2 OLS (Ordinary Least Squares) Flashcards
(17 cards)
What are econometrics used for?
- Estimating economic relationships
- Testing economic theories
- Evaluating policies
Which procedures are not experimental?
- Cross section
- Pooled cross section
- Time series
- Panel data
What is the question of linear regression?
Understanding how y (DV) varies with x (IV).
What is the typical form of a linear regression model?
y = β0 + β1x + u
We wanna estimate β0 & β1
u is the error term, E(u) = 0
What is the zero conditional mean assumption?
E(u⎪x) = E(u) = 0
The estimate value doesn’t depend on the value of x.
Thus, the estimator is unbiased.
How do you compute β1 & β2?
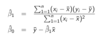
What is th criteria to choose β1 & β2?
They must minimize the sum of squared residuals
(ûi = yi - ŷi)
What is a residual?
The difference between reality and the fitted value found with the regression equation.
What are the 3 mechanical properties of the OLS?
- Σûi = 0
- cov (û, x) = 0
- point (Ẋ, ȳ) always on the regression line
The residual is not correlated with x.
When is the OLS unbiased?
4 conditions.
- Linearity in parameters.
- Random sample
- Zero conditional mean
- Sample variation in the regressor (no variation of x)
β^1 = Δŷ/Δx is equivalent to…
Δŷ = β^1Δx
If the zero conditional mean assumption fails, what could we obtain?
A “spurious correlation”. There is a mistake in the data collection, so the result can’t be right.
Which ratio does measure the quality of the model?
How is it computed?
R²
We need to handle this information with care.

What are the different types of model we can have for a regression?
- Linear
- Quadratic
- Natural logarithms ( y = log (x) )
For non-linear models, Δŷ depends on the initial value of x.
What is a logarithm?
The log of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number.
ex: log10(1000) = 3
1000 = 103
More generally: x = by < = > y = logb(x)
For very small changes in x, how can we compute the change in log?
Δlog(x) = log(x1) - log(x0) ≈ (x1-x0)/x0 = Δx/x0
100Δlog(x) ≈ 100Δx/x0 = %Δx
This is true only for small changes!
For a linear regression, how do you compute an elasticity?



