2a.) Development of Urinary System Flashcards
When concerning ourselves with development of urinary system we are concerned with development of what two specific components?
- Kidneys and ureters
- Bladder and urethras
How many separate kidney sytems form in the process of creating the kidneys
Three separate kidney systems form sequentially; disappearance of one system marks onset of devlopmetn of another system
From what germ layer does the kidney arise?
Intermediate mesoderm
What is the first kidney system to develop and where does it develop?
- Pronephros
- Develops in the cervical region

State the three kidney systems involved in development of definitive kidneys

Given that the pronephros is non-functional, why do we consider it in the devlopment of the kidneys?
The pronephric duct drives the development of next stage
When does the pronephros appear?
When does the pronephros disappear?
4th week
End of week 4
Describe the strucurre of the pronephric duct, include:
- What it is made of
- Where it extends from and to
- Segmented divisions of intermediate mesoderm from nephrotomes (tubules)- 6-10 pairs
- Tubules join to form pronephric duct
- Duct extends from cervical region to cloaca
Describe the development of the mesonephros
Mesonephros develop caudally to pronephros. Pronephric duct induces nearby intermediate mesoderm (in thoraco lumbar region) to form mesonephric tubules. Tubules receive capillaries from dorsal aorta allowing them to filter blood; the tubules then drain into the mesonephric duct (a continuation of the pronephric duct)
Why do we need to continue devloping the urinary system after the mesonephros?
Mesonephros acts as primitive excretory system, as it can filter blood it receives from capillaries from the abdominal aorta, but it has no water conserving function hence we need to “upgrade it”
What two components make up the embryonic kidney?
Mesonephric tubules + mesonephric duct
What does the mesonephros sprout and why is this important?
Mesoneprhos sprouts uretericbud caudally; ureteric bud induces development of definitive kidney
Why is the ureteric bud able to induce devlopment of the definitive kidney?
It has ability to drive development of undifferentiated intermediate mesoderm; it creates the metanephric blastema

Which of the _____neprhos forms the definitive kidneys?
Metanephros
When does the metanephros appear?
When is the metanephros functional by?
- Appears 5th week
- Functional by 12th week
State the two components of the metanephric system which goes on to make definitive kidney
- Collecting system- derived from ureteric bud
- Excretory system- derived from metaneprhic blastema (intermediate mesoderm) under the influence of the ureteric bud
Define blastema
. Blastema just means cells capable of growing or regenerating organs or body parts hence both the ureteric bud and the metanephric blastema may be referred to as blastema
Where does the metaneprhic kidney first appear?
Which way must it move?
Describe the arterial supply as it moves
Metanephric kidney first appears in pelvic region so must then ascend into abdomen. When in pelvis, it receives it’s blood supply from pelvic branch of abdominal aorta and as it ascends new arteries from abdominal aorta supply the kidney and the other arteries including the pelvic arteries USUALLY regress. If they do not regress they will persist as accessory renal arteries.
- “Caudal to cranial shift”
- Crosses the arterial fork formed by vessels returning blood from fetus to placenta
Describe how the ureteric bud develops into the collecting system
It dilates to form the ureter, renal pelvis, major and minor calyces and collecting tubes (terminating at the distal convulted tube)
Describe how the metanphric blastema develops into the excretory system
- Collecting tubule formed
- Collecting tubules covered by metanephric cap which gives rise to excretory tubules which form the neprhon
- Proximal end of excretory tubules form Bowman’s capsule around a glomerulus and distal end elongated to form proximal convoluted tube, loop of Henle and distal convulted tube
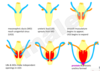
What is the cloaca?
Is it open or closed to outside environment?
- Terminal/end structure of hindgut that is a common chamber for GI and urinary waste
- Closed to outside environment by cloacal membrane
The uro-rectal septum divides the cloaca into what two parts?
- Urogenital sinus (anterior)
- Anal canal (posteior)
The urogential sinus is continuous with the umbilicus via what structure?
Urachus

During what weeks is the cloaca divided into two parts by the uro-rectal septum?
4th - 7th weeks