3e Coordinate Electrical Flashcards
- What is represented by the diagram within the dashed line?

Which voltage types are
- single phase, two wire?
- single phase, three wire?
- three phase, four wire?
- What is represented by the line along the bottom of the diagram below?
1 - Utility company transformer
2 - 120V = single phase, two wire
3 - 120/208V single phase, three wire (120/240V residential)
4 - 120/208V three phase, four wire (all but largest installations)
5 - Grounded neutral
- What is the purpose of a ground neutral?
- How is the ground typically constructed?
- All electrical systems must be grounded to provide protection against shock + electrical fires.
- A rod or electrode firmly imbedded in the earth.
What is the sequence of flow for electrical current supplied to a building’s panel boards. (7)
- Main power line or transformer
- Service drop or underground SERVICE CONDUCTOR
- Service ENTRANCEconductor
- Watt-hour METER measure
- past GROUNDing rod
- service SWITCH (main disconnect to building)
- main SWITCHBOARD
building PANEL boards
What is the purpose of a transformer?
Used by med-large sized buildings to step down from a high-supply voltage to the service voltage.
A - List the 5 types of conduit shown below.
B - What 3 pieces of information are shown on the second conduit?

A
- Armored cable (aka BX cable)
- Nonmetallic sheathed cable (aka Romex) *moisture-resistant, flame-retardant
- Rigid Metal *steel tube joined by screwing into threaded hub
- Electrical metal tubing *thin walled, steel tube joined by compression or set screw couplings
- Flexible metal *used for motors/vibrating equip
B
- voltage class
- number & size of conductors
- type of insulation
A - What is the purpose of a panelboard?
B - Describe the various types of circuits fed by the panelboard. (4)
A - CONTROL, DISTRIBUTE, PROTECT similar branch circuits
B - Circuit types?
- BRANCH circuits
- GENERAL purpose outlets (lights / outlets)
- APPLIANCE circuits supply current to one or more outlets specifically intended for appliances
- INDIVIDUAL circuits supply current to only one piece of elec. equip.
- To avoid drop in voltage, what length should not be exceeded by a branch circuit?
- What % of a branch circuits capacity is reserved for flexibility?
- 100’ (30m)
- 20%
How is electrical current typ. supplied to doorbells, thermostats, intercoms, and HVAC systems?
LOW-VOLTAGE CIRCUITS
- current below 50V
- supplied by a stepdown transformer
List the typical mounting heights in the locations called out below:

- outlet above counter: 1220 (4’)
- switch on latch side of door 1220(4’) max
- 64(2.5”) min to door trim
- outlet above floor: 305 (12”) **455(18”) for accessibility
- No. of Convenience Outlets for residences
- No. of Convenience Outlets for Offices
- Living space: one every 3660(12’)
Countertops/kitchens: one every 1220(4’)
- one every 3050(10’)
OR one every 3.7m2(40ft2) for first 37m2(400ft2) and one every 9.3m2(100FT2)
Describe each of these outlets:


How many of these electrical plan symbols can you identify?


How many of these electrical plan symbols can you identify?


How many of these electrical plan symbols can you identify?


List and describe the 4 switch types.
- TOGGLE - lever knob opens/closes circuit (not shown below)
- 3-WAY - single-pole, double throw to control lights from 2 locations (see below)
- 4-WAY - used w 3-way to control lights from 3 locations (see below)
- DIMMER - rheostat or similar device for regulating the intensity of an ele. light wout affecting spatial distribution. (not shown below)

Define the following terms and their unit of measure:
- Luminous Intensity
- Luminous Flux
- Illuminance
- Exitance
- Luminance
-
Luminous Intensity - Intensity of light emitted from source in a specific direction
- SI unit: Candela (cd) - luminous flux emitted per unit solid angle (monochromatic light @ 540x1012Hz) (direction not distance)
-
Luminous Flux - rate of flow of visible light per unit time
- SI unit: Lumens (lm) - light emitted in a solid angle of 1 steridian w intensity of 1 candela
-
Illuminance - density of light on a surface
- SI unit: lumens per area
- footcandle (lm/ft2)
- lux (lm/m2)
- SI unit: lumens per area
-
Exitance - total light coming off a surface due to reflectance
- SI unit: lumens per area
-
Luminance - brightness of a light source or specific illuminated surface (direction specularity)
- SI unit: candela per area (cd/ft2)

Define the following laws of physics which govern light calculations:
- Inverse square law
- Cosine law
-
Inverse square law - illumination on a surface by a point varies inversely as the square of the distance to the surface.
- point source =d2
-
Cosine law - (aka lambert’s law) illumination of a surface is equal to cosine of angle of incidence (see below)
- lm/area = angle of incidence

- What is the Law of Reflection?
- Define the reactions of light to a surface listed below:
- angle of refraction
- reflectance
- absortance
- transmittance

- Light going in will take the same angle going out
- Diagram:
- angle of refraction - angle that a ray makes with a normal to the interface btwn to media @ point of incidence.
- reflectance - ratio of radiation reflected by surface/total incident on the surface
- absortance - ratio of radiation absorbed by a surface/total incident on the surface
-
transmittance - ratio of rad. transmitted through & emerging from a body to the total incident
- equal to 1 minus the absorptance
Define brightness & glare(2 types).
- Brightness - observable difference in luminance
- Glare - brightness > luminance eyes are adapted to. Two types:
- Direct (insufficiently sheilded light source)
- Reflected/indirect (ex: veiling reflectance which makes details difficult to see during task work - solution angle incident rays away from observer)
- Describe and incandescent light source
- List it’s pros/cons.
- Round point source bulb with filament that resists elec. and gives off light when heated.
- Pros/Cons
+renders colour well
+dims easily with rheostats
-low efficacy

- Describe and flourescent light source
- List it’s pros/cons.
- Tubular discharge lamp - light produced by fluorescence of phosphorous coating inside - linear light.
+efficacy 50-80 lumens/watt (converts power to luminous flux)
-ability to render colour varies

- Describe a high intensity discharge light source.
- List it’s pros/cons. (1)
- (HID) light produced by discharge of elec. through a metallic vapour.
- Pros/Cons
+efficacy of flourescent but form of incandescent
Identify the luminaire element shown below & describe it’s function.

- Reflectors control the distribution of light emitted by a lamp.
- Parabolic reflectors spread, focus, or collimate(make parallel) depending on the location of the light source in relation to reflector.
- Describe the function a lens and how they are used.
- What 2 types of lense are shown below:

- glass or plastic surface used to focus, disperse, or collimate emitted light
- Lense types:
- Fresnel = concentrate light
- Prismatic = redirect (scatter) light
Define:
- candlepower distribution curve
- Isochart
- Isolux
-
candlepower distribution curve
- measures intensity of luminosity emitted by a light source *meased in a single plane
-
Isochart
- plots pattern of illuminance on a surface
-
Isolux line
- lines in an isochart, represent the same level of illuminance all along a line

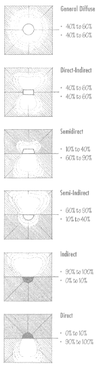
Identify the 6 categories of luminares and the corresponding % of light emitted above and below each of them.
List the recommended illumination levels for the following tasks:
- casual (dining)
- ordinary (reading)
- moderate (drafting)
- difficult (sewing)
- severe (surgery)

What is the maximum recommended brightness ration btwn a visual task area and its immediate background? and the surrounding area?
background = 3:1
surrounding area = 1/5 - 5 times the brightness of the task area
Describe the the qualities of the 2 types of light:
- diffused (3)
- directional (3)
-
diffused
- many sources
- flat/even/uniform
- minimizes contrast/shadows
-
directional
- enhances perception of shape/form/texture
- high in contrast/shadow
- can help relieve dullness with visual accents
**mix of diffused & directional ideal
k(kelvin)


