3 Acute Inflammation Flashcards
Define Inflammation
Response of living tissue to injury
What are the characteristics of Acute Inflammation? (4)
- Immediate
- Short duration
- Innate
- Limits damage
What accumulates in tissues as a result of inflammation?
Exudate
Neutrophils
What are the 4 cardinal signs of acute inflammation?
Rubor
Calor
Tumor
Dolor

What happens in vessels as a result of acute inflammation?
- Vasoconstriction- (seconds)
-
Vasodilation- (mins)
- Heat and redness
- Permeability increase
- Oedema formation- red cell stasis
Why does fluid move into tissues in acute inflammation?
Starling’s law: fluid movement - controlled by balance between:
- Hydrostatic pressure-exerted on vessel wall by fluid
- Oncotic pressure- exerted by plasma protein
- Vasodilation:
- Increases capillary hydrostatic pressure
- Increase vessel permeability- los of plasma protein
- Net fluid movement OUT of VESSELS- oedema
Blood viscosity increases- STASIS

What’s the difference between Exudate and Transudate?
-
Exudate=
- Protein rich
- in Inflammation
- Increased vascular permeability
- Injury site
-
Transudate=
- Low protein content
- Fluid loss
- NO CHANGE in vascular permeability
- Eg. Heart/hepatic/renal failure
How might vascular permeability of vessels be increased? (3)
-
Endothelial contraction- gaps between endothelial cells
- Due to histamine, leukatrienes
- Endothelial Cytoskeleton reorganisation- cytokines, TNF(tumour necrosis factor)
- Direct injury- chemical/toxic burns
What is a neutrophil?
- Primary WBC
- Involved in acute inflammation
- Trilobed nucleus
- Granulocyte

What type of WBC is shown here?
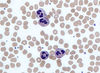
Neutrophil
In 4 steps, outline the process by which neutrophils escape vessels.
- Margination: stasis- neutrophils line up on endothelium edge
- Rolling: sticking intermittently
- Adhesion: Stick avidly
- Emigration: through blood vessel wall (aka Diapedesis)

What is the adhesion molecule found on the neutrophil surface?
Integrins- bind to receptors on endothelial surface
What is the adhesion molecule found on the endothelial surface?
Selectins- on endothelial surface- upregulated by chemical mediators

How do neutrophils move through the interstitium?
Chemotaxis
Along chemical gradient of chemoattractants (eg bacterial peptides)
What do neutrophils do at the site of infection?
- Phagocytosis
- Opsonisation









