19. Economic growth Flashcards
What are the three main macroeconomic goals?
- low unemployment
- low and stable inflation
- economic growth
Define economic growth
ECONOMIC GROWTH: increase in real GDP over time
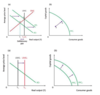
Short term vs long term economic growth
Short-term: approaching full employment level of output (LRAS) and the potential output (PPC)
Long-term: increasing the full employment level of output (LRAS) or potential output (PPC) - increase in quality/quantity of factors of production (by interventionist or market based policies)
Advantages of economic growth
- non-inflationary growth can be achieved (both AD and LRAS shift proportionately) - lower unemployment as more labout needed to produce higher Q
- GDP increases - wages increase - more tax - higher gov spending + improvement of improvements in medicine, technology, transportation - higher living standards - higher levels of human capital/education
- economic growth comes from higher productivity - net exports increase
Disadvatages of economic growth
- poor living standards: focus on work - neglect relationships - never satisfied with material goods
- econ growth involves structural changes in economy - structural unemployment - inequality increase
- increased pollution: higher emissions, waste, resource depletion - at expense of sustainable development
Explain management of deflationary gaps and growth trend in business cycle
Deflationary gaps (output gaps) - result of fall in econ growth in short-run - solved by demand management (expansionary fiscal/monetary) - narrow fluctuations of business cycle
The trend growth line - influenced by supply side policies - long-term econ growth

How can reforms in the labour market lead to economic growth?
Labour market reforms which are aimed at economic growth
- unemployment benefits
- labour union power at protecting workers
- elimination of minimum wage
All fo these reforms would help the firms to be more flexible in hiring and firing workers - resulting in larger outputs - larger econ growth


