3) Electricity Flashcards
1
Q
What does a cell do?
A
- pushes current around a circuit- the current comes out of the + and back into the -
2
Q
What is a battery?
A
- two or more cells
3
Q
What is a lamp?
A
- when a current flows the filament gets hot and glows
4
Q
What is a switch ‘open’
A
- ‘open’ means ‘off’
5
Q
What is a switch (closed)
A
- ‘closed’ means ‘on’
6
Q
What is a fuse?
A
- a fuse will melt if too much electricity flows
7
Q
What is a voltmeter?
A
- measures voltage in volts
8
Q
What is an ammeter?
A
- measures current, in Amps
9
Q
What is a diode?
A
- a diode only lets current flow one way
10
Q
What is a resistor?
A
- is difficult for a current to go though
11
Q
What is a variable resistor?
A
- a resistor that we can adjust
12
Q
What is a thermistor?
A
- allows current to flow when you heat it
13
Q
What is an LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)?
A
- allows current to flow when light hits it
14
Q
What is the symbol for a cell?
A

15
Q
What is the symbol for a battery?
A

16
Q
What is the symbol for a switch (open)?
A

17
Q
What is the symbol for a switch (closed)?
A

18
Q
What is the symbol for a fuse?
A

19
Q
What is the symbol for a voltmeter?
A

20
Q
What is the symbol for an ammeter?
A

21
Q
What is the symbol for a diode?
A

22
Q
What is the symbol for a resistor?
A

23
Q
What is the symbol for a variable resistor?
A
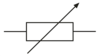
24
Q
What is the symbol for a thermistor?
A

25
What is the symbol for a LDR?

26
An electric current in solid ________ conductors is a flow of __________ charged electrons
- metallic- negatively
27
Define current?
- current is the 'flow' of electricity- rate of flow of charge
28
What do we measure current with?
- ammeter
29
How do we put an ammeter in the circuit?
- in series with the thing we're measuring- because ammeters have a very low resistance
30
What is the current like in a series circuit?
- the current is always the same
31
What is the current like in a parallel circuit?
- the current is split up in a parallel circuit
32
Define voltage
- the 'push' from the battery that makes a current flow- also called potential difference
33
How do we put a voltmeter in a circuit?
- in parallel with the thing we're measuring
34
What is the voltage like in a series circuit?
- not the same voltage- if you add V1 and V2 you get V3
35
What is the voltage like in a parallel circuit?
- voltage is always the same
36
Current (I) is ________ \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ to Voltage (V) in a __________ wire
- directly proportional- resistance
37
What is the relationship between the current (I) and voltage (V) in a diode?
- negative bias - no current flows (resistance very high)- positive bias (0V-0.6V) no current flows (resistance is high)- positive bias - (above 0.6V) current increases quickly because resistance has decreased
38
What does the I-V graph look like for a diode?
""
39
What does the I-V graph look like for a resistance wire?
""
40
What does the I-V graph look like for a metal filament bulb?
""
41
Equation for the relationship between voltage, current and resistance:
voltage = current by resistance V =IR
42
What is resistance measured in?
- ohms
43
What causes resistance?
- as the electrons move through the conductor, come collide with atoms, other electrons, or impurities in the metal- these collisions cause resistance
44
How to calculate charge?
charge (coulombs) = current (amps) by time (seconds) Q = It
45
How do you calculate charge?
Q=E/V - E energy transferred (Joules) - Q = charge (coulombs) - V = potential difference (volts)
46
What is voltage?
- energy transferred per unit charged passed
47
How to calculate voltage?
V=E/Q volts = joule/coulomb
48
What is the symbol for resistance?
"- ohms "
49
What is the qualilative variation of a thermistor with temperature?
- As temperature increases, resistance decreases- as temperature increases, more electrons are freed up for conduction
50
What is the qualilative variation of an LDR with illumination?
- as light intensity increases, the resistance decreases- more electrons are freed up for conduction
51
There is a ______ current through the resistor in bright light because the __________ is \_\_\_\_\_
- higher- resistance- lower
52
Electric current in solid metallic conductors is a flow of __________ charged \_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\_
- negatively- electrons
53
What is the electricity provided for the home called?
- mains supply
54
Label a plug diagram:
""
55
Why are wires made of copper?
- conducts eectricity- ductile
56
Why is the Earth pin longer than others?
- makes contact first - so its always connected (afety)
57
What are 5 electrical safety features?
- insulation- double insulation- earthing- fuses- circuit breaker
58
What is insulation?
- when plastic is used to protct the user from getting a shock when touching the component
59
What is double insulation?
- when plastic is used to protct the user from getting a shock when touching the component
60
Where do we find insulation?
- electrical components that don't need an earth wire
61
Where do we find double insulation?
- electrical components that don't need an earth wire
62
How does insulation work?
- plastic is an insulator- thus the electric component does not need an earth wire to protect the user from getting a shock
63
How does double insulation work?
- plastic is an insulator- thus the electric component does not need an earth wire to protect the user from getting a shock
64
What is the symbol for double insulation?
- one smaller square inside a bigger square
65
What is earthing?
- this is a wire that is attached to the earth
66
Where do find earthing?
- found earth wire and earth pin in plugs
67
How does earthing work?
- with the earth wire in place, the current goes through the earth wire and not the person touching it- the pole and coil are burried 2-3 meters underground
68
How do fuses work?
- contains a thin wire that heats up and melts if the current is too high
69
Where are fuses found?
- normally found in between an electrical power source and the electrical component
70
Why is it important to choose the correct fuse?
- the wire needs to melt once the current is too high
71
What is a circuit breaker?
- automatically operated electrical switches that protect circuits from overloading or short circuiting
72
Where are circuit breakers found?
- found in fuse boxboards in modern houses instead of the fuses
73
How does a circuit breaker work?
- electromagnetic switch opens when the current is greater than a certain value- this enables the circuit to be turned off when there is a risk of danger
74
Why are circuit breakers better than fuses?
- more sensitive than fuses- can be reset more quickly
75
How do you calculate power?
P=VI power = voltage by current
76
What is a.c ?
- alternating current - the voltage and current change directions many times each second
77
What is d.c?
- direct current - constant current in one direction
78
What is an RCCB?
- circuit breaker - the device disconnects a circuit when it detects that the current is not the same in the live and neutral wires - when the currents are different, there is a small current leaking to earth, which could be through the body of a person who accidentally touches the live wire
79
How do you calculate energy transferred (E)?
E = VQ E = energy transferred (Joules (J)) V = potential difference (Volts (V)) Q = charge (Coulombs (C)) E = IVt E = energy transferred (Joules (J)) V = potential difference (Volts (V)) I = current (Amps (A)) t = time (seconds (s)
80
What are watts?
joules per second (J/s)


