1 Introduction to Cardiovascular System Flashcards
Is the left ventricle of the heart filled with deoxygenated or oxygenated blood?
Oxygenated
Name and identify the 6 layers of the pericardium:

1-
2-
3-
4-
5-
6-
1- Fibrous pericardium
2- Parietal layer
3- Visceral layer (Epicardium)
4- Pericardial cavity
5- Myocardium
6- Endocardium

Identify the coronary arteries in red:

(LAD a.k.a Anterior interventricular artery)

Identify the major cardiac veins in the following diagram:


Identify the following arteries:


Name and identify the arteries in red shown on the upper limb:


Name and identify the veins in blue shown on the upper limb:


Name and identify the arteries in red shown on the lower limb:


Name and identify the veins in blue shown on the lower limb:


What is the role of perforating veins?
Drain blood from superficial veins to deep veins.

Where is the heart located?
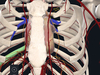
- Middle mediastinum (area in thoracic cavity between right and left pleural sacs)
- Lies within the pericardium
- Phrenic nerve on side of pericardium

What does the pericardium consist of?
- Strong outer fibrous layer
- Inner serous membrane made of two layers

What is the oblique sinus?
Space under the heart that is a blind end, swabs can get lost in there during surgery, posterior to left atrium

What is the transverse sinus?
Allows surgeon to cut off heart by isolating aorta and pulmonary trunk

Label this diagram of the heart


Label this posterior view of the heart


Name the valves of the heart and their structure
- Pulmonary and Aortic Valve
- Mitral valve (left)
- Tricuspid valve (right)
Only bicuspid valve is the mitral valve



Label these coronary veins


Where are the renal and testicular veins?


Label all of the arteries with a dot next to them


What are the borders of the heart?

Why might the heart shadow become enlarged?
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Pericardial effusion
- Dilated left ventricle

What are the sequence of changes that occur in the arterial wall to cause an arterial occlusion?
- Atheroma plaque
- Plaque ruptures
- Thrombus forms
- Embolism
(stroke in cerebral artery, MI in coronary artery)

What are the typical symptoms of an MI?
- Central crushing chest pain which may radiate to arm, neck or jaw
- Breathlessness

What would you hear in a leaky mitral valve?
Systolic murmur due to regurgitation of blood
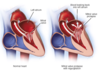
What would you hear in mitral valve-stenosis?
- Mid diastolic murmur
- Diastole turbulent blood flow

What is cardiac tamponade and how is it treated?
- Compression of the heart leading to a fall in arterial blood pressure as ventricles cannot fill in diastole
- Pericardiocentesis where a fine needle is placed in pericardium to aspirate fluid

What is diastole and systole?
Diastole = ventricles relaxed so AV valves open (tricuspid and mitral)
Systole = ventricles contract so SL valves open (pulmonary and aortic)
Why do patients with stab wounds to the heart have tachycardia, low b.p and distended neck veins?
Veins are distended as the jugular is carrying more blood than the heart can pump out. Low blood pressure due to low cardiac output as some blood leaking from the heart
What can cause pericardial effusion?
- Pericarditis (viral/bacterial infeciton)
- Autoimmune diseases
- Stab wounds
- Kidney failure
- Injury
How do you treat pericardial effusion?
Aspiration technique called pericardiocentesis
What is the blood flow to the brain (in ml/min)?
750ml/min
Where would you feel for the apex beat if the heart is normal?
- 5th intercostal space at the midclavicular line
What is the function of the chordae tendinae?
Remain taut when the ventricles contract to prevent prolapse of the valve

What would happen if a large ventricular septal defect was left untreated?
- Vascular remodelling and increased pulmonary resistance leading to Eisenmenger syndrome
(Eisenmenger syndrome: pressure in the pulmonary arteries becomes so high that it causes oxygen-poor (blue) blood to flow from the right to left ventricle and then to the body, causing cyanosis)
What is cardiac/thoracic ratio and what might an increased ratio mean?
Done on an PA film as better quality

What method can you use to visualise the coronary arteries?
2 or 3D angiography using CT

Draw a graph to show aortic pressure changes in 1 cardiac cycle.

What are the layers of the heart wall?

Why does the left ventricle have the highest pressure?
It has the thickest myocardium, 8-10mm thick, and has to pump systemically not pulmonary
What do the phrenic nerves do?
Supply the pericardium and the diaphragm
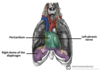
Label this 3D angiography


What stops heart valves from prolapsing?
Papillary muscles attached to chordae tendinae

What is the cardiac output per minute and how is this defined?
5l/min
SV = 55-83ML
HR = 60-90 bpm
Max HR= 220-age
When looking at an MRI what does dead unhealthy heart tissue look like?
White
Where do the coronary arteries stem from and where does the coronary sinus drain into?
Coronary artery from the aorta
Sinus drains back into the right atrium


