4 - Epithelial Cells and Specialisations Flashcards
What is the definition of epithelia?
Sheets of contiguous cells that cover the external surface of the body and line the internal surfaces
What is a serous membrane?
Thin two part membrane that line certain close body cavities and envelop the viscera

Simple squamous epithelium + Thin Layer of connective Tissue
(peritoneum, pleural sacs, pericardial sac)
What does the serous membrane do in the lungs?
Gives them lubrication to allow heart and lungs to rub against one another with no friction
Where are epithelial cells found when they are derived from each germ layer?
- Ectoderm: epidermis
- Endoderm: GI tract
- Mesoderm: inner linings of body cavities
Where are simple epithelia found?
- Absorptive, secretory or lining surfaces
Where are simple cuboidal cells found and what is their function?
Where?
- Thyroid follicles
- Secretory part of exocrine gland and intercalated duct
- Collecting duct
- Covering ovary
What?
- Absorption
- Secretion
- Barrier/covering
- Conduct (duct)
- Hormone synthesis and storage

Where are simple squamous cell found and what is their function?
Where?
- Bowman’s capsule
- Endothelium
- Mesothelium
What?
- Fast exchange
- Barrier
- Tissue lubrication

Where are simple columnar cells found and what is their function?
Where?
- Stomach lining
- SI and colon
- Gastric glands
- Striated ducts
What?
- Secretion
- Lubrication
- Absorption

Where are pseudostratified columnar cells found and what are their functions?
Where?
Upper respiratory tracts e.g trachea, ear, nasal cavity
What?
- Mucociliary escalator
- Lining
- Secretion
- Mucous secretion
- Sensory reception in ear

Can you see the basal lamina under the microscope?
NO!
However can see it in upper respiratory tracts as it is so thick.
Where are stratfied squamous non-keratinised cells found and what is their function?
Where?
- Oesophagus
- Vagina
- Buccal cavity
- Moist surfaces
What?
- Protect against abrasion
- Prevent water loss

Where are stratified squamous keratinised cells found and what is their function?
Where?
- Skin
What?
- Prevent water loss
- Protect against abrasion
- Prevent ingress of pathogen
- Protect from UV and outside environment
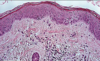
What cell shapes are in each layer of the skin?

Where are stratified cuboidal cells found and what is their function?
Where?
- Sweat glands, not secretory portion
What?
- Absorption of Na from sweat so it is hypotonic

Where are stratified columnar epithelium found and what is their function?
Where?
- Male urethra
- Conjuctiva of eye
What?
- Protection
- Secrete tears

Where are transitional epithelium found and what is their function?
Where?
- Bladder
SURFACE CELLS ARE ROUNDED SO CAN FLATTEN
What?
- Distension
- Chemical protection

What is a Langerhans cell?
Antigen presenting cell in the skin. Involved in contact dermatitis
What is the structure and function of goblet cells?
- Have microvilli on surface NOT cilia
- Release mucins to form mucus
What is cystic fibrosis?
- Mutation in CFTR gene so cannot move chloride into lumen
- Sticky mucus so no mucocilliary escalator
- Problems with infertility, GI tract, respiratory tract, liver, pancreas

What are clara (club) cells?
- In terminal bronchioles to protect them
- No cillia on surface, rounded
- Stem cell to repair bronchiole epithelia
- Detoxify harmful substances
- Secretre uteroglobin to break down water for fast gaseous exchange

What are microfold cells?
- Only in SI, close to lymph nodes
- Mushroom cap samples by endocytosis
- Immune cells reside in cell and then present any antigens to T-cells
- Bacteria can get in this way
What are sterocilia?
- In the ear
- Respond to fluid motion for hearing and balance
- Contain actin and myosin

How does smoking cause damage to the respiratory tract?
- Smoking thickens mucus, killing cillia
- Columnar cells die as thick mucus so goblet and basal cells proliferate
- Clara cells die
- Smoking can induce mutations in cells
- Pneumocytes die in alveoli and fibroblasts lay down collagen. Remaining type II pneumocytes will divide into type I and II

How long does it take for cells in the respiratory tract to renew?
Clara - NEVER
Cilia - 2 - 4 days
Trachea - 1-2 months
Alveoli - 8 days
Goblet cells - 10 days
What are pneumocytes?

What is acute and chronic bronchitis?

What is Emphysema?
- Shortness of breath due to widening of alveoli, with no fibrosis
- Loss of elastic recoil and changes to size of alveoli

What is COPD?
Umbrella term for chronic bronchitis and emphysema

What is asthma?
Wheezing and shortness of breath due to bronchospasms and excess mucus production


