitis
What are the guidelines for ANNUAL GC/Chlamydia Screening
(Women vs Men)
Annual Gonococcal and Chlamydia Screening (via vaginal/cervical NAAT) for:
Women:
{IF SEXUAL <– [24⼀AGE⼀25] –> ONLY IF HIGH RISK SEXUAL}
_________________
Men:
Insufficient evidence :-(
▨ Pelvic Inflammatory Disease presents with what 4 sx?
________________
⊙ Name the ideal abx duo for PID tx
▨ [Mucopurulent cervical discharge] + [Cervical Motion Tenderness] + [Abd Pain] + Fever
________________
⊙ [ceFOXitin + doxy]
covers N.Gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, [Vaginal Flora =E.Coli/Mycoplasma]
The most common causes of pathological gynecomastia are [INC estrogen], [DEC androgen] or [Medication adverse effect]
List the conditions that cause gynecomastia by [INC estrogen] (5)

The most common causes of pathological gynecomastia are [INC estrogen], [DEC androgen] or [Medication adverse effect]
List the conditions that cause gynecomastia by [DEC androgen] (3)

The most common causes of pathological gynecomastia are [INC estrogen], [DEC androgen] or [Medication adverse effect]
List the common medications that cause gynecomastia (5)

The most common causes of pathological gynecomastia are [INC estrogen], [DEC androgen] or [Medication adverse effect]
① the most common cause of pathologic gynecomastia in older men is ⬜.
_________________
② How does this cause gynecomastia in older men?
① Spironolactone ⼀Medication Adverse Effect
_________________
② Spironolactone has 2 MOA
- often used in HFrEF patients as an [aldosterone R blocker]
- it also is an [androgen R blocker] ➜ [DEC androgen] ➜ pathologic gynecomastia in men
tx = switch to Eplerenone (has less androgen R blockade)

The most common causes of pathological gynecomastia are [INC estrogen], [DEC androgen] or [Medication adverse effect]
① the most common cause of pathologic gynecomastia in older men is ⬜.
_________________
② what’s the treatment?
① Spironolactone ⼀Medication Adverse Effect
_________________
② tx = switch to Eplerenone (has less androgen R blockade)

In terms of presentation, describe the 3 possible types of Male Breast Enlargement

Describe Physiologic Gynecomastia
especially in overweight/obese, PG is a benign glandular proliferation of male breast tissue occurring 2/2 imbalanced
[DEC testicular testosterone (with normal aging)]
and [INC adipocyte (androgen → estrogen) (with Obesity)]

[T or F] History alone (i.e. phone consultation) is sufficient to diagnose acute uncomplicated cystitis, and can be treated empirically without urine culture
TRUE
_________________
physical exam is only required for complicated cystitis (fever, chills, flank pain, CVA TTP = pyelonephritis) and urine cx if initial tx fails

[T or F] History alone (i.e. phone consultation) is sufficient to diagnose acute uncomplicated cystitis, and can be treated empirically without urine culture
TRUE
_________________
physical exam is only required for complicated cystitis (fever, chills, flank pain, CVA TTP = pyelonephritis)

uncomplicated cystitis = no PPP
What are the 1st line antibiotic options for [uncomplicated cystitis] - 8
[CAN Fosfomycin Control] Basic Uncomplicated Cystitis ??
- Cephalexin (Pregnancy)
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Pregnancy)
- Nitrofurantoin (Pregnancy)
- Fosfomycin (Pregnancy)
- Ceftriaxone (Pregnancy and PYELO)
- 6.[Bactrim (2nd trimester only) - [1TM➜ NTD] & [3TM ➜ kernicterus]]
7. *Urine Cx only if initial Tx fails
8. Cipro (fluoroquinolone if 1-6 can’t be used)
What are the 3 GATEWAY questions for Acute Cystitis?
1st: PPP? ➜ [Complicated cystitis (obtain PEx, UCx before tx)]
2nd: Pregnant? ➜ [CAN Fosfomycin Control]3-7d
3rd: Preference/NKDA?: [Uncomplicated cystitis ([CAN Fosfomycin Control] Basic Uncomplicated Cystitis) ]
_________________
PPP: Pyelo|Pervasive Systemic illness|Pelvic MALE pain
How are Pregnant patients with c/f acute cystitis managed?
Symptomatic or [≥100K CFU in Asx Pregnant Patient]
[empiric “CAN Fosfomycin Control” x 3-7d]
_________________
CAN Fosfomycin Control Bad Cystitis ??
Pregnant Pt p/w uncomplicated cystitis
Name Abx treatment options for uncomplicated cystitis in pregnancy? (5)
and for how long?
[CAN Fosfomycin Control]3-7d
- Cephalexin (Pregnancy)
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Pregnancy)
- Nitrofurantoin (Pregnancy)
- Fosfomycin (Pregnancy)
- Ceftriaxone (Pregnancy and PYELO)
_________________
[Bactrim (2nd trimester only) - [1TM➜ NTD] & [3TM ➜ kernicterus]]
Urine Cx only if initial Tx fails
The presence of any of which 3 factors makes cystitis Complicated?
PPP
Pyelo? (Fever, Flank/CVA)
Pervasive Systemic illness?
Pelvic MALE pain
_________________
Complicated _PPP_➜ Obtain Physical Exam and UCx before tx
Complicated Cystitis indicates presence of 1 of what 3 factors?
Abx treatment options for Complicated Cystitis (5)
Pyelo? / Pervasive Systemic illness?/ Pelvic MALE pain
_________________
ALL: [PEx and UCx before tx ➜ tailor abx]
Outpatient: [Cipro Fluoroquinolone]
Inpatient: [Ceftriaxone or PipTazo or imipenem]
Turner = what 3 main clinical features?
Why does Turner syndrome cause Amenorrhea ?
SHORT
[AMENORRHEA1º > 2º] =Turner syndrome causes [streak ovaries gonadal dysgenesis] = 1º ovarian insufficiency
→ [DEC PiE and T (which DEC feed back on hypothalamus/ANT PIT)] → Elevated FSH & LH
_________________
PiE_T: Progesterone/inhibin/Estrogen _ Testosterone
[hyPOPUBERTAL (pubertal arrest I.e. Tanner3 instead of Tanner5 at 18yo)]

What is the clinical course of Testicular CA? (4)
[uL painless ovoid testicular swelling] →
[BL scrotal US : solid lesion]→
[Tumor markers(AFP, bHCG) and CT staging]
= [CHEMO + RADICAL INGUINAL ORCHIECTOMYDx and Tx]95% 5y Survival
treatment for Varicocele
venous embolization
“bag of worms”
What are the key points regarding Prostate Cancer (4)
- Because Prostate CA is typically indolent = men with prostate CA usually die from other causes
- Prostate CA screening with PSA can be used age 55-69 but absolute benefit is small
- Screening NOT recommended [age to 55-69] or [life expectancy<10y]
- **1-3 does NOT apply to [HIGH RISK DEMOGRAPHICSBlack, fam hx, symptomatic men]
average menopause occurs 51 yo
How is Pelvic radiation related to Estrogen HRT? (2)
Explain how Estrogen HRT is or is not beneficial (2)
▶Pelvic radiation (CA tx) commonly → Primary Ovarian Insufficiency = Amenorrhea < 40 yo = premature menopause
▶Tx =
PO/Transdermal[Estrogen (+progestin if uterus present)]until 51 yo
▶Estrogen DEC [hypOestrogen sxhot flashes/vaginal dryness & bone loss] and should be replaced until [nml menopause age 50].
▶We stop HRT at [nml menopause age 50] because postmenopause estrogen HRT has INC risk for VTE
unopposed estrogen causes endometrial CA
average menopause occurs 51 yo
Explain why [estrogen/progestin HRT] is recommended for treating menopause sx in [premenopause (primary ovarian insufficiency)] but not [menopause sx in postmenopause]?
⼀[postmenopause e(p) HRT] has [INC vascularVTE & CAD risk] = NOT RECOMMENDED
⼀[(premenopause POI) e(p) HRT]** DEC hypOestrogenic menopause sx but has substantially DEC vascular risk = RECOMMENDED
e(p) : [estrogen (+ Progestin in Presence of uterus)]
[Estrogen unopposed → Endometrial CA] so.. [Progestin added in Presence of a Uterus] **
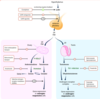
a. Explain why [Prolactinoma > 200 prolactin level] is a common cause of amenorrhea and infertility in Women
* * *
b. name the other manifestations of Prolactinoma (7)
a. ⇪ Prolactin suppresses GnRH → ⬇︎LH → ⬇︎E2 .
- No LH surge = no ovulation = amenorrhea and infertility
* * *
b. 📸

Prolonged Prolactinoma can → female osteoporosis
Tx for Prolactinoma (2)
{[Cabergoline v Bromocriptine(dopamine R agonist)] = inhibits prolactin secretion → ⬇︎Prolactinoma size}
–(if fails)–>
Surgery

How do you manage HIV in a newly pregnant patient?
________________
How is the newborn managed once it’s born?
MOM = [TRIPLE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY] THROUGHOUT PREGNANCY
________________
newborn = Zidovudine ≥ 6 wks
________________
viral load/CD4 count labs q 3 months

At what HIV viral load count is Vaginal Delivery safe?
Vaginal Delivery ≤ 1000 HIV copies
________________
> 1000 copies = C Section

Breastfeeding contraindications -7
- active TB
- HIV (unless in poor country)
- Herpes breast lesion
- Active varicella
- Chemoradiation
- Active Substance Use Disorder (but methadone regimen for tx is OK)
- Galactosemia
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome etx
rare complication of ovulation induction.
etx: hCG injections which artifically matures follicles for IVF ➜BILATERAL OVARY ENLARGEMENT WITH TOO MANY FOLLICLES
PLUS ovaries overexpress [Vascular endothelial growth factor] =
[INC Ovarian VEGF] ➜ INC capillary permeability ➜ abd 3rd spacing ➜ [ascites/effusions/electrolyte imbalance] ➜ eventually
renal failure, hypOvolemic shock, hemoconcentration, hypercoagulability, DIC, death
Full term infant = 37 -42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor 32 to 33+6 WG - 3
Pregnant Bitches Take
Full term infant = 37 - 42WG
How do you manage Preterm Labor < 32WG - 4
Pregnant Bitches Take Money

Full term infant = 37- 42WG
Most Tocolytics are not used in managing Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG
Why specifically is Nifedipine not used?
Pregnant Bitches
Maternal hypOtension with reflex tachycardia

Full term infant = 37- 42WG
Most Tocolytics are not used in managing Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG
Why specifically is Nifedipine not used?
Pregnant Bitches
Maternal hypOtension with reflex tachycardia

Full term infant = 37- 42WG
Most Tocolytics are not used in managing Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG
Why specifically is Indomethicin not used? - 2
Pregnant Bitches
- Premature closure of ductus arteriosus
- Oligohydramnios

Full term infant = 37- 42WG
Most Tocolytics are not used in managing Preterm Labor 34 to 36+6 WG
Why specifically is Mg not used?
Pregnant Bitches
It’s a weak tocolytic so it doesn’t actually help with slowing contractions down in preterm delivery

When it’s indicated, Group B Strep prophylaxis abx (which consist of ⬜ ) must be given ⬜ hours before delivery to be adequate!
________________
How do you manage neonatal GBS prevention POSTpartum
[PCNor ampicillin or ceFAZolin] ; ≥4
________________

When it’s indicated, Group B Strep prophylaxis abx must be given ≥4 hours before delivery to be adequate!
________________
How do you manage postpartum neonatal GBS prevention

[Cell-free fetal DNA test] is routinely offered at ⬜ weeks gestation prenatal screens to ⬜ patients due to ⬜
________________
What does [Cell-free fetal DNA test] screen for? -4
≥10WG ; [Advanced Maternal age > 35 yof] ; higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities in this group
________________
- [Pateau trisomy 13]
- [Edwards trisomy 18]
- [Down syndrome trisomy 21]
- Sex Chromosome aneuploidies

Select mode of Delivery (Vaginal | Cesarean) for [Dichorionic Diamniotic twins] positioned:
Vertex/Vertex
________________
Vertex/BREECH
________________
BREECH/Vertex
________________
BREECH/BREECH

During pregnancy, what’s Oxytocin indicated for?
labor protraction 2/2 inadequate uterine contractions < every 3-5 min
[1st trimester combined test] screens for ⬜ by measuring what 3 things?
________________
positive [1st trimester combined test] ➜ ⬜
aneuploidy; [(BNP - (βHCG/Nuchal translucency/[Pregnancy associated plasma protein A])
________________
confirmation by [chorionic villus sampling] or amniocentesis
to evaluate fetal karyotype
Uterine Sarcoma is an aggressive CA originating from ⬜ or ⬜ tissue, and has 2 major risk factors
What are they?
endometrium or myometrium
________________
RF = tamoxifen vs pelvic radiation
How does [GnRH agonist] help treat Leiomyoma?
GnRH agonist ➜ temporary amenorrhea ➜ ⬇︎Leiomyoma size and ⬇︎vaginal bleeding
What does APGAR stand for? ; How is it done? ; How is it used?
Appearance, Pulse, Grimace(reflex irritability), Activity(tone), Respiration
Performed at 1 and 5 min postpartum, All scaled from 0 to 2 and then added together
[< 3 = Critical] / [4-6 = fair: PPV] / [7-10 = normal: No intervention]
What does APGAR stand for? ; How is it done? ; How is it used?
Appearance, Pulse, Grimace(reflex irritability), Activity(tone), Respiration
Performed at 1 and 5 min postpartum, All scaled from 0 to 2 and then added together
[< 3 = Critical] / [4-6 = fair: PPV] / [7-10 = normal: No intervention]
how do you treat acute asthma exacerbation in pregnant patients? -3
same as non-pregnant asthma exacerbation = BOC
[BronchoDilator (albuterol+ipratropium ➜ terbutaline ➜ Magnesium IV)]
CTS PO
Oyxgen to SaO2 ≥95% (nonpregnant ≥90%)
________________
short term CTS benefit > minor risk in pregnant patients
What are the 4 main inquries pts should be asked when coming in for L&D checks?
Can Mom Feel Baby?
Contractions?
Movement from Fetus?
Fluid leak vaginally?
Blood leak vaginally?
Which 4 drugs can you give to treat HTN in pregnant patients?
Mothers Loathe Nefarious HTN
Methyldopa / Labetalol > Nifedipine / Hydralazine
What are 5 ways to determine if a pt truly has Leakage of Amniotic Fluid?
- Amnisure immunoassay (detects placental ⍺-microglublin1)
- POOL test (there’s pool of fluid in vaginal vault)
- NITRAZINE test (fluid turns blue when placed on nitrazine paper since amniotic fluid is alkaline)
- FERN test (fern-like estrogen crystals under microscopy)
- US to determine fluid quantity (Normal = 6-23 cm AFI)
[Nausea/Vomiting in Pregnancy] ranges from mild to severe. Severe NVP is AKA ⬜
What’s sx discern [mild NVP] from [SEVERE NVP] -3
________________
How do you manage mild NVP? -3
- SEVERE NVP = HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM*
- ________________*

[Nausea/Vomiting in Pregnancy] ranges from mild to severe. Severe NVP is AKA ⬜
What’s sx discern [mild NVP] from [SEVERE NVP] -3
________________
How do you manage [SEVERE NVP]? -3
- SEVERE NVP = HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM*
- ________________*

Pt (without previous DM) now with gestational DM delivers baby w/o complication
How do you manage her postpartum course? -2
d/c antiHyperglycemic therapy after delivery
➜ At [6-12 wk postpartum] = [2h oral glucose tolerance test] (due to ⇪ DM2 risk)
Adolescents have ⇪ risk for peripartum complications
What are the fetal complications?
________________
etx?
- PRETERM DELIVERY
- low birth wt
- perinatal Mortality
- [Maternal anemia]
- [Maternal Preeclampsia]
________________
Inadequate nutrition and physiologic immaturity
Genetic Consultation for recurrent miscarriage is required for women with ≥ ⬜ spontaneous abortions
≥3
All women planning pregnancy should take
[⬜ mg (or ⬜ mg if HIGH RISK) of ⬜ for ⬜] prior to conception to ⬇︎risk of Neural Tube Defects
________________
[0.4 (or 4 IF HIGH RISK) mg daily] of folic acid B9 ; ≥1 month
________________
high risk = antiepileptics / prior NTD pregnancy
What are the risk factors for Uterine Rupture? -4
[PRIOR UTERINE SURGERY (CSection/myomectomy)]
Truama
Macrosomia
abnl placentation
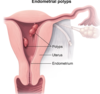
Endometrial Polyps cause what type of vaginal bleeding?
intermenstrual vaginal bleeding
pt with Eisenmenger syndrome wants to get pregnant
What should you tell her?
Pregnancy is a contraindication for pts with Eisenmenger syndrome (untreated VSD/HF) due to high maternal mortality rate and poor fetal pgn
Pregnancy should be avoided/terminated
What’s the general recommendation regarding
Exericse during Pregnancy?
Healthy uncomplicated pregnant women are recommended to do
[Moderate exercise 30 minutes daily - for most days of the week]
________________
yoga/walking/running/light strength training/swimming
Women who have sex with Women are INC risk of what 2 things?
_________________
Describe why for each
Cervical CA (2/2 lower HPV vaccination rates than hetero)
and
Bacterial Vaginosis (2/2 greater exchange of vaginal secretions than hetero)
What are the causes of Acute Cervicitis? -5

4 major signs of Acute Cervicitis?

Why is maternal thyroid hormone so important during pregnancy?
the fetus completely depends on maternal thyroid hormone for brain development up until 12WG when fetal thyroid gland forms
how do you manage a Newly pregnant patient who has preexisting hypOthyroidism? -2
[⇪ baseline Levothyroxine dose] at time of pregnancy detection
then
[get TSH q4 wks ➜ Levothyroxine dose adjusted per trimester]
Pregnancy requires 50% greater thyroid hormone requirements
________________
How does the body achieve this? -2
- 1st trimester, fetal βhCG stimulate maternal TSH receptors ➜ [⇪ maternal T3/T4 production] (but remember, this INC T3/T4 feed back on ANT Pit ➜ low TSH 1st trimester)
and
- elevated maternal estrogen ➜ [⇪ thyroxine binding globulin] ➜ [⇪ binding sites for T4 to travel on] ➜ [⇪ TOTAL (not free) maternal T4 available]
________________
(hypOthyroid patients wont be able to INC maternal T3/T4 production ➜ requires INC exogenous dose/Levothyroxine )
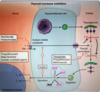
What is the greatest risk factor for PID?
Multiple Sexual Partners
_________________
other RF = [age 15-25], previous PID, inconsistent condom, partner with STI
Vulvodynia cp
________________
tx -2
≥3 mo idiopathic raw burning vulvar pain
________________
Tx = [pelvic floor physiotherapy] and CBT
Exercise during pregnancy ⬇︎ risk of (⬜3)
gestational DM
PreEclampsia
Cesarean
What are the contraindications to Exercise during pregnancy? -3
- cervical insufficiency
- underlying comorbidity preventing exercise
- active vaginal bleeding
Describe [Simple breast cyst]
________________
benign fluid filled mass 2/2 breast duct obstruction
________________
What are the risk factors for Cervical Insufficiency? -4
- Cervical Conization
- Uterine abnl
- Prior obstretric trauma
- congenital (intrauterine DES exposure, collagen abnl)
Rett syndrome sx -3
- [microcephaly with developmental regression]
- epilepsy
- unique hand gestures
patient is diagnosed with breast cyst
Describe your workup -5

What are the 4 major risk factors for [Spontaneous Abortion < 20WG]?
PREVIOUS SPONTANEOUS ABORTION
[Maternal Age > 35]
[Maternal Substance Use]
[BMI extremes]