14. Abdominal and Pelvic Walls Flashcards
What is the pelvic girdle?
- The pelvic (hip) girdle is formed from two hip bones, known as the os coxae.
- At birth, each hipbone is composed of three separate bones which fuse together, called the ilium, ischium and pubis.
- The pelvic girdle directly articulates with the vertebral column at the sacroiliac joints.



What bones make up the hip bone? What is the position of each?
- Ilium -> Top
- Ischium -> Bottom, Back
- Pubis -> Bottom, Front

What are the main landmarks of the hip bone?
Ilium:
- Iliac crest (palpable)
- Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) (palpable)
- Posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) (palpable)
- Anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS)
- Greater sciatic notch
Ischium:
- Ischial spine
- Ischial tuberosity (palpable)
Pubis:
- Pubic tubercle (palpable)
All 3:
- Acetabulum -> Articulates with head of femur

What does the pelvic girdle articulate with?
- Medially -> With sacrum at sacroiliac joint
- Laterally -> With femur at acetabulum
Give a summary of the ligaments at the sacroiliac joint.
- Sacroiliac ligament
- Anterior sacroiliac ligament -> From the ala of the ilium to pelvic surface of
- Posterior sacroiliac ligament -> Similar to anterior counterpart, except on the posterior side
- Sacrotuberous ligament -> From inferior sacrum to iliac tuberosities
- Sacrospinous ligament -> From lateral sacrum to ischial spine
- Intrinsic ligaments

Draw the position of the anterior sacroiliac ligament.

Draw the position of the posterior sacroiliac ligament, sacrospinous ligament and sacrotuberous ligament.

What ligaments at the sacroiliac joint do you need to know about?
- Intrinsic
- Sacrotuberous
- Sacroiliac
What are the greater and lesser sciatic foramina?
- Greater sciatic foramen -> Formed by the ilium, sacrotuberous ligament and sacrospinous ligaments
- Lesser sciatic foramen -> Formed by the ischium, sacrotuberous ligament and sacrospinous ligaments

What are the pelvic inlet and outlet, and what bones border each?
- Pelvic inlet
- This is the superior opening to the pelvis
- Formed by the pubic symphysis anteriorly, and the pectineal line of the pubis, the arcuate line of the ilium, and the sacral promontory
- Pelvic outlet
- This is the inferior opening to the pelvis
- Formed by the inferior margin of the pubic symphysis anteriorly, and the ischiopubic ramus, the ischial tuberosity, the sacrotuberous ligament, and the inferior tip of the coccyx posteriorly

What is the importance of the pelvic inlet?
Forms the boundary between the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
What is the pelvic brim?
The edge of the pelvic inlet.
What is the true pelvis?
The region between the pelvic inlet and outlet.
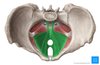
What is shown in red here?

Pelvic brim
What is shown in blue here?

Pelvic outlet
Describe the orientation of the pelvis.
- When standing up, the pelvis is tilted in such a way that the anterior superior iliac spines are in the same coronal plane as the pubic symphysis and pubic tubercles.
- This means that the pelvic inlet inclines anteriorly at 50-60° to the horizontal, whilst the pelvic outlet inclines anteriorly by around 10-15

Compare the male and female pelvis.

Is this the male or female pelvis?

Male
Is this the male or female pelvis?

Female
What’s the difference between the perineum and pelvic floor?
- The pelvic floor is just above the perineum, separating it from the rest of the pelvic cavity.
- The perineal body serves as an attachment for many of the pelvic floor muscles.
What is the pelvic floor?
- A funnel-shaped diaphragm that separates the perineum from the rest of the pelvic cavity.
- It is formed of muscle and connective tissue that functions to support the overlying pelvic viscera, including the bladder, intestines and uterus.
- The pelvic floor also plays a role in urinary and faecal continence.
What are the components of the pelvic floor?
Muscles:
- Levator ani -> Formed from three separate muscle components, called the puborectalis, pubococcygeus and iliococcygeus. Fibres insert into the central perineal body. Puborectalis forms a sling around the lower part of the rectum, creating a sphincter-like structure. Relaxation of the sling allows defaecation if combined with relaxation of the internal and external anal sphincters.
- Coccygeus -> Posterior part of the pelvic floor.
- Anococcygeal raphe (body) -> Musculotendinous structure passing between the anterior coccyx and the posterior aspect of the anus.
Non-muscular:
- Pelvic fascia -> Contributes to the floor of the pelvis by enveloping the superior and inferior aspects of the pelvic diaphragm.
- Perineal body -> A fibromuscular structure into which many muscles of the perineum, as well as the levator ani, insert. The structure lies just deep to the skin, between the urogenital and anal triangles of the perineum.
Note that the diagram is a superior view with the pubic symphysis at the bottom.