2. Correlation Flashcards
(25 cards)
Correlation
A statistical method for measuring the extent to which two variables are related It measures the pattern of responses across variables
Correlation: measuring relationships
As one variable increases does the other increase, decrease, or stay the same
Variance
Calculated by subtracting all scores by the mean score. Add this and then sum it.
Covariance
We look at how much each score deviates from the mean. If both variables deviate from the mean by the same amount, they are likely to be related.
How to determine the relationship between two variables
Visual inspection > scatterplot Numerical calculation > correlation coefficient
Covariance Equation
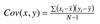
Problems with covariance
Depends upon the unit of measurement Solution: standardise it (divide by the standard deviation)
Correlation Coefficient
Standardised covariance
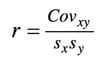
Correlation Assumptions
Linearity Normality Check: scatterplots, Q-Q/P-P plots, histograms
Correlation - assumptions violated
Bootstrap, Spearmans r, Kendall’s tau
Pearson’s R
To get the Pearson’s R correlation co-efficient we do the above but times the bottom by the standard deviation for both. This gives us a standardized r value. R values range between -1 to +1.Definition
Correlation Effect Sizes
1 = small effect 3 = medium effect 5 = large effect
Coefficient of Determination
R2 By squaring the value of r you get the proportion of variance in one variable shared by the other
Correlation significance testing
Significant for r tells us whether a sample with a correlation of r = .86 could come from a population where r = 0. Alpha = 0.05 - probability of 5% or less that there is a correlation significantly different from 0 when in reality there is no correlation
Factors affecting correlations
Non-linear relationships between variables Restrictions of range Outliers
Correlation and Causality
The third variable problem Direction of causality
The third variable problem
Causality between two variables cannot be assumed because there may be other measured or unmeasured variables affecting the results
Direction of causality
Correlation coefficients say nothing about which variable causes the other to change
Nonparametric correlation: Spearman’s Rho (Rs)
Pearson’s correlation on the ranked data Minimises the effects of extreme scores or effects of violations of assumptions
Nonparametric correlation: Kendall’s Tau (t)
Better than spearmans for small samples with large number of tied ranks Better estimate of correlation in population
Partial Correlations
Measures the relationship between two variables, controlling for the effect that a third variable has on them both
Semi-partial Correlation
Measures the relationship between two variables controlling for the effect that a third variable has on only one of the other variables
Point-biserial correlation
categorical/dichotomous data E.g. being dead (can’t be a bit dead) Can be dummy coded
Biserial Correlation
Continuum underlying dichotomy e.g. passing or failing a test Cannot be run in SPSS



