100 or so IGCSE Physics things to learn Flashcards
(201 cards)
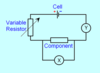
What component is this?

Variable resistor
Electrical hazards include….
Frayed cables, damaged sockets, water near sockets and metal objects in sockets
How many alpha-particles take this path?
What does this show?

Some of the particles take this path.
It shows there is a charged region

Give the unit and unit symbol for
Volume, V
metre cubed (m3)
The initial linear part of a force-extension graph is linked to what law?
Hooke’s Law (Force is directly proportional to extension)
What type of radioactive decay is most penetrating?
Gamma
How does a fuse work
When the current goes higher than the value of the fuse it melts. This breaks the circuit and stops current flowing
What are the artificial sources of background radiation?
Medical sources, fallout from nuclear weapons testing and use, nuclear accidents
Define amplitude
Amplitude is the maximum displacement above the equilibrium

What happens to the resistance of a thermistor as it is heated
High temperatures reduces the resistance of a thermistor
Comets orbit what? What shapes are their orbits?
Comets orbit stars (e.g. the Sun) in elliptical orbits

What are the dangers of ionising radiation?
Mutation and damage to cells and tissues
What are the energy transfers involved with solar cells
light ⇒ electrical
What equation links;
wave speed, frequency and wave length
wave speed = frequency x wave length
Describe the motion of gas particles
gas particles move in a random fast motion
What are the energy transfers involved with nuclear power
nuclear ⇒ thermal ⇒ kinetic ⇒ electrical
After two half-lives, how much of an original sample is left?
One quarter
Give the unit and unit symbol for
Power, P
watt (W)
Why is the image in a mirror virtual?
The image in a mirror can’t be projected onto a screen
The gradient of a velocity-time graph gives
Acceleration
What are the energy transfers involved with wind power
kinetic ⇒ electric
What makes something an elastic material
Material regains original shape once stretching force is removed
What type of radioactive decay is most ionising?
Alpha
In what two ways can radioactive decay be detected?
By photographic film and by a Geiger-Müller (GM) Tube