09.16.2013 - Cholesterol and Lipoprotein Metabolism Flashcards

Tendon xanthoma

Xanthelasma - not specific for familial hypercholesterolemia


Palmar xanthoma associated with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia type III

What are the three types of mutations that lead to Type IIa phenotypes?
- Familial hypercholesterolemia. 2. Familial defect in the APOB100 receptor binding region for LDL 3. Autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia - Pcsk9 mutation
What is PCSK9?
It binds LDLR, targets it for degradation. Autosomal dominant mutations in this gene give you autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia.
Seven disorders of lipid metabolism that we covered in class not related to HDL.
- Familial chylomicronemia Type I
- Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia Type III
- Familial hypercholesterolemia Type IIa
- Familial defect APOB100 Receptor Type IIa
- Autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia Type IIa
- Familial hypertriglyceridemia IV or V
- Familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCHL) IIb
Three disorders of HDL metabolism.
- ApoA1 mutation
- Tangier disease (ABCA1) - tonsils loaded with cholesterol
- LCAT Deficiency - eyes

LCAT deficiency

Eruptive Xanthomas associated with familial chylomicronemia type I


ABCA1 mutation - Tangier’s disease

Tuberous xanthoma associated with familial dysbetalipoproteinemia Type III

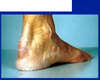
Tendon xanthoma - specific for familial hypercholesterolemia


Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia cutaneous xanthoma




Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia cutaneous xanthoma again

What is reverse cholesterol transport?
Describes what HDL does, transporting cholesterol out of macrophages and back to the liver via first ABCA1 and then LCAT


