3.1.7 DNA, Genes & Chromosomes Flashcards
What is the basic function of DNA?
Used to store genetic information
(all instructions organism needs to grow and develop from fertilised egg to adult)
What is the main function of RNA?
Transfer genetic information from DNA to ribosomes
What do ribosomes (AKA body’s ‘protein factories’) do?
Read RNA to make polypeptides in process called translation
What are ribosomes made from?
RNA and proteins
What 3 things does a nucleotide consist of?
- Nitrogen-containing organic base
- Pentose sugar
- Phosphate group

What are monomers that make up DNA & RNA?
Nucleotides
How are polynucleotides formed?
- Nucleotides join via condensation reaction between phosphate group of one nucleotide and sugar of another
- This forms a phosphodiester bond
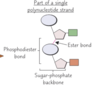
What is a chain of sugar and phosphates called?
Sugar-phosphate backbone
What is the pentose sugar in a DNA nucleotide?
Deoxyribose
Each DNA nucleotide has same sugar & phosphate group but a different ___
base
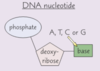
Name the 4 possible bases in a DNA nucleotide
- Adenine (A)
- Thymine (T)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
What is the pentose sugar in a RNA nucleotide?
Ribose
Name the 4 possible bases in a RNA nucleotide
- Adenine (A)
- Uracil (U)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)

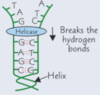
Describe how the structure of DNA is formed
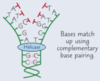
- 2 DNA polynucleotide strands join together by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs
- 2 hydrogen bonds form between A & T, and 3 hydrogen bonds form between C & G
- 2 antiparallel polynucleotide strands twist to form DNA double-helix

What does adenine pair with?
Thymine (A - T)
What does cytosine pair with?
guanine (C - G)
There is always _____ amounts of A & T in DNA molecule and C & G
EQUAL
Ratio of A & T to G & C varies from…
species to species
Describe the structure of RNA
Made from single polynucleotide chain = much shorter than most DNA polynucleotides
Name the 3 Types of RNA in every cell
- tRNA
- rRNA
- mRNA
What does rRNA do?
Type of RNA that makes up ribosomes
Explain how the structure of DNA is related to its functions (6)
- Double helix protects bases from corruption
- Large molecule so can store lots of genetic information
- Helix/coiled so compact
- Double stranded so replication can occur semi-conservatively
- (Weak) H-bonds for replication
- Many H-bonds so stable
- Complementary base pairing so accurate identical copies can be made
- Base sequence allows information to be stored
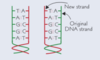
Explain why the replication of DNA is described as semi-conservative (2)
- Each strand copied / acts as a template
- DNA has one new strand & one orginial
Describe stage 1 of semi-conservative replication
DNA helicase breaks H bonds between bases = backbone is unzipped = helix unwinds