2 Covalent Bonding Flashcards
Why do giant covalent compounds have high melting points?
- many strong covalent bonds
- in giant lattice structure
- require a lot of energy to overcome
What state of matter is chlorine, bromine and iodine at room temperature?
Chlorine- gas
Bromine- liquid
Iodine-solid
How do you draw the structure of graphite?
- Draw a minimum of three hexagons in each layer
- Off set the layers and add dotted vertical lines between layers to represent the weak force between layers

What sort of bond is between the carbon and oxygen in carbon dioxide?

Double covalent bond
If chlorine water is added to sodium iodide solution, the solution turns from colourless to brown.
Why does this happen?
Chlorine water (colourless) is more reactive than iodide
Cl2+ 2NaI –> 2NaCl + I2
colourless brown
Chlorine displaces the iodide ion to form iodine
Describe the forces on any outer shell electrons
Force of attraction between outer electrons (-) and (+) positive nucleus
Force of repulsion between outer electrons (-) and electrons (-) in middle shells (called electron shielding)

What is the dot cross diagram for chlorine?

Describe the appearance of the element chlorine
pale green gas at room temperature
What are the names of the two types of covalently bonded substances?
Simple covalent e.g. water
Giant covalent e.g. diamond
Below are the many possible structure of the element sulfur.
What are these structures called, which are different structural forms of the same element?

allotropes
How do you draw the structure of diamond?

What is the dot cross diagram for oxygen?

Iodine is a larger atom than bromine.
This means the outer shell is further from nucleus and there is a weaker force of attraction on electrons
This also means there is more electron shielding, more repulsion on the outer shell electrons
What affect does this have on iodine’s reactivity compared to bromine?
Iodine is less reactive than bromine.
Remember group 7 wants to gain or share 1 electron and i_odine has less of a pull from the nucleus_ and more repulsion from electrons in the middles shells.
Describe the appearance of chlorine, bromine and iodine

Chlorine- pale green gas
Bromine- red liquid
Iodine- grey solid
What would you observe if you add colourless chlorine water to potassium iodide
KI + Cl2
It would turn from colourless to brown
chlorine is more reactive than iodine
chlorine will displace iodide ion
2KI + Cl2 –> KCl + I2
colourless brown

Graphite is made of layers which have weak intermolecular forces between them
The layers can easily slide over one another
Does this make graphite hard or soft?
soft
What would you observe if you add orange bromine water to potassium iodide
KI + Br2
It would turn from orange to brown
bromine is more reactive than iodine
bromine will displace iodide ion
2KI + Br2 –> 2KBr + I2
orange brown

Diamond is an allotrope of carbon.
Carbon has 4 bonds and forms a tight tetrahedral structure with no layers.
It is entirely made of strong covalent bonds and has no weak intermolecular forces
Will diamond be hard or soft?
hard
contains no layers which easily slide over one another.
State two uses of diamond and two uses of graphite
diamond- cutting tools, jewellery
graphite- lubricant and electrodes for electrolysis
Describe the difference in solubility of both ionic and covalently bonded substances in water
-Ionic compounds have generally high solubility
(polar solvents like water can easily pull oppositely charged ions from the structure- dissolving it)
-Covalent compounds have generally low solubility
What is a allotrope? Give two examples
Same element but different structure - or are chemically bonded in a different way
e.g.
diamond and graphite are allotropes
What type of atoms covalently bond together?
metal & metal
non-metal & metal
non-metal and non-metal
non-metal and non-metal atoms covalently bond
they share electrons.
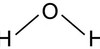
What is the displayed formula for water?
Which sort of bond will form between sulfur and oxygen?
Both non-metals, so covalent bond
Draw the dot cross diagram for ammonia

Covalent bonds form between which types of atoms?
Ionic bonds form between which types of atoms?
Covalent bonding happens between non-metals- they share electrons
Ionic bonding happens between metals and non-metals- electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal
Give three examples of simple covalent compounds
- water H2O
- methane CH4
- ammonia NH3
- chlorine Cl2
- Carbon dioxide CO2
Chlorine is a green gas
Bromine is a red liquid
Iodine is a grey solid
What colours are these halogens when in solution such as in displacement reactions?
Chlorine solution is colourless
Bromine solution is orange
Iodine solution is brown
Hydrogen chloride is a covalently bonded substance. What happens when hydrogen chloride is added to methylbenzene?
- In methylbenzene (which is a non-polar solvent) hydrogen chloride does not dissociate, it is not pulled apart.
- There are no H+ ions present therefore blue litmus paper stay blue.
- It is not acidic
Fluorine is a smaller atom than chlorine.
This means the outer shell is closer to nucleus and there is a greater force of attraction on electrons
This also means there is l_ess electron shielding_, less repulsion on the outer shell electrons
What affect does this have on fluorine’s reactivity?
Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine.
Remember group 7 wants to gain or share 1 electron!
What would you observe if you add colourless chlorine water to sodium chloride?
NaCl + Cl2
Nothing
Solution would stay colourless
chlorine will not displace chloride ion
chlorine will not displace itself

Describe the reactivity in Group 7- The halogens
Reactivity increases up group 7
Fluorine is the most reactive halogen
- lowest number of shells, outer shell closer to positive nucleus
- larger attractive forces between nucleus and outer electrons
- less electron shielding - less repulsion from electrons
- greater pull on electrons, less energy required to react, more reactive

Is the substance below simple covalent or giant covalent?

Simple covalent
What is the dot cross diagram for ethene?
Notice the double bond between the two carbon atoms!

Describe the appearance of the element chlorine
pale green gas at room temperature
Why are simple molecular substances usually gaseous at room temperature?
They have low melting points
weak intermolecular forces
little energy is needed to overcome them
Use the change in appearance of the halogens below to deduce the appearance of astatine (Below iodine in Group 7)
Chlorine- pale green gas
Bromine- red liquid
Iodine- grey/purple solid
Black solid
What sort of bond is between the nitrogen atoms in nitrogen?
Triple covalent bond
What giant covalent substance is shown in the image below?

diamond
What would you observe if you add colourless chlorine water to sodium bromide?
KBr + Cl2
It would turn orange
chlorine will displace bromide ion
chlorine is more reactive than bromine
2KBr + Cl2 –> 2KCl + Br2

What is the dot cross diagram for nitrogen?
Notice the triple bond between the nitrogen!

Hydrogen chloride is a covalently bonded substance. What happens when hydrogen chloride is added to water?
- In water (which is a polar solvent) hydrogen chloride dissociates (or is pulled apart) into an H+ ion and Cl- ion.
- There are H+ ions present therefore blue litmus paper would turn red.
- This is forms hydrochloric acid.
What sort of bond is between oxygen atoms in oxygen?
Double covalent bond
Why is graphite soft?
- It has weak intermolecular forces between its layers
- layers can easily slide over each other
- it does not hold its structure when deformed
What would you observe if you add colourless chlorine water to sodium chloride?
NaCl + Cl2
Nothing
Solution would stay colourless
chlorine will not displace chloride ion
chlorine will not displace itself

What would you observe if you add colourless chlorine water to potassium iodide
KI + Cl2
It would turn from colourless to brown
chlorine will displace iodide ion
chlorine is more reactive than iodine
2KI + Cl2 –> 2KCl + I2

What type of bond is an electrostatic force of attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the positively charged nucleus of an atom.
Covalent bond
Describe what happens to the boiling point as you go down Group 7 (The Halogens)

Boiling point increases down the group
What is a covalent bond?
The electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nucleus of an atom.
What are the similarities and differences between a covalent bond and an ionic bond?
Same- both electrostatic attraction
Different-
Covalent bond- non-metals & non-metal
Ionic bond - metal & non-metal
Different-
Covalent bond- between a shared pair of electrons and nucleus of an atom
Ionic bond- between oppositely charged ions
What would you observe if you add brown iodine water to sodium chloride?
NaCl + I2
Nothing
Solution would stay brown
Iodine will not displace chloride ion
Iodine is less reactive than chlorine

What is the dot cross diagram for hydrogen chloride?

Name all the diatomic molecules- remember that they are covalently bonded
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Fluorine
Oxygen
Iodine
Chlorine
Bromine
A goof mneumonic is ‘Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer’
Why do simple covalent compounds have low melting points?
- weak intermolecular forces
- require little energy to overcome
- low melting point
Br2 + CuI2 –> CuBr2 + I2
In the halogen displacement bromine is more reactive than iodine and displaces it, what is oxidised and what is reduced?
Br2 + 2e- –> 2Br-
2I- –> I2 + 2e-
OIL RIG
Bromine is reduced- gained electron
Iodide ion is oxidised- loses electron
Which sort of bond will form between magnesium and oxygen?
One metal and other non-metal. Ionic bond would form.
What would you observe if you add colourless chlorine water to sodium bromide?
KBr + Cl2
It would turn from colourless to orange
chlorine will displace bromide ion
chlorine is more reactive than bromine
2KBr + Cl2 –> 2KCl + Br2

Explain why covalent compounds do not conduct electricity
- There are no mobile ions or electrons
- No charged particles to carry charge
What is similar between a metallic structure, ionic structure and giant covalent structure?
- They all have many strong bonds in a giant structure.
- They all require a lot of energy to overcome
- They all have high melting points
What is the dot cross diagram for carbon dioxide?

Why do carbon & carbon share electrons when bonded but sodium & chlorine transfer electrons when bonded?
- Two carbon atoms have equal ‘pull’ or ‘affinity for electrons. Therefore they share electrons.
whereas,
- Chlorine has a large‘pull’ or affinity for electrons and sodium does not. Therefore sodium transfers one electron to chlorine.
What is the dot cross diagram for water?

Is the substance below simple covalent or giant covalent?

Giant covalent
Compare and contrast the state of ionic and simple covalent compounds at room temperature
- Ionic compounds are all solid
- Simple covalent compounds can be gaseous, liquid or solid at room temperature
Describe the appearance of the element iodine
grey/purple solid at room temperature
How are metallic bonds different from/similar to covalent bonds?
Same: both are an electrostatic attraction
Different:
Metallic- attraction is between positive metal ions and a sea of delocalised electrons
Covalent is between a nucleus and a shared pair of electrons.
What is the dot cross diagram for hydrogen?

Which sort of bond would form between copper and copper?
Both metals - metallic bond.
What is the dot cross diagram for methane?

Why does graphite (a non-metal) conduct electricity?
- Graphite is made of layers of carbon atoms with three bonds.
- Carbon is in group 4 and has four outer electrons.
- This one electron is free to move (delocalised) within the layers of carbon
- and can carry charge.
What are the similarities and differences between a covalent bond and metallic bond?
Same: They are both an electrostatic attraction
Difference:
Covalent bond- is between a shared pair of electrons and the nucleus of an atom
Metallic bond- is between a metal ion and a sea of delocalised electrons
Difference:
Covalent bond- between non-metals only
Metallic - between metals only
Compare and contrast the properties of graphite and diamond
appearance
harness
thermal conductivity
electrical conductivity
use

What is the dot cross diagram from ammonia?

How many outer electrons do the halogen group have?

seven outer electrons
All halogens atoms form diatomic simple molecular molecules
F2
Cl2
I2
What would you observe if you add orange bromine water to sodium chloride?
NaCl + Br2
Nothing
Solution would stay orange
Bromine will not displace chloride ion
Bromine is less reactive than chlorine

Explain why graphite makes a good lubricant
- Graphite has weak forces between the layers
- layers can slide over one another easily

Give three examples of giant covalent compounds
- graphite
- diamond
- silicon dioxide
Describe the appearance of the element bromine
red liquid at room temperature
Describe the appearance of the element bromine
red liquid at room temperature
Fluorine is a smaller atom than chlorine.
This means the outer shell is closer to nucleus and there is a greater force of attraction on electrons
This also means there is l_ess electron shielding_, less repulsion on the outer shell electrons
What affect does this have on fluorine’s reactivity?
Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine.
Remember group 7 wants to gain or share 1 electron!
How are the covalent bonds between carbon in diamond different from the covalent bonds between carbon in graphite?
Diamond- all four outer shell electrons are used
Graphite- only 3 outer shell electrons are used- fourth electron exists between the layers and is delocalised
Why does tetrachloromethane have a higher boiling point than trichloromethane?

Tetrachloromethane has a higher formula mass, therefore has a higher boiling point
- larger forces between the molecules*
- -more energy needed to overcome them*
Is fullerene giant covalent or simple covalent?

Simple covalent
It is molecular and has a definite size


