4. Drug delivery Flashcards
Give examples of applications of nanotechnology in life sciences which use the iv delivery route.
- treatment of cancer, siRNA and gene delivery, intracellular infections.

Give examples of applications of nanotechnology resulting in improved drug delivery via the oral route.
improvement of solubility, delivery of peptides, proteins and vaccin

describe the evolution of drug delivery systems since the 1970s
sof natural organic drug carriers, soft synthetic drug carriers, hard inorganic particles for imaging and drug delivery

Mention 5 forms in which can you deliver a drug using nanomaterials.
as a nanocrystal of the active substance or embeded in nanocarriers (depo, matrix, dendrimer, layer-by-layer)
What are the possible benefits of using nanomaterials in drug delivery?
-tissue targetting (efficiency, toxicity), protection against degradation (clearance, dosing frequency), use of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR)

Which pre-requisits must be fulfilled before a drug can be absorbed into the blood?
the active substance needs to have solubility and permeability
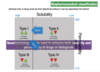
What are the consequences when a drug is poorly soluble?
- poor and variable bioavailability, no dose-response, slow onset of action

How are poorly soluble compounds being called?
brick dust, grease balls

The Lipinski rule of 5 is used for the selection of candidate drugs for further development. Which type of drugs?
drugs to be given orally, absorbed via passive diffusion.

Give the rules of Lipinski.
-

What does the Ostwald-Freundlich equation describe?
- the relationshipe between solubility and particle size, in similarity to the Kelvin equation for the condensation of gasses. - smallest particles dissolve first
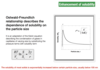
Why is the solubility of irregular particles underestimated by Ostwald - Freundlich?
xx

What is supersaturation and how can you prolong this?
- more dissolved than in equilibrium situation. rate nucleation and rate of crystal growth.

Describe 5 models of nucleation and growth
LaMer burst nucleation, Ostwald and digestive ripening, coalescence and oriented attachment, finke-watzky 2 step mechanism, intraparticle growth

What is nucleation?
- Wikipedia: Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organised structure appears.
What are the benefits of using nanosusspensions, and challenges?
- higher bioavailbility, less variability due to food, increased rate of absoprtion, improved absorption of higher doses (tox testing), rapid formulation development ? - agglomeration

Mention characteristics of an amorphous state
short-range order (?), low enthalpy of dissolution, metastable, recrystalise at varying T, rel humidity, p and agitation.

How can you stabilise an amorphous compound using nanotechnology. Give an example.
- Pb in carbon nanotubes. amorphous compound in a poreous nanomaterial Study with CaCO3; amorpheous, vaterite (poreous), aragonite (non-poreous), calcite (non-poreous) ibuprofen in upsalite

Cancer treatment. Why may NPs be a good tool for the passive targetting of tumor tissue?
- poor lymfatic draining, high vascularisation, leaky vessels. EPR effect

What are the important physicochemical characteristics of rigid core nanoparticles to enable an optimal bioavailability?
- zeta-potential (neg); size (100-200 nm); hydrophylicity (high) ; these characteristics are good for Enhanced Permeability and Retention.

How do you avoid RES (reticuloendothelial system = part of immune response)?
- polyethylene glycol of brush type (vs mushroon type (intermediate PEG density) and pancake type)

Describe 2 examples of the use of nanothechnologically-induced hyperthemia.
- photothermal plasmon resonance (Au nanorods); magnetic hyperthermia through Néel or Brownian relaxation.

You want to develop a treatment to eradicate a tumor by hyperthermia induced by Au nanorods. At which wavelength should the rods preferably absorb?
NIR (650 - 900 nm) because hemoglobin has minimal absorption below that and water above that.

What are today’s challenges for the use of nanotechnology in cancer treatment?
- variable EPR effect, rapid clearance, drug resistance, inefficient cargo delivery (?)



