12. Market failure Flashcards
Define market failure
MARKET FAILURE: when supply does not meet demand and the resources are allocated inefficiently
Types of market failure
- Lack of public goods
- Under-supply of merit goods
- Oversupply of demerit goods
- Existence of externalities
Define public goods
PUBLIC GOODS: goods that would not be provided at all in a free market
Market failure: lack of public goods, explain
- public goods benefit to society, so lack is considered failure, ex: national defence, flood barriers
- quasi public goods: public goods but also can be supplied in free markets, ex: street lighting, lighthouse
- public goods not supplied in free market because: non-excludable (all benefit), non-rivalrous (one person consumes it, does not rpevent other person from consuming it)
How gov can interve to solve market failure: lack of public goods
- gov provide public goods themselves
- subsidise private firms to supply
Market failure: under-supply of merit goods, explain
- gov thinks that merit goods bring positive benefits for people and whole society - should be consumed at a greater degree
- all public goods are merit goods (education, health, sports, opera)
- depending on the importance of merit good, gov can completely finance some goods but also in cost of taxpayers, less important - subsidise
Define merit goods
MERIT GOODS: goods which are under-suplied by the market therefore they are under-consumed
Market failure: over-supply of demerit goods
Demerit goods - overprovided - overconsumed goods
- gov thinks they are bad for people and society - want to decrease consumption (cigarettes, alcohol)
- depends on how harmful - drugs - illegal, not that harmful - taxed - cigarettes, alcohol
Market failure: existence of externalities
Externalities - consumption/production effects on third parties
Both positive and negative
Externalities exist when: MPC=/MSC and MPB=/MSB
Define externality
EXTERNATILITY: occurs when consumption of production of a good or service has affects to third parties
Types of externalities
- Neg extern. of production (external costs)
- Neg. extern. of consumption
- Pos. extern. of production (external benefits)
- Pos. extern. of consumption
Explain negative externalities of consumption (external costs)
Usually relate to pollution: factories pollute air - additional costs for the society - MSC > MPC of production
Gov intervene to eliminate market failure:
- tax firm for pollution to increase production costs - gov internalise externality BUT hard to determine how much pollute
- could ban polluting firms / restrict their output - increase private costs BUT decrease job positions
- gov could issue tradable emission permits - limited permits - can buy/trade them between firms - can create certainamount of pollution: cap and trade system (ex chlorofluorocarbons in US controlled by tradable emission permits, Kyoto protocol issues for green house gases GHG)

Explain positive externalities of production
- ex: firm provides high quality training, looks after health at private cost
Gov could decrease market failure by:
- subsidise the firms taht offer psoitive externalities to reduce MPC BUT difficult to estimate level of subsidy, opportunity cost - reallocate its spending
- provide vocational training in training centres in trageted industries BUT high costs

Explain negative externality of consumption
- ex: cigarettes - secondary/passive smoking, cars - air pollution, alcohol - MPB>MSB
Gov act to eliminate negative externality:
- ban the consumption of good or in certain areas BUT on burden on stakeholders
- impose indirect taxes (on price) BUT inelastic demand - bought anyways, deter only young smokers, black market
- provide education about harm of those goods BUT high costs and doubtful if effective

Explain positive externalities of consumption
- ex: education, healthcare - no disease spread, MSB > MPB
Gov intervene:
- subsidise, provide the goods BUT high costs - reallocate speniding
- positive advertising to encourage consume BUT high costs, long-term effects
- pass laws ex people vaccinate BUT civil liberties
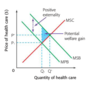
Diagram of reducing market failure (pos ext of consumption)

Define common acess/common pool/common property resources
typically natural resources such as fishing grounds or forests. Probelm with them - very difficult/expensive to exclude poeple from using them - overconsumption - depletion of resources
Define marginal utility
MARGINAL UTILITY: extra satisfaction that a person gets from consuming one more unit of good or service
Define sustainability
SUSTAINABILITY: where consumption needs of current generations are met without limiting the future generations to meet their needs
Forms: over-exploitation, pollution, corrosion, land degradation, deforestation, use of fossil fuels
Sustainability is in danger in poverty and in economic growth
Governememnts responses to sustainability threats
- Cap and trade system: tradeable emssion permits
- clean technologies: renewable E - solar panels, wind farms
- Subsidise sustainable businesses


