2. Skull Flashcards
What are the bones that make up the skull and facial skeleton?
Skull (8):
- Frontal
- Parietal (x2)
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Temporal (x2)
- Ethmoid
Facial skeleton (15):
- Paired bilateral:
- Maxilla
- Inferior nasal concha
- Zygomatic
- Palatine
- Nasal
- Lacrimal
- Unpaired:
- Mandible
- Ethmoid
- Vomer

Label this.


Which bones make up the base of the skull?

What bone is this?

Frontal bone
What bone is this?

Occipital bone
What bone is this?

Parietal bone
What bone is this?

Temporal bone
What are the important structures in the temporal bone you need to know about?
- Squamous part -> Anterior superior portion of the temporal bone that forms the lateral part of the middle cranial fossa
- Petrous part -> Posterior inferior portion of the temporal bone that contains the inner ear
- External acoustic meatus
- Mandibular fossa -> An oval depression behind the anterior root of the zygomatic where the mandible connects.
- Styloid process -> Projects from the inferior part of the petrous temporal bone and offers attachment to the stylohyoid ligament and the stylohyoid, stylopharyngeus, and styloglossus muscles.
- Mastoid process -> A smooth conical projection of bone located at the base of the temporal bone. It allows the attachment of muscles such as the occipitofrontalis muscle, as well as certain muscles of the neck like the sternocleidmastoid.

Show the location of the temporal bone and name the 3 main parts of the bone.

What bone is this?

Zygomatic bone
What bone is this?

Sphenoid bone
What bone is this?

Sphenoid bone
Describe the structure of the sphenoid bone and how it appears in the skull.
- Greater wings -> These are the bits that can be seen on the lateral skull wall
- Lesser wings
- Pterygoid plates
- Pituitary fossa (in the body) -> Where the pituitary gland is found
- Sphenoid sinuses (in the body)

What bone is this?

Ethmoid bone
What is the cribriform plate?
- It is the portion of the ethmoid bone that forms the roof of the nasal cavity.
- This narrow bony structure contains deep grooves known as olfactory fossa, which supports the olfactory bulb.

What bone is this?

Nasal bone
What bone is this?

Maxilla
What bone is this?

Mandible
What are the clinoid processes?
Parts of the sphenoid bone.

Describe the different types of ossification that form the skull.
- Cranial roof and facial bones -> Intramembranous ossification (the bones need to form quickly)
- Cranial base -> Endochondral ossification
What are the sutures of the skull and what are the joining points you need to know?
- Sagittal suture -> Joins the two parietal bones
- Coronal suture -> Joins the frontal bone to the parietal bones
- Bregma -> The point where the coronal suture meets with the sagittal suture and is the location of the anterior fontanelle during infancy.
- Lambda -> The point where sagittal suture meets with the parieto-occipital (lambdoid) suture and the location of the posterior fontanelle during infancy.

What suture is this?

Coronal suture
What suture is this?

Sagittal suture
What suture is this?
Lambdoid suture (parieto-occipital suture)

Label these.

Bregma is the one you need to know.

What is the pterion?
The pterion is a point of weakness on the lateral surface of the skull where the frontal, parietal, temporal and sphenoid bones meet.

What is the clinical significance of the pterion?
- It is a point of weakness, beneath which is the middle meningeal artery
- This means that fracture of the pterion is a well-known cause of an extradural haemorrhage
- A hard blow to the side of the head maylead to a haematoma that exerts pressure on the underlying cerebral cortex, which may cause death in a few hours.
What are the major fossae of the skull?

What is the pituitary fossa? In which bone is it?
The fossa in the sphenoid bone where the pituitary gland sits.

How many paranasal sinuses are there? What are their names?
There are 2 copies of each of these 4 types:
- Maxillary
- Ethmoid
- Sphenoid
- Frontal
Sometimes the mastoid process is also considered to have sinuses due to the existence of mastoid cells, which are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium.

What are mastoid air cells?
The mastoid cells are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium.
Label the air sinuses.


Where is the sphenoid air sinus?
It is a single midline structure in the sphenoid bone inferior to the pituitary gland.
What are the ethmoid air cells?
These are sinuses in the ethmoid bone.

Describe the meninges of the brain and the spaces containing fluid.
- The meninges from deep to superficial are the pia mater, arachnoid mater and dura mater
- The subarachnoid space, located between the arachnoid and pia, is filled with CSF.
- The dura mater is split into an outer periosteal layer (which is continuous with the periosteum of the bony cranium) and an inner meningeal layer that more closely conforms to the surface of the brain.
- In certain locations, these layers separate to form intralaminar spaces to accommodate the dural venous sinuses, which receive venous blood from the brain and drain predominantly to the internal jugular vein.
What are CSF cisterns?
They are subarachnoid spaces in the superficial portion of the brain which are filled with CSF and are continuous with the ventricles.

What are the venous sinuses in the brain you need to know about?
- Superior sagittal
- Straight
- Sigmoid
- Cavernous

Summarise the venous drainage of the brain.
[IMPORTANT]
- Superior sagittal sinus runs between the two hemispheres, receiving many smaller veins. This drains into the transverse sinus on either the left or right of the brain.
- The great cerebral vein is formed by the confluence of multiple deep veins and it drains multiple structures posterior to the ventricles. It drains into the straight sinus, which also drains into the transverse sinus.
- The transverse sinus on each side runs horizontally around the occipital bone.
- It then becomes the sigmoid sinus, which curves inferiorly and medially in a deep groove on the mastoid part of the temporal bone.
- This then drains into the internal jugular vein.
- The cavernous sinuses lie lateral to the pituitary beside the body of the sphenoid bone, between two layers of dura. The main tributaries of each cavernous sinus are the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins, the retinal vein and the superficial middle cerebral vein. They also eventually drain into the internal jugular vein.

What is this vein and what is its function? What does it drain into?

- Superior sagittal sinus
- Receives veins that drain the cerebral hemispheres, falx cerebri, meninges and scalp
- Drains into the transverse sinus on either the left or right of the brain.
What is this vein and what is its function? What does it drain into?

- Sigmoid sinus
- Drains the transverse sinus
- Drains into the internal jugular vein
What is this vein and what is its function?

- Cavernous sinus
- Drains the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins, the retinal vein and the superficial middle cerebral vein.
- Drains into the internal jugular vein
What is this vein and what is its function?

- Straight sinus
- Drains the inferior sagittal sinus and the great cerebral vein
- Drains into the confluence of sinuses
Explain what is seen here and how it could occur.

- Extradural haemorrhage
- A large area of high signal (white) is see just inside the skull in the region of injury. It has not spread more generally within the cranial cavity. Fresh blood appears white on CT.
- This is an extradural haemorrhage caused by rupture of the middle meningeal artery which runs across the pterion between the bone and the underlying fibrous dura mater.
Is there a latent period with extradural haemorrhage?
Yes, the patient may maintain consciousness for a while before collapsing.
What is a sign of extradural haemorrhage that can be seen when still conscious?
3rd CN palsy (oculomotor nerve)
Explain what is seen here and how it could occur.

- Subdural haemorrhage
- A is older than B, since B is lighter and so it reflects more fresh blood
- The symptoms have developed slowly, so this is very unlikely to represent arterial bleeding.
- Subdural haematomas arise from rupture of the small veins that connect the superficial veins on the surface of the brain to the superior sagittal sinus.
- These bleed very slowly and the blood does not enter the CSF space.
Explain what is seen here and how it can occur.

- Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- It presents with fresh (white) blood filling the spaces around the brain typically occupied by CSF all around the brain, so the brain doesn’t appear as smooth.
- It is very rapid.
- SAH occur most commonly as a result of rupture of a ‘berry’ aneurysm at the base of the brain, usually in the circle of Willis.
- Classically, they present with a sudden onset, severe headache.
Summarise each type of haemorrhage.
- Extradural -> Due to blow to the head and arterial bleeding. Develop quickly, although there can be a latent period. Middle meningeal artery rupture presents with CN 3 palsy. Typically biconvex in shape.
- Subdural haemorrhage -> Due to blow to the head and bleeding from cerebral veins joining the superiod sagittal sinus. Develops slowly. Typically cresent-shaped.
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage -> Due to berry aneurysm in circle of Willis. Develops rapidly. Presents with severe headache.

What is another name for intracerebral haemorrhage?
Stroke
What is hydrocephalus?
Raised intracranial pressure due to increased fluid in the ventricles of the brain.

Summarise the contents of the foramen rotundum.
Maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve
Summarise the contents of the foramen ovale.
Mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve
Summarise the contents of the foramen spinosum.
Middle meningeal artery
Summarise the contents of the jugular foramen.
CN 9, 10, 11 and internal jugular vein
Summarise the contents of the foramen magnum.
Spinal cord, vertebral arteries, SPINAL PORTION of CN 12
Summarise the contents of the carotid canal.
Internal carotid artery, Sympathetic plexus
Summarise the contents of the stylomastoid foramen.
(IMPORTANT)
CN 7
The stylomastoid foramen is just lateral to the jugular foramen.
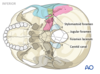
Summarise the contents of the hypoglossal canal.
CN 12
Summarise the contents of the optic foramen.
CN 2, Opthalmic artery
Summarise the contents of the superior and inferior orbital fissures.
CN 3, 4, 6, Ophthalmic branch of 5, Ophthalmic veins
Summarise the contents of the internal acoustic meatus.
CN 7, 8, Labyrinthine artery
Draw the structures within the cavernous sinus.
The relative positions of the contents of the cavernous sinus can be remembered using the phrase “O TOM CAT”:
Lateral wall contents (superior to inferior):
- Oculomotor nerve
- Trochlear nerve
- Ophthalmic nerve
- Maxillary nerve
Sinus contents (medial to lateral):
- Carotid artery (internal)
- Abducens nerve
- Trochlear nerve (in lateral wall)

Aside from the pterion, what is another area of weakness in the skull?
- Fractures involving the base of the skull often pass through the foramina of the base which creates areas of relative weakness.
- Skull fractures may damage underlying tissues including vessels, cranial nerves, para-nasal sinuses and the brain within the dural sac.
What is a basliar fracture and what does it involve?
A linear fracture at the base of the skull. It usually is associated with a dural tear and is found at specific points on the skull base.
What is otorrhoea and what can it indicate?
- CSF discharge from the ear
- It can indicate fractures of the petrous temporal bone
What is rhinorrhoea and what can it indicate?
- CSF discharge from the nose
- It can indicate fractures through the anterior cranial fossa
Aside from otorrhoea, what else is an indicator of a fracture of the petrous temporal bone?
Bruising over the mastoid processes (Battle sign)
Aside from rhinorrhoea, what else is an indicator of a fracture through the anterior cranial fossa?
Bruising around the eyes
What is a late consequence of a depressed fracture of the skull?
Epilepsy




What are the two main arteries supplying the brain?
- Vertebral arteries:
- Provide about 20% of the total supply
- Supply the posterior part of the cerebrum and the contents of the posterior cranial fossa
- Downstream arteries include the basilar artery, which splits into the posterior cerebral arteries that are responsible for supplying the visual cortex.
- Internal carotid arteries:
- Provide about 80% of the total supply
- Supply the anterior and middle parts of the cerebrum and the diencephalon
- Downstream arteries include the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
What are the two main arteries supplying the brain?
- Vertebral arteries:
- Provide about 20% of the total supply
- Supply the posterior part of the cerebrum and the contents of the posterior cranial fossa
- Internal carotid arteries:
- Provide about 80% of the total supply
- Supply the anterior and middle parts of the cerebrum and the diencephalon.
Summarise the areas of the outer brain supplied by each of the cerebral arteries.
- Blue = Anterior cerebral artery
- Red = Middle cerebral artery
- Yellow = Posterior cerebral artery

Summarise the areas of the sagittal cross-section of the brain supplied by each of the cerebral arteries.
- Blue = Anterior cerebral artery
- Red = Middle cerebral artery
- Yellow = Posterior cerebral artery



