(1) Intro to Infectious Diseases and Bacteria (Putthoff) Flashcards
(126 cards)
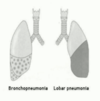
What is the most common cause of community aquired lobar pneumonia?
Strep pneumoniae
What are the important aspects to consider in a clinical approach to pathogens and those agents that may become pathogens?
- With which type(s) of infection/infestation is an agent most commonly associated?
- Clinical presentation
- Virulence factors?
- Most common cause of…
- Unique charactteristics
- Overarching clinical conceptualizations
- Prognosis?
Rules to write scientific names:
What is always written first?
What is always written second?
Homo sapiens
An organisms genus is always written first
An organisms species is always written second
Rules to write scientific names:
What is always capitalized?
What is always lower case?
Homo sapiens
Genus is capitalized
Species is lower case
Rules to write scientific names:
What is always underlined or italicized?
Scientific names of organisms are always italicized or underlined
As Dr. Putthoff put it…
What is the easiest [potentially overly simplified] way to distinguish prokaryotes vs eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes = single celled organisms
Eukaryotes = multicelled organisms
Do MOST bacteria stain by the gram stain?
No.
They stained very poorly
What are the 7 most clinically relevant gram (+) bacteria?
- Streptococcus
- Enterococcus
- Staphylococcus
- Bacillus
- Clostridium
- Corynebacterium
- Listeria
Which of the 6 most clinically relevant gram (+) bacteria are categorized as “SPORE producing”?
Bacillus
Clostridium
(These produce spores. Spheres that protect a dormant bacterium from the harsh enviornment)
Which of the 7 most clinically relevant gram (+) bacteria are categorized as “NOT SPORE FORMING”?
Corynebacterium
Listeria
Behold:
The most common gram stain reference bacteria
What are the purple ones?
What are the pink ones?

Purple = Staphoreous (Gram positive)
Pink = E.Coli (Gram negative)

Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What is the name for a circular bacteria?
Coccus
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram positive CIRCULAR bacteria?
Streptococcus
Enterococcus
Staphylococcus
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram negative CIRCULAR bacteria?
Neisseria
Moraxella
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What is the term for a rod shaped bacteria?
Bacillus
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram positive rod bacteria?
Corynebacterium
Listeria
Bacillus
Clostridum
Mycobacterium (acid-fast)
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram negative rod bacteria?
There are SOO MANY! Learn by exclusion. Remember the earlier flashcard with the 7 most common Gram POSITIVE bacteria. But here is the list on the table for your enjoyment:
ENTERICS = Escherichia coli, Shingella, Salmonella, Yersinia, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterobacter, Serratia, Vibrio, Campylobacter, Helicobacter, Pseudomonas, Bacteroides
Also….not included in enterics = Haemophilus, Bordetella, Legionella, Yersinia, Francisella, Brucella, Pasteurella, Gardenerella
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram positive spiral bacteria?
Lol there aren’t any
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram negative SPIRAL bacteria?
Spirochetes:
- Treponema
- Borrelia
- Leptospira
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram positive “Branching filamentous growth” bacteria?
Actinomyces
Nocardia
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram negative“Branching filamentous growth” bacteria?
There are none, lol
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram positve pleomorphic bacteria?
There are none, lol
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram negative pleomorphic bacteria?
Chlamydia
Rickettsiae
Figure 1-9 Bacterial Morphology
What are examples of gram positve/gram negative bacteria with NO CELL WALL?
Mycoplasma