YEAR 1 - GONADS Flashcards
What are the functions of the gonads?
- Gametogenesis
- Steroidogenesis
What is gametogenesis?
Production of gametes - spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females
What is Steroidogenesis?
Production of steroid hormones - androgens in males and oestrogen and progesterone in females
What is the activation of germ cells like in males?
- Germ cells proliferate reaching numbers of around 6-7 million during embryogenesis
- They remain high throughout life but have a dormant period until puberty

What is the activation of germ cells like in females?
During embryogenesis the germ cells proliferate reaching numbers around 6-7 million
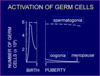
Draw a graph showing the levels of germ cells in males and females throughout lifespan

Describe the process of spermatogenesis
- Germ cells start to multiply and differentiate into spermatogonia (DIPLOID)
- during puberty - FSH begins to be released -> supermatogonia divide by mitosis to produce either more spermatogonia or primary spermatocytes (DIPLOID)
- primary -> secondary is first meiotic division (HAPLOID)
- secondary to spermatids is second meiotic division
*

Describe the process of oogenesis
- As soon as the oogonia get to the first meiotic division (prophase), development is halted
- the oocytes form a layer of cells around them to create the primordial follicles (happens at pre-birth)
- oocytes lie dormant for 12-50 years
- during puberty - some oocytes rescued by FSH release and some begin atresia
- at ovulation , oocytes complete first meiotic division to create a secondary oocyte and a polar body
- secondary oocyte enters 2nd division which completes upon fertilisation -> ovum and second polar body

What are the principal structures in the testes

Where does spermatogenesis take place?
Seminiferous tubules
Where is spermatozoa collected and stored
collection in the rete testis, and then drained by the vasa efferentia into the epididymis to be stored
Label the seminiferous tubules

What are the functions of Sertoli cells?
- Provide structural and metabolic support for spermatogenesis
- forms seminiferous tubukles
- synthesize FSH and androgen receptors
- Produces INHIBIN in response to FSH, which inhbits FSH secretion|
What are the functions of the Leydig cells?
Synthesises LH receptors
What are Graffian follicles?
Where are all follicles embedded?
What does the Graffian follicle become after ovulation?
Label the ovaries

Using simple flow charts, illustrate the synthesis of progesterone, 17B-oestradiol, and testosterone

What do oestrogens do?
Summarise the principal ovarian and endometrial changes that occur during the menstural cycle
- Oestrogen causes the effects of the proliferative phase
- ie: stimulates mitosis and an increase in progesterone and oestrogen receptors
- Endometrium gets thicker, glands get bigger and blood vessels lengthen
- in the luteal phase, oestrogen and progesterone are produced which induces a secretory phase
- progesterone reverses the effect of oestrogen
- reduced proliferation by reducing oestrogen receptors
- increases secretory activity of cells of myometrium - glands become wider and produce substances that make the environment suitable for implantation to occur
- reduced proliferation by reducing oestrogen receptors
Explain the hormone level changes during the menstrual cycle

Draw a graph of the hormone changes during menstruation

What are the ovarian changes that occur during the menstrual cycle?



